匈牙利算法
本文转自大牛博客:http://www.byvoid.com/blog/hungary/
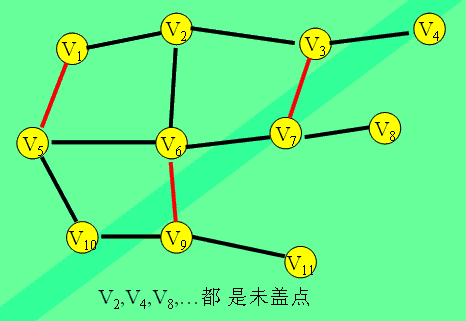
这是一种用增广路求二分图最大匹配的算法。它由匈牙利数学家Edmonds于1965年提出,因而得名。 定义 未盖点:设Vi是图G的一个顶点,如果Vi 不与任意一条属于匹配M的边相关联,就称Vi 是一个未盖点。
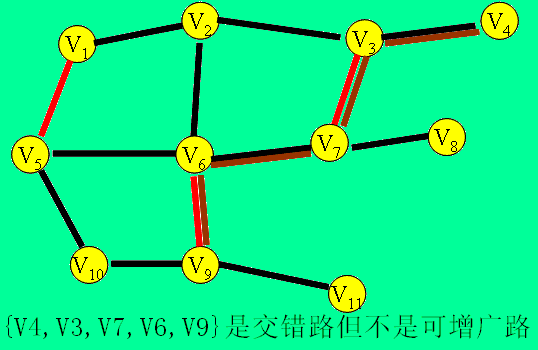
交错路:设P是图G的一条路,如果P的任意两条相邻的边一定是一条属于M而另一条不属于M,就称P是一条交错路。
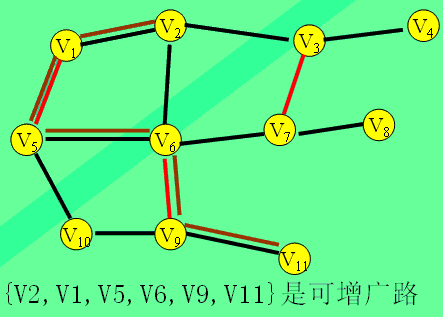
可增广路:两个端点都是未盖点的交错路叫做可增广路。
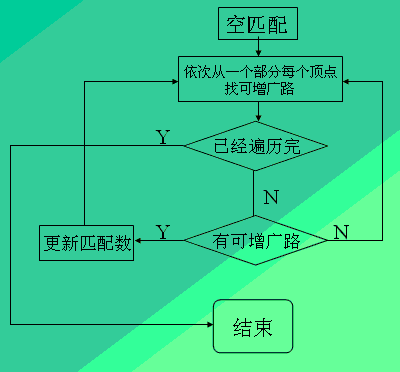
流程图
伪代码
bool 寻找从k出发的对应项出的可增广路
{
while (从邻接表中列举k能关联到顶点j)
{
if (j不在增广路上)
{
把j加入增广路;
if (j是未盖点 或者 从j的对应项出发有可增广路)
{
修改j的对应项为k;
则从k的对应项出有可增广路,返回true;
}
}
