hbase0.98 源码分析-读数据流程
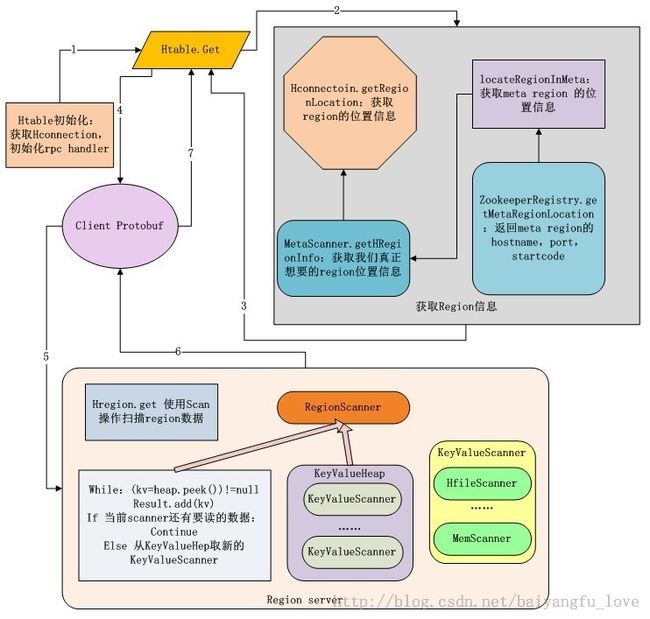
先贴一个总体架构图吧:
我们的客户端程序读取数据(以get为例)通过HTable和Get进行操作,我们从客户端代码开始分析读取数据的流程
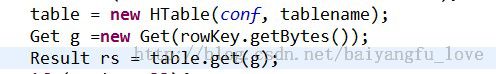
HTable的构造函数:
public HTable(Configuration conf, final TableName tableName)
throws IOException {
this.tableName = tableName;
this.cleanupPoolOnClose = this.cleanupConnectionOnClose = true;
if (conf == null) {
this.connection = null;
return;
}
this.connection = HConnectionManager.getConnection(conf);
this.configuration = conf;
this.pool = getDefaultExecutor(conf);
this.finishSetup();
}
这个方法有三个比较重要的操作:
1、获取HConnection
HConnectionImplementation connection = CONNECTION_INSTANCES.get(connectionKey);
if (connection == null) {
connection = (HConnectionImplementation)createConnection(conf, true);
CONNECTION_INSTANCES.put(connectionKey, connection);
createConnection 方法通过反射生成HConnectionImplementation对象,通过这个反射对象进行连接
String className = conf.get("hbase.client.connection.impl",
HConnectionManager.HConnectionImplementation.class.getName());
Class<?> clazz = null;
try {
clazz = Class.forName(className);
反射之后,创建连接:
Constructor<?> constructor =
clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Configuration.class,
boolean.class, ExecutorService.class, User.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
return (HConnection) constructor.newInstance(conf, managed, pool, user);
2、获取ExecutorService,这是一个线程池,这个线程是的一个线程对应一个regionserver
3、finishSetup:配置HTable相关参数,创建 rpcCallerFactory 和 rpcCallerFactory,用于和 regionserver 进行 rpc 调用;还会初始化一个AsyncProcess,用于处理autoflush为false 或者 multiputs 的操作:
/** The Async process for puts with autoflush set to false or multiputs */ protected AsyncProcess<Object> ap; …… this.rpcCallerFactory = RpcRetryingCallerFactory.instantiate(configuration); this.rpcControllerFactory = RpcControllerFactory.instantiate(configuration); ap = new AsyncProcess<Object>(connection, tableName, pool, null, configuration, rpcCallerFactory, rpcControllerFactory);
ok,HTable初始化基本完成,进入HTable.get 方法
public Result get(final Get get) throws IOException {
// have to instanatiate this and set the priority here since in protobuf util we don't pass in
// the tablename... an unfortunate side-effect of public interfaces :-/ In 0.99+ we put all the
// logic back into HTable
final PayloadCarryingRpcController controller = rpcControllerFactory.newController();
controller.setPriority(tableName);
RegionServerCallable<Result> callable =
new RegionServerCallable<Result>(this.connection, getName(), get.getRow()) {
public Result call() throws IOException {
return ProtobufUtil.get(getStub(), getLocation().getRegionInfo().getRegionName(), get,
controller);
}
};
return rpcCallerFactory.<Result> newCaller().callWithRetries(callable, this.operationTimeout);
}
ok,一步一步分析:
这个PayloadCarryingRpcController 这个类是用来通过protobuf获取Cells数据的载体,也就是说这个类通过protobuf与regionserver通信,调用regionserver的查询方法,然后将 Result 返回
/**
* Optionally carries Cells across the proxy/service interface down into ipc. On its
* way out it optionally carries a set of result Cell data. We stick the Cells here when we want
* to avoid having to protobuf them. This class is used ferrying data across the proxy/protobuf
* service chasm. Used by client and server ipc'ing.
