java并发-协作对象之间死锁测试
协作对象间的死锁问题
在协作对象之间可能存在多个锁获取的情况,但是这些获取多个锁的操作并不像在LeftRightDeadLock或transferMoney中那么明显,这两个锁并不一定必须在同一个方法中被获取。如果在持有锁时调用某个外部方法,那么这就需要警惕死锁问题,因为在这个外部方法中可能会获取其他锁,或者阻塞时间过长,导致其他线程无法及时获取当前被持有的锁。
《java并发编程实践》中出租车调度例子中,涉及到外部方法调用的代码,虽然没有显示地获取锁,但是当前方法和外部调用方法都需要单独获取某个锁,导致整个操作本质上是需要顺序的获取两个锁,那么它就跟LeftRightDeadLock中的方法等效了。测试代码编写如下。
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Dispatcher {
private Set<Taxi> taxis;
private Set<Taxi> availableTaxis;
public Dispatcher(){
taxis= new HashSet<Taxi>();
availableTaxis= new HashSet<Taxi>();
}
public synchronized void notifyAvailable(Taxi taxi) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" notifyAvailable.");
availableTaxis.add(taxi);
}
/**
* 打印当前位置:有死锁风险
* 持有当前锁的时候,同时调用Taxi的getLocation这个外部方法;而这个外部方法也是需要加锁的
* reportLocation的锁的顺序与Taxi的setLocation锁的顺序完全相反
*/
public synchronized void reportLocation(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" report location.");
for(Taxi t:taxis){
t.getLocation();
}
}
public void addTaxi(Taxi taxi){
taxis.add(taxi);
}
} Taxi类
public class Taxi {
private String location;
private String destination;
private Dispatcher dispatcher;
public Taxi(Dispatcher dispatcher,String destination){
this.dispatcher = dispatcher;
this.destination = destination;
}
public synchronized String getLocation(){
return this.location;
}
/**
* 该方法先获取Taxi的this对象锁后,然后调用Dispatcher类的方法时,又需要获取
* Dispatcher类的this方法。
* @param location
*/
public synchronized void setLocation(String location){
this.location = location;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" taxi set location:"+location);
if(this.location.equals(destination)){
dispatcher.notifyAvailable(this);
}
}
} 测试类:
/**
* 在协作对象之间发生死锁的测试用例
* 如果在持有某个锁时调用外部方法,那么当这个外部方法中需要获取锁时
* 就需要警惕死锁问题
* @author bh
*/
public class TestDeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Dispatcher d1 = new Dispatcher();
final Taxi t1 = new Taxi(d1,"光谷软件园");
d1.addTaxi(t1);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
//先获取dispatcher锁,然后是taxi的锁
d1.reportLocation();
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
//先获取taxi锁,然后是dispatcher的锁
t1.setLocation("光谷软件园");
}
});
//最后二者陷入死锁
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
} 测试结果
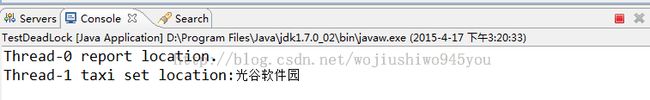
刚一执行,程序就陷入死锁了,而且每次执行都会死锁,说明这种协同对象间相互调用,死锁的风险很大。因此,在持有锁的情况下调用某个外部方法,就需要警惕死锁。解决这个问题的方法是:开放调用。
开放调用
开放调用,是指在调用某个方法时不需要持有锁。开放调用可以避免死锁,这种代码更容易编写。上述调度算法完全可以修改为开发调用,修改同步代码块的范围,使其仅用于保护那些涉及共享状态的操作,避免在同步代码块中执行方法调用。修改Dispatcher的reportLocation方法:
/**
* 同步块只包含对共享状态的操作代码
*/
public void reportLocation(){
Set<OpenCallTaxi> copy;
synchronized(this){
copy = new HashSet<OpenCallTaxi>(taxis);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" report location.");
for(OpenCallTaxi t:copy){
t.getLocation();
}
} 同时修改Taxi的setLocation方法为开放调用:
/**
* 开发调用,不持有锁期间进行外部方法调用
* @param location
*/
public void setLocation(String location){
synchronized(this){
this.location = location;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" taxi set location:"+location);
if(this.location.equals(destination)){
dispatcher.notifyAvailable(this);
}
} 测试结果:死锁不再发生,程序正常结束:
结论:在程序中尽量使用开放调用。与那些在持有锁时调用外部方法的程序相比,更易于对依赖开放调用的程序进行死锁分析。