}
则从k的对应项出没有可增广路,返回false;
}
void 匈牙利hungary()
{
for i->1 to n
{
if (则从i的对应项出有可增广路)
匹配数++;
}
输出 匹配数;
}
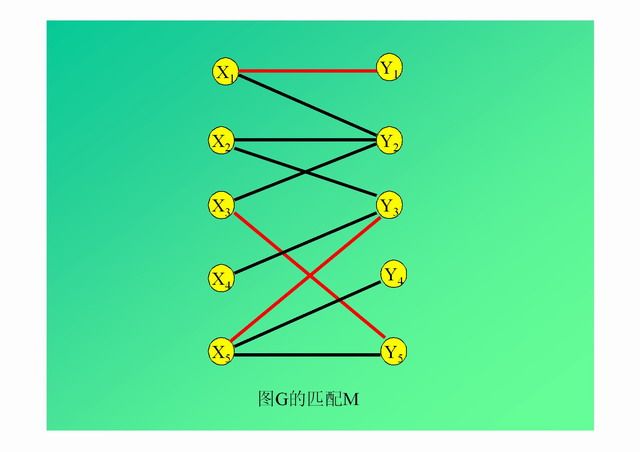
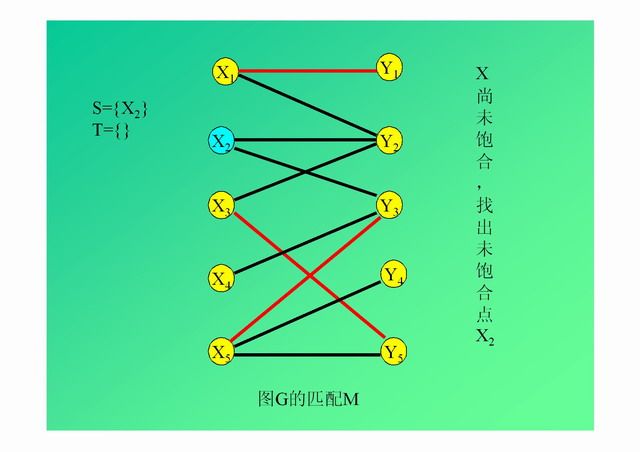
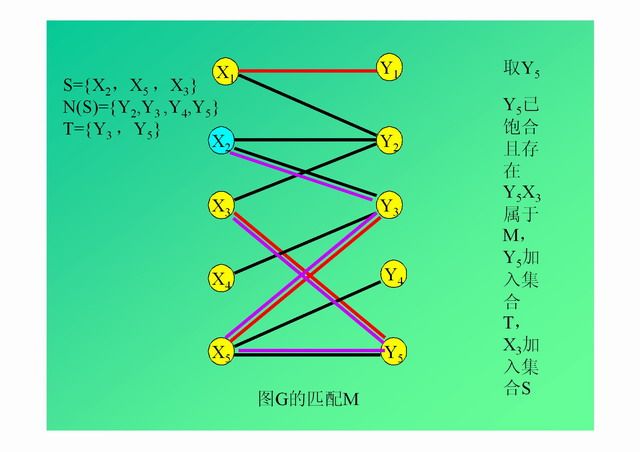
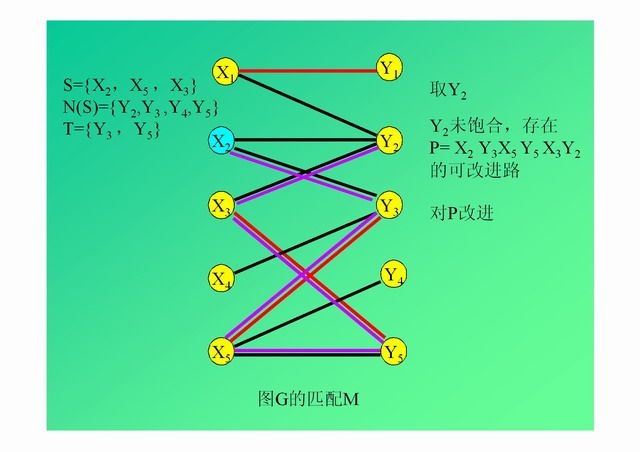
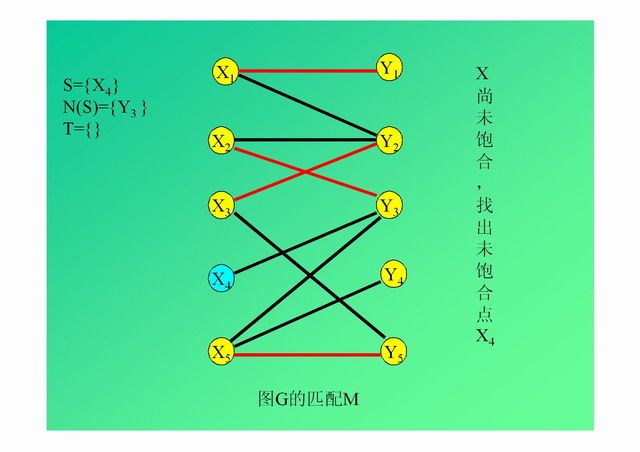
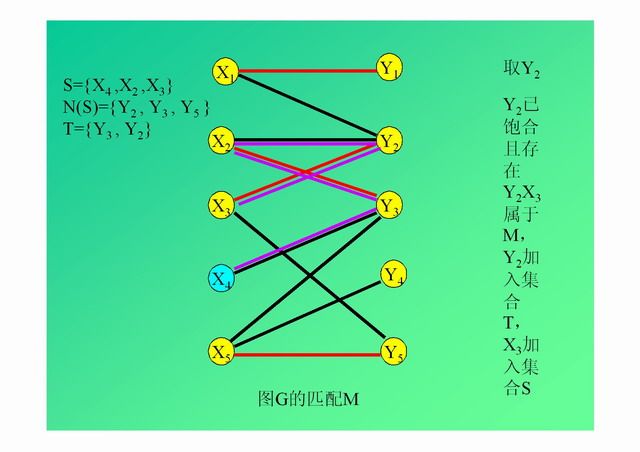
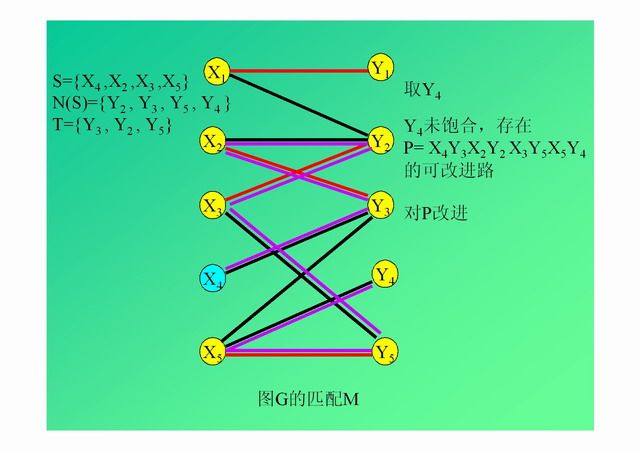
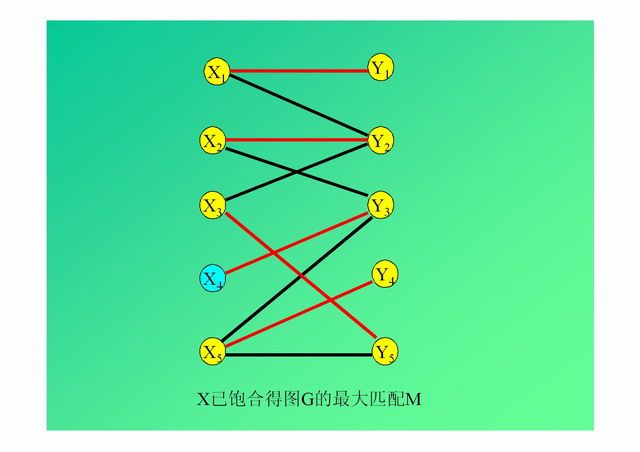
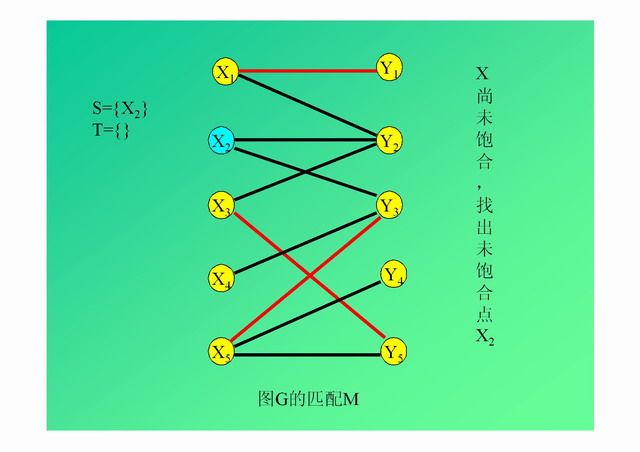
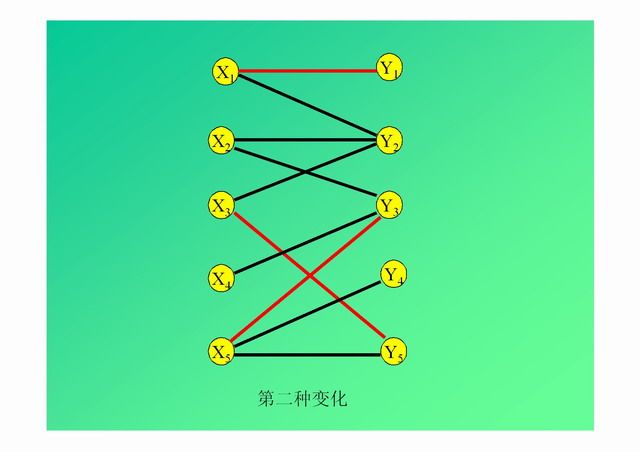
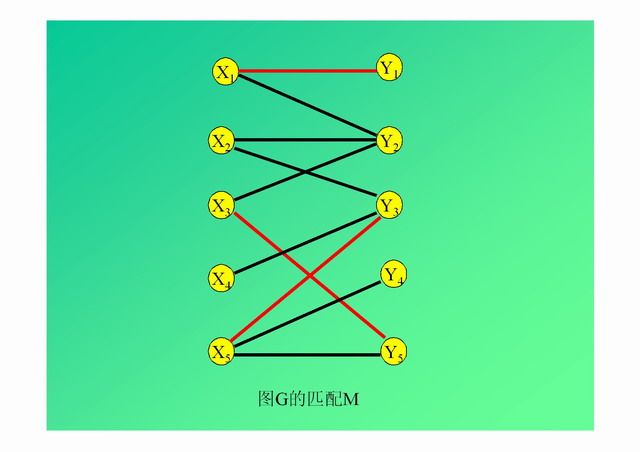