*/
@InterfaceAudience.Private
public class PayloadCarryingRpcController implements RpcController, CellScannable {
controller.setPriority(tableName) : 设置rpc的请求级别,系统级的快,用户级别的表慢
public void setPriority(final TableName tn) {
this.priority = tn != null && tn.isSystemTable()? HConstants.HIGH_QOS: HConstants.NORMAL_QOS;
}
调用顺序是从最后的 return 语句开始
return rpcCallerFactory.<Result> newCaller().callWithRetries(callable, this.operationTimeout);
进入RpcRetryingCaller.callwithRetries:
try {
beforeCall();
callable.prepare(tries != 0); // if called with false, check table status on ZK
return callable.call();
} catch (Throwable t) {
beforeCall 用来设置rpc 请求超时时间
主要的还是看 prepare :找到 region 的location host
/**
* Prepare for connection to the server hosting region with row from tablename. Does lookup
* to find region location and hosting server.
* @param reload Set this to true if connection should re-find the region
* @throws IOException e
*/
public void prepare(final boolean reload) throws IOException {
this.location = connection.getRegionLocation(tableName, row, reload);
……
setStub(getConnection().getClient(getLocation().getServerName()));
}
connection:也就是上面生成的 HConnectionImplementation
tablename:这个简单
row:在HTable.get()方法中,传进去的row是这么来的:
new RegionServerCallable<Result>(this.connection, getName(), get.getRow())row 也就是你要查的rowkey
进入HConnectionImplementation.getRegionLocation 看一下:
public HRegionLocation getRegionLocation(final TableName tableName,
final byte [] row, boolean reload)
throws IOException {
return reload? relocateRegion(tableName, row): locateRegion(tableName, row);
}
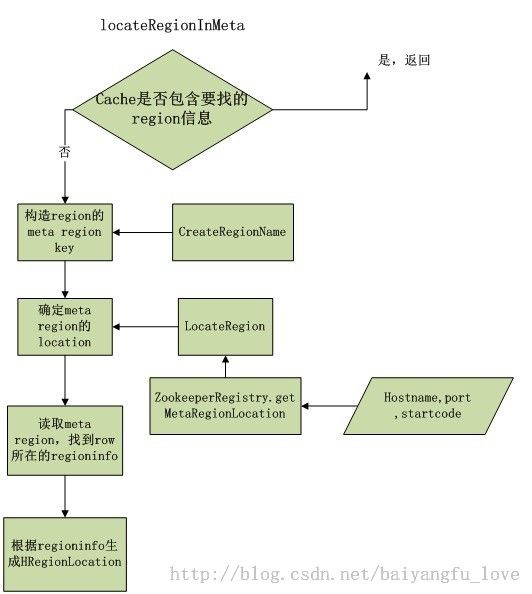
private HRegionLocation locateRegion(final TableName tableName,
final byte [] row, boolean useCache, boolean retry)
throws IOException {
……
if (tableName.equals(TableName.META_TABLE_NAME)) {
return this.registry.getMetaRegionLocation();
} else {
// Region not in the cache - have to go to the meta RS
return locateRegionInMeta(TableName.META_TABLE_NAME, tableName, row,
useCache, userRegionLock, retry);
}
}
/*
* Search the hbase:meta table for the HRegionLocation
* info that contains the table and row we're seeking.
*/
private HRegionLocation locateRegionInMeta(final TableName parentTable,
final TableName tableName, final byte [] row, boolean useCache,
Object regionLockObject, boolean retry)
throws IOException {看一下流程图:
ok,我们要找的 region 信息已经找到,我们返回HTable.get() 方法中:
return ProtobufUtil.get(getStub(), getLocation().getRegionInfo().getRegionName(), get,
controller);
这里用到了protobuf,自hbase0.96版本,hbase的通信架构就用了google的protobuf,之前也写过一个简单的protobuf编程例子,http://blog.csdn.net/baiyangfu_love/article/details/36887705。
先看一下 hbase的protobuf都有哪些接口:
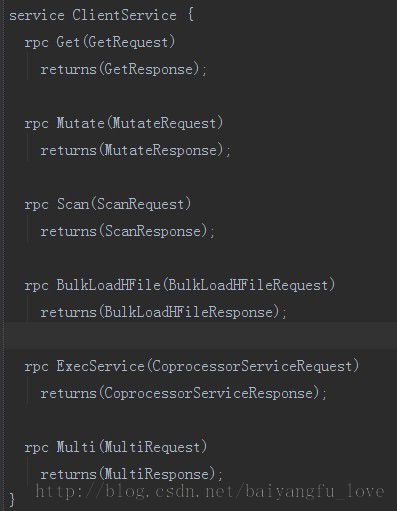
基本每个模块都有对应的proto通信接口文件,get 调用是从client 端与集群通信,应该从Client.proto 中找对应的接口:
这里有Get相关的message: Get 、Result、GetRequest、GetResponse,还有ClientService,这个service就是负责远程调用的接口:
下面看一下具体是怎么通信的:进入 ProtobufUtil.get() 方法:
/**
* A helper to invoke a Get using client protocol.
