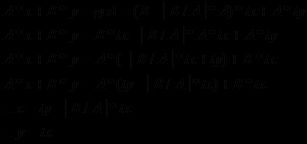数论之拓展欧几里得求解不定方程和同余方程组(一)
今天接到scy的压缩包,开始做数论专题。那今天就总结一下拓展欧几里得求解不定方程和同余方程组。
首先我们复习一下欧几里得算法:
1 int gcd(int a,int b){ 2 if(b==0) return a; 3 return gcd(b,a%b);
4 }
拓展欧几里得算法:
推导过程:
给出A和B,求它们的最大公约数,并且求出x和y,满足Ax+By=gcd(A,B)。
当A=0时,x=0,y=1;
当A>0时,
因为exgcd(A,B,x,y)表示Ax+By=gcd(A,B)
而且exgcd(B%A,A,tx,ty)表示 B%A * tx + A*ty = gcd(B%A,A)
又gcd(A,B)== gcd(B%A,A),所以B%A * tx + A*ty ==Ax+By
方程:
![]()
![]()
程序实现:
1 int tx,ty; 2
3 int exgcd(int a,int b) 4 { 5 if(b==0) {tx=1,ty=0;return a;} 6 int d=exgcd(b,a%b); 7 int x=ty,y=tx-(a/b)*ty; 8 tx=x;ty=y; 9 return d; 10 }
求解不定方程
已知a,b,n,求x,使得![]() ,可以转化为:
,可以转化为:![]() ,则要求gcd(a,n)|b,否则无解。
,则要求gcd(a,n)|b,否则无解。
poj2115--C Looooops
http://poj.org/problem?id=2115
题意:裸题。
//poj2115
#include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cstring> #include<iostream>
using namespace std; typedef long long LL; LL bit[40]; LL tx,ty; LL exgcd(LL a,LL b) { if(b==0) {tx=1,ty=0;return a;} LL d=exgcd(b,a%b); LL x=ty,y=tx-(a/b)*ty; tx=x;ty=y; return d; } int main() { //freopen("a.in","r",stdin); //freopen("a.out","w",stdout); bit[0]=1; for(LL i=1;i<=32;i++) bit[i]=bit[i-1]*2; LL a,b,c,k; while(1) { scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d",&a,&b,&c,&k); if(!a && !b && !c && !k) return 0; LL A=c,B=bit[k],C=b-a; LL g=exgcd(A,B); if(C%g) printf("FOREVER\n"); else { LL x=tx*(C/g); x=(x%(B/g)+(B/g))%(B/g); printf("%I64d\n",x); } } return 0; }
poj1061 青蛙的约会
http://poj.org/problem?id=1061
题意:裸题。注意负数。
//poj1061
#include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cstring> #include<iostream>
using namespace std; typedef long long LL; LL tx,ty; LL exgcd(LL a,LL b) { if(b==0) {tx=1,ty=0;return a;} LL d=exgcd(b,a%b); LL x=ty,y=tx-(a/b)*ty; tx=x;ty=y; return d; } int main() { // freopen("a.in","r",stdin); // freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
LL x,y,m,n,l; scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d",&x,&y,&m,&n,&l); LL g=exgcd(m-n,l); // printf("g = %I64d\n",g);
if((y-x)%g!=0) printf("Impossible\n"); else { LL rx=tx*(y-x)/g; LL r=l/g; if(r<0) r*=-1; rx=(rx%r+r)%r; printf("%I64d\n",rx); } return 0; }
同余方程组
中国剩余定理:
从网上找到一段解释,觉得很好:
《孙子算经》中有“物不知数”问题:“今有物不知其数,三三数之余二 ,五五数之余三 ,七七数之余二,问物几何?”答为“23”。
--------这个就是传说中的“中国剩余定理”。 其实题目的意思就是,n % 3 = 2, n % 5 = 3, n % 7 = 2; 问n是多少?
那么他是怎么解决的呢?
看下面:
题目中涉及 3, 5,7三个互质的数、
令:5 * 7 * a % 3 = 1; --------------> a = 2; 即5 * 7 * 2 = 70;
3 * 7 * b % 5 = 1; --------------> b = 1; 即3 * 7 * 1 = 21;
3 * 5 * c % 7 = 1; --------------> c = 1; 即3 * 5 * 1 = 15;
为什么要使余数为1:是为了要求余数2的话,只要乘以2就可以,要求余数为3的话,只要乘以3就可以!
( 因为题目想要n % 3 =2, n % 5 =3, n % 7 =2; )
那么:要使得n % 3 = 2,那么( 5 * 7 * 2 )*2 % 3 = 2;( 因为5 * 7 * 2 % 3 = 1 )
同理: 要使得n % 5 = 3,那么( 3 * 7 * 1 )*3 % 5 = 3;( 因为3 * 7 * 1 % 5 = 1 )
同理:要使得n % 7 = 2,那么( 3 * 5 * 1 )* 2 % 7 = 2;( 因为3 * 5 * 1 % 7 = 1 )
那么现在将( 5 * 7 * 2 )* 2和( 3 * 7 * 1 )* 3和( 3 * 5 * 1 )* 2相加会怎么样呢?我们知道
( 5 * 7 * 2 )* 2可以被5和7整除,但是%3等于2
( 3 * 7 * 1 )* 3可以被3和7整除,但是%5等于3
( 3 * 5 * 1 )* 2可以被3和5整除,但是%7等于2
那么即使相加后,%3, 5, 7的情况也还是一样的!
