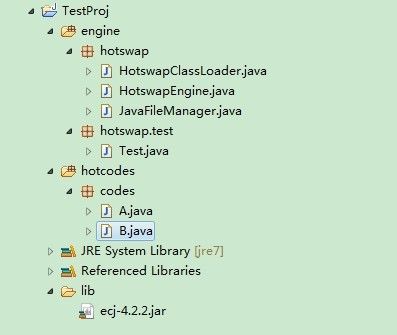
动态编译执行java类
最近几天看了一些热加载方面的资料,然后动手搭建了个基本框架,暂时实现了有限制性的热加载功能,先和大家分享一下
功能的实现上,主要分为2步:
1. 编译.java文件,生成.class文件。
这里我使用了eclipse的编译器类 EclipseCompiler 来实现
2.加载编译后的.class文件。
自定义一个类加载器,每次热更新都新建一个类加载器实例来实现。java传统的类加载是走双亲委派模式,当要加载一个类的时候,需要先由自身的父加载器来加载,只有父加载器还未加载过该类,才能由自身来加载。(我们也可以覆盖ClassLoader.loadClass()方法,打破这个规则)。由于不同的类加载器实例具有独立的空间,而且处于同一继承等级,具有同一个父加载器,这就确保了实例A加载的类,实例B也能重新加载,互不影响。
好了,下面就看代码实现吧。
package hotswap.test;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import hotswap.HotswapEngine;
public class Test {
/**
* @author Nate
* @date 2013-11-19
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//需要热加载的类路径
final String classPath = System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/hotcodes";
//需要热加载执行的类源文件路径
final String javaFilePath = classPath + "/codes/A.java";
HotswapEngine engine = new HotswapEngine();
//第一次加载执行
Class<?> clazz1 = engine.reload(classPath, javaFilePath);
evalMainMethod(clazz1);
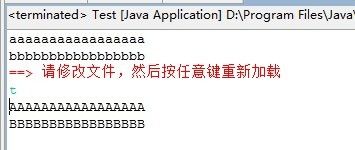
System.err.println("==> 请修改文件,然后按任意键重新加载");
System.in.read();
//修改代代码后,再次加载执行
Class<?> clazz2 = engine.reload(classPath, javaFilePath);
evalMainMethod(clazz2);
}
/**
* 执行指定类的main方法
*
* @author Nate
* @date 2013-11-19
*/
public static void evalMainMethod(Class<?> clazz, String...args) {
try {
Method mainMethod = clazz.getMethod("main",
new Class[] { String[].class });
if (mainMethod == null) return;
int modifiers = mainMethod.getModifiers();
if (!Modifier.isPublic(modifiers) ||
!Modifier.isStatic(modifiers))
return;
mainMethod.invoke(null, new Object[]{args});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package hotswap;
import hotswap.JavaFileManager.JavaSourceObject;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.tools.JavaCompiler;
import javax.tools.JavaFileObject;
import javax.tools.JavaCompiler.CompilationTask;
import org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.tool.EclipseCompiler;
public class HotswapEngine {
private final JavaCompiler compiler = new EclipseCompiler();
public Class<?> reload(String classPath, String javaFilePath) {
try {
File javaFile = new File(javaFilePath);
if (!javaFile.exists() || !javaFile.isFile())
return null;
//文件名
String fileName = javaFile.getName();
//完全类名
String classFullName = javaFilePath.substring(classPath.length() + 1, javaFilePath.lastIndexOf('.'));
classFullName = classFullName.replace('/', '.').replace('\\', '.');
//编译选项
List<String> options = new ArrayList<String>();
options.add("-warn:-enumSwitch");
options.add("-g");
options.add("-deprecation");
options.add("-1.7");
options.add("-encoding");
options.add("UTF-8");
//options.add("-sourcepath");
//options.add(classPath);
options.add("-classpath");
options.add(classPath);
//java文件管理器
JavaFileManager fileManager = new JavaFileManager();
//编译单元集合
List<JavaFileObject> compilationUnits = new ArrayList<JavaFileObject>(1);
//加载java文件源码
String sourceCode = loadJavaSourceCode(javaFile);
//生成java源码对象
JavaSourceObject sourceObj = JavaFileManager.newJavaSourceObject(fileName, sourceCode);
compilationUnits.add(sourceObj);
//执行编译任务
CompilationTask task = compiler.getTask(null, fileManager, null, options, null, compilationUnits);
if (!task.call()) {
//编译失败
return null;
}
//获取编译后的class文件
Map<String, byte[]> classBytes = fileManager.getClassBytes();
fileManager.close();
//加载class文件
HotswapClassLoader loader = new HotswapClassLoader(classBytes, classPath, ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
Class<?> clazz = loader.findClass(classFullName);
return clazz;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static String loadJavaSourceCode(File javaFile) {
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(javaFile)));
char[] arr = new char[8 * 1024];
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder();
int numChars;
while ((numChars = reader.read(arr, 0, arr.length)) > 0) {
buf.append(arr, 0, numChars);
}
return buf.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "";
}
}
package hotswap;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLClassLoader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class HotswapClassLoader extends URLClassLoader {
private final Map<String, byte[]> classBytes;
public HotswapClassLoader(Map<String, byte[]> classBytes, String classPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(toURLs(classPath), parent);