*
* @param client
* @param regionName
* @param get
* @param controller to use when writing the rpc
* @return the result of the Get
* @throws IOException
*/
public static Result get(final ClientService.BlockingInterface client, final byte[] regionName,
final Get get, PayloadCarryingRpcController controller) throws IOException {
GetRequest request =
RequestConverter.buildGetRequest(regionName, get);
try {
GetResponse response = client.get(controller, request);
if (response == null) return null;
return toResult(response.getResult());
先构造一个GetRequest,通过ClientService调用get service,这个ClientService其实是protobuf 对 Client.proto 生成的代码
buildGetRequest 的作用应该初始化getrequest 相关配置信息:
/**
* Create a protocol buffer GetRequest for a client Get
*
* @param regionName the name of the region to get
* @param get the client Get
* @return a protocol buffer GetRequest
*/
public static GetRequest buildGetRequest(final byte[] regionName,
final Get get) throws IOException {
GetRequest.Builder builder = GetRequest.newBuilder();
RegionSpecifier region = buildRegionSpecifier(
RegionSpecifierType.REGION_NAME, regionName);
builder.setRegion(region);
builder.setGet(ProtobufUtil.toGet(get));
return builder.build();
}
GetRequest.Builder 和 RegionSpecifier 都是protobuf生成的代码
ok,生成GetRequest,下面就应该是将request发送到对应的regionserver,这个过程是如何实现的呢?
之前分析过,通过查找meta region的内容,找到对应的region信息,生成HRegionLocation。这里有regionserver的相关信息
/**
* HRegionServer makes a set of HRegions available to clients. It checks in with
* the HMaster. There are many HRegionServers in a single HBase deployment.
*/
@InterfaceAudience.Private
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class HRegionServer implements ClientProtos.ClientService.BlockingInterface,
AdminProtos.AdminService.BlockingInterface, Runnable, RegionServerServices,
HBaseRPCErrorHandler, LastSequenceId {
下面就开始是分析在region server 端是如何处理请求的 HRegionServer.get() 方法:
try {
checkOpen();
requestCount.increment();
HRegion region = getRegion(request.getRegion());
GetResponse.Builder builder = GetResponse.newBuilder();
ClientProtos.Get get = request.getGet();
Boolean existence = null;
Result r = null;
getRegion() : 由client端传进来的RegionSpecifier的值通过ProtobufUtil的转换获取可读的region name
protected HRegion getRegion(
final RegionSpecifier regionSpecifier) throws IOException {
return getRegionByEncodedName(regionSpecifier.getValue().toByteArray(),
ProtobufUtil.getRegionEncodedName(regionSpecifier));
}
看一下缓存没有的情况怎么处理:
Get clientGet = ProtobufUtil.toGet(get);
if (get.getExistenceOnly() && region.getCoprocessorHost() != null) {
existence = region.getCoprocessorHost().preExists(clientGet);
}
if (existence == null) {
r = region.get(clientGet);读数据的操作在 :
r = region.get(clientGet);
HRegion.get():
Scan scan = new Scan(get);
RegionScanner scanner = null;
try {
scanner = getScanner(scan);
scanner.next(results);
} finally {
if (scanner != null)
scanner.close();
}由此可见,get操作最终还是要化成scan操作
RegionScanner 是主要干活的?不一定
protected RegionScanner getScanner(Scan scan,
List<KeyValueScanner> additionalScanners) throws IOException {
startRegionOperation(Operation.SCAN);
try {
// Verify families are all valid
prepareScanner(scan);
// 验证要查找的列族
return instantiateRegionScanner(scan, additionalScanners);
进入初始化regionscanner
if <反向scan>
return ReversedRegionScannerImpl
else
return RegionScannerImpl
ok,我们进入正常的RegionScannerImpl的构造函数,这里将初始化Store的scanner,我们知道,hregion下面是hstore、hmemstore、hwal 这些存储数据的结构。
for (Map.Entry<byte[], NavigableSet<byte[]>> entry :
scan.getFamilyMap().entrySet()) {
Store store = stores.get(entry.getKey());
KeyValueScanner scanner = store.getScanner(scan, entry.getValue(), this.readPt);每一个列族都会对应一个store,当然,也会对应一个storescanner,将这些storescanner存到一个排序堆里,也就是KeyValueHeap中。
我们关心的是如何读的数据?
