stl变易算法(一)
C++ STL的变易算法是一组能够修改容器元素数据的模板函数,可进行序列容器的复制、交换、替换、填充、移除、旋转等。这些算法对迭代器有较高的要求,具体的迭代器类型随各个算法而定,或向前迭代器、或双向迭代器、又或者是随机迭代器,以提供算法所需要的迭代器操作。应用变易算法时,先要检查容器的迭代器是否符合要求,防止产生编译错误。
元素复制copy
C++STL提供一个用于容器间元素拷贝的copy算法,将迭代区间[first,last)的元素复制到由复制目标迭代器result给定的区间[result,result+(last-first))中,原型如下:
template <class InputIterator, class OutputIterator>
OutputIterator copy (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, OutputIterator result);具体代码如下:
template<class InputIterator, class OutputIterator>
OutputIterator copy (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, OutputIterator result)
{
while (first!=last) {
*result = *first;
++result;
++first;
}
return result;
} //实例
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void print(int x){
cout << x << " ";
}
int main(void){
//初始化向量v
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(5);
//初始化双向链表l
list<int> l;
l.push_back(2);
l.push_back(4);
l.push_back(6);
l.push_back(8);
l.push_back(10);
//复制v到l
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), l.begin());
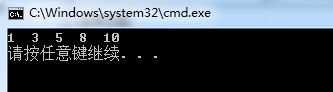
//链表l打印l 3 5 8 10
for_each(l.begin(), l.end(), print);
cout <<endl;
return 0;
}反向复制copy_backward
与copy算法相似,copy_backward算法也是将一个迭代器区间元素复制到另一迭代器区间上,只是复制的过程是从最后的元素开始复制,直到首元素复制出来。
它使用的原型如下,将迭代器区间[first,last)的元素,复制到以result为结束位置的区间[result-(last-first))中,顺序为*(last-1)复制到*(result-1)、*(last-2)复制到*(result-2)、*(last-3)复制到*(result-3)、……
//copy_backward算法函数的代码
template<class BidirectionalIterator1, class BidirectionalIterator2>
BidirectionalIterator2 copy_backward ( BidirectionalIterator1 first,
BidirectionalIterator1 last,
BidirectionalIterator2 result )
{
while (last!=first) *(--result) = *(--last);
return result;
}//测试用例
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void print(int x){
cout << x << ' ';
}
int main(void){
vector<int> v(10);
for(unsigned int i=0; i<v.size(); i++)
v[i]=i+1;
copy_backward(v.begin(), v.begin() + 3, v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print);
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}元素交换swap
虽然大多数容器的内部提供了swap函数,但c++STL还是以更一般的迭代器形式,提供更一般的swap算法来实现两个元素的交换。
//swap算法函数的代码
template <class T> void swap ( T& a, T& b )
{
T c(a); a=b; b=c;
}//实例
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int a = 5;
int b = 26;
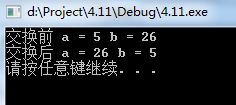
cout << "交换前 " << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;
swap(a, b);
cout << "交换后 " << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;
return 0;
}迭代器交换iter_swap
iter_swap算法是swap算法的迭代器形式,使交换算法更易用于一般的容器。
template <class ForwardIterator1, class ForwardIterator2>
void iter_swap (ForwardIterator1 a, ForwardIterator2 b)
{
swap (*a, *b);
}//例子
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int a = 5;
int b = 26;
cout << "交换前 " << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;
iter_swap(&a, &b);
cout << "交换后 " << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}区间元素交换swap_ranges
直观来说,swap_ranges算法用于进行两个迭代器区间元素的交换。它的使用原型如下,将[first1,last1)迭代器区间的元素,与[first2,first2+(last1-first1))迭代器区间元素交换,其中*first1和*first2交换,*(first1+1)和*(first2+1)交换、……、*(last1-1)和*(first2+(last1-first1)-1)交换。
template<class ForwardIterator1, class ForwardIterator2>
ForwardIterator2 swap_ranges (ForwardIterator1 first1, ForwardIterator1 last1,
ForwardIterator2 first2)
{
while (first1!=last1) {
swap (*first1, *first2);
++first1; ++first2;
}
return first2;
}//实例
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void print(int x)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
int main(void)
{
vector<int> v1, v2;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(5);
v2.push_back(2);
v2.push_back(4);
v2.push_back(6);
//打印v1、v2
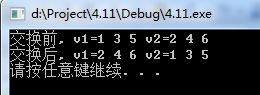
cout << "交换前, v1=";
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), print);
cout << "v2=";
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print);
cout << endl;
//交换v1、v2
swap_ranges(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());
//打印v1、v2
cout << "交换后, v1=";
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), print);
cout << "v2=";
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}未完待续……
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lsh_2013/article/details/46854397