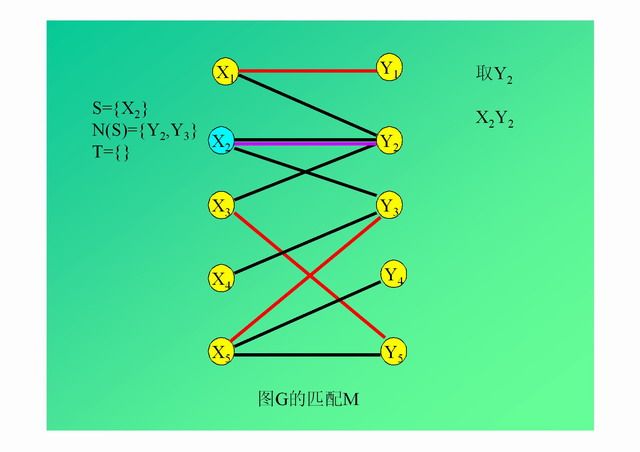
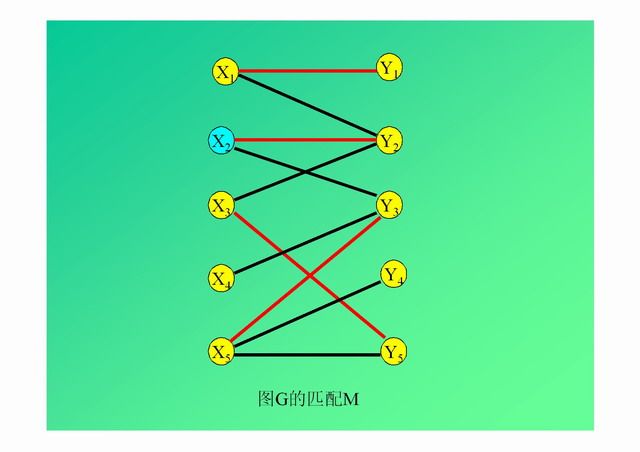
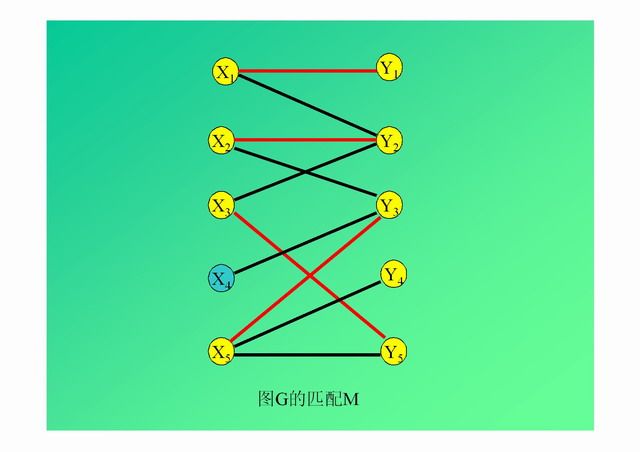
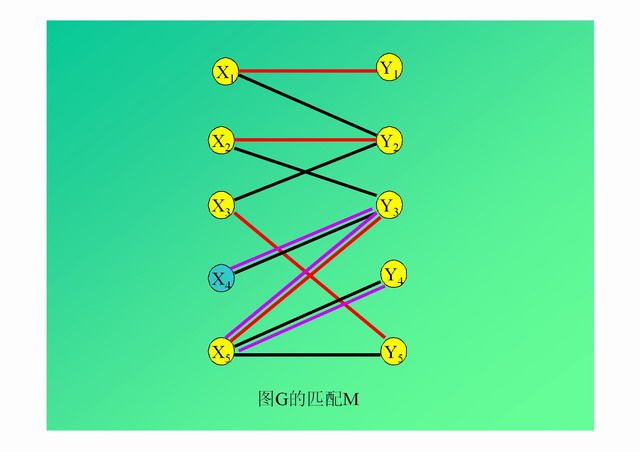
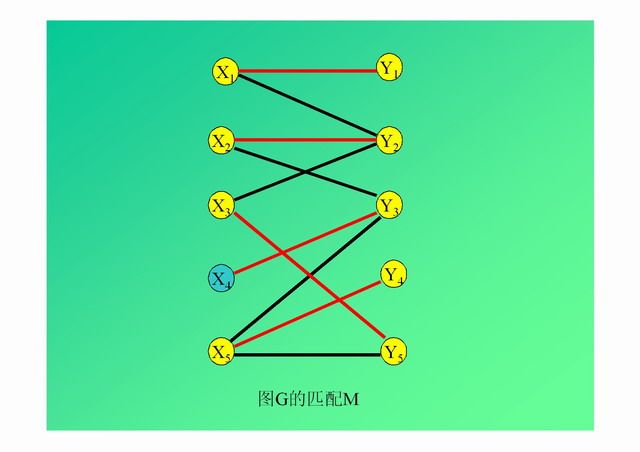
演示:
C实现(作者BYVoid)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX 102
long n,n1,match;
long adjl[MAX][MAX];
long mat[MAX];
bool used[MAX];
FILE *fi,*fo;
void readfile()
{
fi=fopen("flyer.in","r");
fo=fopen("flyer.out","w");
fscanf(fi,"%ld%ld",&n,&n1);
long a,b;
while (fscanf(fi,"%ld%ld",&a,&b)!=EOF)
adjl[a][ ++adjl[a][0] ]=b;