由之前的HRegion.get() 方法知道,获取到了regionscanner,开始调用 scanner.next()方法读取数据了,也就是StoreScanner.next():
next 方法首先会对一些条件十分满足进行判断:
1、判断KeyValueHeap的top是否发生变化:checkReseek,如果发生变化,return true,表示还有更多的row,否则,继续往下走
2、判断KeyValueHeap的top是否为null
下面是next 的主要逻辑:
LOOP: while((kv = this.heap.peek()) != null) {
if (prevKV != kv) ++kvsScanned; // Do object compare - we set prevKV from the same heap.
checkScanOrder(prevKV, kv, comparator);
prevKV = kv;
ScanQueryMatcher.MatchCode qcode = matcher.match(kv);
switch(qcode) {
case INCLUDE:
case INCLUDE_AND_SEEK_NEXT_ROW:
case INCLUDE_AND_SEEK_NEXT_COL:
……
// add to results only if we have skipped #storeOffset kvs
// also update metric accordingly
if (this.countPerRow > storeOffset) {
outResult.add(kv);
count++;
}
if (qcode == ScanQueryMatcher.MatchCode.INCLUDE_AND_SEEK_NEXT_ROW) {
if (!matcher.moreRowsMayExistAfter(kv)) {
return false;
}
seekToNextRow(kv);
} else if (qcode == ScanQueryMatcher.MatchCode.INCLUDE_AND_SEEK_NEXT_COL) {
seekAsDirection(matcher.getKeyForNextColumn(kv));
} else {
this.heap.next();
}
主要的读取操作就是这几行代码,对于一个KeyValueScanner来说,如果还有要读的row,继续玩下读,如果还有要读的column,继续读column
如果这个KeyValueScanner没有要读数据了,就从KeyValueHeap中取下一个KeyValueScanner继续循环,直到没有KeyValueScanner或者KeyValueScanner 已经没有要读取的数据了。
既然读取数据的操作在KeyValueScanner的peek方法,那这个KeyValueScanner到底用的是哪个KeyValueScanner,这里应该是用的StoreFileScanner。我们看一下StoreFileScanner的peek方法:
public KeyValue peek() {
return cur;
}这里只是取出当前的KeyValue,怎么指向下一个kv 呢?
是通过StoreScanner.seekToNextRow(kv) 方法改变StoreFileScanner 的 cur 当前kv对的,其实调用的是StoreFileScanner.reseek(kv) 方法:
public boolean reseek(KeyValue key) throws IOException {
if (seekCount != null) seekCount.incrementAndGet();
……
if (!reseekAtOrAfter(hfs, key)) {
close();
return false;
}
cur = hfs.getKeyValue();通过HFileScanner.getKeyValue() 方法获取新的KeyValue对赋值给cur
ok,StoreFileScanner.hfs 是一个 HFileScanner ,这是一个接口,我们看一下StoreFileScanner的hfs 是怎么来的?
在之前的RegionScannerImpl 构造函数中,调用了HStore.getScanner() 方法,通过一步一步的往下追:
HStore.getScanner()->new StoreScanner->StoreScanner.getScannersNoCompaction()->HStore.getScanners()-> StoreFileScanner.getScannersForStoreFiles->StoreFile.Reader.getStoreFileScanner->getScanner()
这里的getScanner() 其实是 HFileReaderV2 的方法(我们用的是v2 版本的hfile):
public HFileScanner getScanner(boolean cacheBlocks, final boolean pread,
final boolean isCompaction) {
if (dataBlockEncoder.useEncodedScanner()) {
return new EncodedScannerV2(this, cacheBlocks, pread, isCompaction,
hfileContext);
}
return new ScannerV2(this, cacheBlocks, pread, isCompaction);
}
用的是他的子类ScannerV2,看一下他的getKeyValue():
@Override
public KeyValue getKeyValue() {
if (!isSeeked())
return null;
KeyValue ret = new KeyValue(blockBuffer.array(), blockBuffer.arrayOffset()
+ blockBuffer.position(), getCellBufSize());
if (this.reader.shouldIncludeMemstoreTS()) {
ret.setMvccVersion(currMemstoreTS);
}
return ret;
}这个KeyValue的构造函数如下:
/**
* Creates a KeyValue from the specified byte array, starting at offset, and
* for length <code>length</code>.
* @param bytes byte array
* @param offset offset to start of the KeyValue
* @param length length of the KeyValue
*/
public KeyValue(final byte [] bytes, final int offset, final int length) {
this.bytes = bytes;
this.offset = offset;
this.length = length;
}
HFileReaderV2.ScannerV2 将 HFile 视为byte数组,通过偏移量和长度截取这个byte数据获取keyvalue的值