this.classBytes = classBytes;
}
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//先从我们编译后的class文件缓存里面找
byte buf[] = classBytes.get(className);
if (buf != null) {
classBytes.put(className, null);
return defineClass(className, buf, 0, buf.length);
}
return super.findClass(className);
}
private static URL[] toURLs(String classPath) {
if (classPath == null) {
return new URL[0];
}
List<URL> list = new ArrayList<URL>();
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(classPath, File.pathSeparator);
while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
String token = st.nextToken();
File file = new File(token);
if (file.exists()) {
try {
list.add(file.toURI().toURL());
} catch (MalformedURLException mue) {}
} else {
try {
list.add(new URL(token));
} catch (MalformedURLException mue) {}
}
}
URL res[] = new URL[list.size()];
list.toArray(res);
return res;
}
}
package hotswap;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FilterOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.URI;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.tools.FileObject;
import javax.tools.JavaFileObject;
import javax.tools.SimpleJavaFileObject;
import javax.tools.JavaFileObject.Kind;
import org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.tool.EclipseFileManager;
public class JavaFileManager extends EclipseFileManager {
//保存已经重新编译的class文件
protected Map<String, byte[]> classBytes;
public JavaFileManager() {
super(null, null);
classBytes = new HashMap<String, byte[]>();
}
public Map<String, byte[]> getClassBytes() {
return classBytes;
}
@Override
public JavaFileObject getJavaFileForOutput(Location location, String className, Kind kind, FileObject sibling)
throws IOException {
if (kind == Kind.CLASS) {
return new JavaClassObject(className.replace('/', '.'));
}
return super.getJavaFileForOutput(location, className, kind, sibling);
}
/**
* 新建一个java源文件对象
*
* @author Nate
* @param name 文件名
* @param source java源码字符串
*
* @date 2013-11-21
*/
public static JavaSourceObject newJavaSourceObject(String name, String source) {
return new JavaSourceObject(name, source);
}
/**
* java class文件对象(.class)
*
* @author Nate
* @date 2013-11-21
*/
public class JavaClassObject extends SimpleJavaFileObject {
protected final String name;
protected JavaClassObject(String name) {
super(toURI(name), Kind.CLASS);
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 编译器编译时回调, 这里我们用自己的输出流来接受编译后的class文件
*/
@Override
public OutputStream openOutputStream() throws IOException {
return new FilterOutputStream(new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
out.close();
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = (ByteArrayOutputStream)out;
classBytes.put(name, bos.toByteArray());
}
};
}
}
/**
* java 源文件对象(.java)
*
* @author Nate
* @date 2013-11-21
*/
public static class JavaSourceObject extends SimpleJavaFileObject {
final String source;
JavaSourceObject(String name, String source) {
super(toURI(name), Kind.SOURCE);
this.source = source;
}
@Override
public CharBuffer getCharContent(boolean ignoreEncodingErrors) {
return CharBuffer.wrap(source);
}
}
static final String JAVA_FILE_EXT = ".java";
static URI toURI(String name) {
File file = new File(name);
if (file.exists()) {
return file.toURI();
}
try {
final StringBuilder newUri = new StringBuilder();
newUri.append("file:///");
newUri.append(name.replace('.', '/'));
if (name.endsWith(JAVA_FILE_EXT)) {
newUri.replace(newUri.length() - JAVA_FILE_EXT.length(), newUri.length(), JAVA_FILE_EXT);
}
return URI.create(newUri.toString());
} catch (Exception exp) {
return null;
}
}
}
package codes;
public class A {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa");
//System.out.println("AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA");
//看看引用的类能不能也热更新
new B().say();
}
}
package codes;
public class B {
public void say() {
System.out.println("bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb");
//System.out.println("BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB");
}
}
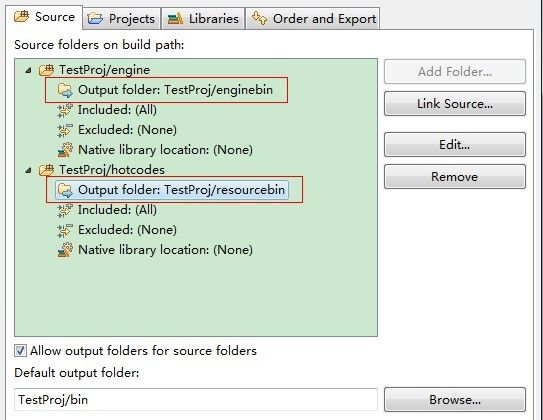
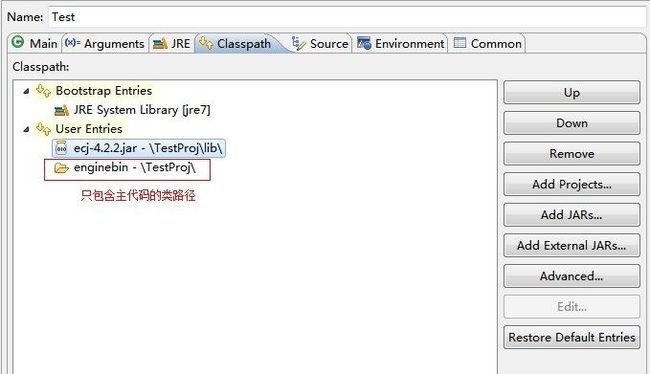
这里有个地方要注意一下的,需要将主代码和需要热加载的代码分开来放,并且要把主代码运行的类路径设为只包含主代码的文件夹,不能让主代码的类路径覆盖了主代码和需要热加载的代码,不然的话,新的加载器实例会加载不了,因为都被父加载器先加载了。 另外还可以更直接点,把需要热加载的代码放到另外一个项目。