match=0;
}
bool crosspath(long k)
{
for (long i=1;i<=adjl[k][0];i++)
{
long j=adjl[k][i];
if (!used[j])
{
used[j]=true;
if (mat[j]==0 || crosspath(mat[j]))
{
mat[j]=k;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void hungary()
{
for (long i=1;i<=n1;i++)
{
if (crosspath(i))
match++;
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
}
}
void print()
{
fprintf(fo,"%ld",match);
fclose(fi);
fclose(fo);
}
int main()
{
readfile();
hungary();
print();
return 0;
}
Pascal实现(作者魂牛)
var
a:array[1..1000,1..1000] of boolean;
b:array[1..1000] of longint;
c:array[1..1000] of boolean;
n,k,i,x,y,ans,m:longint;
function path(x:longint):boolean;
var
i:longint;
begin
for i:=1 to n do
if a[x,i] and not c[i] then
begin
c[i]:=true;
if (b[i]=0) or path(b[i]) then
begin
b[i]:=x;
exit(true);
end;
end;
exit(false);
end;
procedure hungary;
var
i:longint;
begin
fillchar(b,sizeof(b),0);
for i:=1 to m do
begin
fillchar(c,sizeof(c),0);
if path(i) then inc(ans);
end;
end;
begin
fillchar(a,sizeof(a),0);
readln(m,n,k);
for i:=1 to k do
begin
readln(x,y);
a[x,y]:=true;
end;
ans:=0;
hungary;
writeln(ans);
end.