那么就得到一个我们暂时需要的数( 5 * 7 * 2 )* 2 +( 3 * 7 * 1 )* 3 +( 3 * 5 * 1 )* 2 = 233
但不是最小的!所有我们还要 233 % ( 3 * 5 * 7 ) == 23 得解!
该解释来自博客http://blog.csdn.net/shanshanpt/article/details/8724769
poj1006 biorhythms
1 //poj1006 2 /* 3 x%23=a; 4 x%28=b; 5 x%33=c; 6 */ 7 #include<cstdio> 8 #include<cstdlib> 9 #include<cstring> 10 #include<iostream> 11 using namespace std; 12 13 int tx,ty; 14 /* 15 void exgcd(int a,int b) 16 { 17 if(b==0) {tx=1,ty=0;return ;} 18 exgcd(b,a%b); 19 int x=ty,y=tx-(a/b)*ty; 20 tx=x;ty=y; 21 } 22 */ 23 int main() 24 { 25 freopen("a.in","r",stdin); 26 freopen("a.out","w",stdout); 27 int T=0; 28 while(1) 29 { 30 int a,b,c,d; 31 scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&d); 32 if(a==-1 && b==-1 && c==-1 && d==-1) return 0; 33 int x=6*a*28*33; 34 int y=-9*b*23*33; 35 int z=2*c*23*28; 36 int g=23*28*33; 37 int ans=(x+y+z)%g; 38 while(ans-d <= 0) ans+=g; 39 while(ans-d > g) ans-=g; 40 printf("Case %d: the next triple peak occurs in %d days.\n",++T,ans-d); 41 } 42 return 0; 43 }
不互素怎么办?同余方程组:
中国剩余定理求的同余方程组mod 的数是两两互素的。mod的数可能不是互素,所以要转换一下再求。
P=b1(mod a1); P / a1 ==?~~~~b1
P =b2(mod a2);
P =b3(mod a3);
……
P =bn(mod an);
a1~an,b1~bn是给出来的。
解:
第一条:a1*x+b1=P
第二条:a2*y+b2=P
第一条减去第二条: a1*x - a2*y = b2-b1
设A=a1,B=-a2,K=b2-b1,得到了x(实际调用exgcd的时候不理会a2前面的负号)
如果K%d!=0,无解
否则,X=[ (x* K/d)%(B/d)+(B/d) ]%(B/d)
LCU表示最小公倍数
P= a1*X+b1+ 若干倍的LCU(a1,a2)(或者把Y=(K-AX)/B,再P=a2*Y+b2+ 若干倍的LCU(a1,a2)
所以新的b= a1*x+b1,新的a= LCU(a1,a2),
把新的b当成b1,新的a当成a1,再去和a3和b3结合,一直到最后结束,最后新的b就是X
poj2891 Strange Way to Express Integers
http://poj.org/problem?id=2891
题意:同余方程组。
1 //poj2891 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstdlib> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<iostream> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 typedef long long LL; 9 const LL N=11000; 10 LL a[N],b[N]; 11 LL tx,ty; 12 13 LL exgcd(LL aa,LL bb) 14 { 15 if(bb==0) {tx=1,ty=0;return aa;} 16 LL d=exgcd(bb,aa%bb); 17 LL x=ty,y=tx-(aa/bb)*ty; 18 tx=x;ty=y; 19 return d; 20 } 21 22 LL lcu(LL aa,LL bb) 23 { 24 LL d=exgcd(aa,bb); 25 return aa*bb/d; 26 } 27 28 int main() 29 { 30 freopen("a.in","r",stdin); 31 freopen("a.out","w",stdout); 32 // printf("%d\n",(-5)%3); 33 LL n,a1,b1,x; 34 while(scanf("%I64d",&n)!=EOF) 35 { 36 bool bk=1; 37 for(LL i=1;i<=n;i++) 38 scanf("%I64d%I64d",&a[i],&b[i]); 39 LL A=a[1],B=a[2],C=b[2]-b[1]; 40 LL g=exgcd(A,B); 41 if(C%g) bk=0; 42 else { 43 x=((tx*C/g)%(B/g)+(B/g))%(B/g); 44 b1=a[1]*x+b[1]; 45 a1=lcu(a[1],a[2]); 46 } 47 for(LL i=3;i<=n;i++) 48 { 49 A=a1,B=a[i],C=b[i]-b1; 50 g=exgcd(A,B); 51 if(C%g) {bk=0;break;} 52 x=((tx*C/g)%(B/g)+(B/g))%(B/g); 53 b1=a1*x+b1; 54 a1=lcu(a1,a[i]); 55 } 56 if(bk) printf("%I64d\n",b1); 57 else printf("-1\n"); 58 } 59 return 0; 60 }
今天就学了这么些,要加油啊!