cpp-tests Node及NodeTest
~~~~我的生活,我的点点滴滴!!
一、Node类
Node 是cocos2dx中最常用,很重要的一个类,好多类都继承于他,这里我不一一列举了,所以有必要好好理解一下他。
/** Node 是场景元素的基类,场景中的元素基本都是Node的子类,像常用的Scene、Layer、Sprite、 Menu、Label等等。 一、Node主要特性: 1、Node能作为容器添加、删除任何他的子类,通过 addChild、getChildByTag、getChildByName、removeChild等。 2、Node能定期安排执行回调函数,通过 schedule、unschedule等等。 3、Node还能执行动作,通过runAction、stopAction等等。 二、Node子类需要注意点: 1、重载init去初始化资源与回调函数。 2、创建回调函数去处理更新。 3、重载draw去渲染自己。 三、Node的一些基本属性: 1、默认位置position为 x=0,y=0。 2、默认缩放scale 为 1。 3、默认旋转rotation为顺时针方向角度为0。 4、默认锚点anchor为(0,0)。 5、默认内容大小contentSize为(0,0)。 6、默认是否可见visible为true。 三、限制点: Node可以看作是一个“空的”物体,所以如果要在screen上画一些东西,要去继承Node或者使用Sprite(Sprite也是继承于Node)去重载draw()函数去在里面操作。 */
Node内容太丰富了,丰富到说一天一夜也说不完,我写出一些我知道的、想知道、将来要知道的一些接口注释与注意点。
看下面源码:
class CC_DLL Node : public Ref
{
public:
/**
设置结点Node的本地zOrder顺序,他将要把所有的node放一块,按大小值排序,如果值相同,
按先添加在前面的原则,这样就是稳定的排序了。
*/
virtual void setLocalZOrder(int localZOrder);
/**
定义了结点Node渲染的顺序,值越小越先渲染。全局zOrder相同的,渲染先后顺序是随机的。
唯一的意外是Node的全局zOrder不为0,因为0被场景使用了。全局zOrder主要用处可以按不
同的顺序来渲染其结点。
*/
virtual void setGlobalZOrder(float globalZOrder);
/**
设置在其父亲中的位置,他和OpenGL坐标系相同。
*/
virtual void setPosition(const Vec2 &position);
/**
归一化,他的值在0-1之间,他暗含setposition()这个动作。
伪代码:
void setNormalizedPosition(Vec2 pos)
{
Size s = getParent()->getContentSize();
_position = pos * s;
}
后面有一个例子讲其效果。
*/
virtual void setNormalizedPosition(const Vec2 &position);
/** returns the normalized position */
virtual const Vec2& getNormalizedPosition() const;
/**
* Sets the anchor point in percent.
*
* anchorPoint is the point around which all transformations and positioning manipulations take place.
* It's like a pin in the node where it is "attached" to its parent.
* The anchorPoint is normalized, like a percentage. (0,0) means the bottom-left corner and (1,1) means the top-right corner.
* But you can use values higher than (1,1) and lower than (0,0) too.
* The default anchorPoint is (0.5,0.5), so it starts in the center of the node.
* @note If node has a physics body, the anchor must be in the middle, you cann't change this to other value.
*
* @param anchorPoint The anchor point of node.
*/
/**
锚点是所有对本身操作的坐标值,像旋转、放大、缩小、转变等,就像一个钉子钉住一个物体,那物体就只能绕这个点做运动了。
锚点是归一化的坐标值,(0,0)左下角,(1,1)右上角,(0.5,0.5)中间,锚点是可以大于(1,1)和小于(0,0),如果这个node是一
个刚体,那么锚点必须在正中间(0.5,0.5),并且你不能改变其值。
*/
virtual void setAnchorPoint(const Vec2& anchorPoint);
/**
设置结点的原始大小,不管这个结点是放大缩小还是旋转,这个值是不会变,除非人为设置其他的值。
Layer和scene的contentsize就是屏幕的大小。
*/
virtual void setContentSize(const Size& contentSize);
/**
* Sets whether the anchor point will be (0,0) when you position this node.
*
* This is an internal method, only used by Layer and Scene. Don't call it outside framework.
* The default value is false, while in Layer and Scene are true
*
* @param ignore true if anchor point will be (0,0) when you position this node
* @todo This method should be renamed as setIgnoreAnchorPointForPosition(bool) or something with "set"
*/
/**
设置锚点始终为(0,0),不管怎么设置node的位置,仅仅在Layer和Scene上使用。
默认为false不开启的,但是在Layer和Scene中是默认为true。
*/
virtual void ignoreAnchorPointForPosition(bool ignore);
/**
添加其到node容器中,默认zOrder为0,他会retain一次,所以如果使用addChild不需要手动retain。
如果添加到一个running的node中,会立刻调用'onEnter'和'onEnterTransitionDidFinish'
*/
virtual void addChild(Node * child);
/**
带有本地zOrder值添加到node容器中,其他同上。
*/
virtual void addChild(Node * child, int localZOrder);
/**
同上。
*/
virtual void addChild(Node* child, int localZOrder, int tag);
/**
添加一个name为标签,后续可以通过name来查找。
*/
virtual void addChild(Node* child, int localZOrder, const std::string &name);
/**
通过tag标签,得到其对象指针。
*/
virtual Node * getChildByTag(int tag) const;
/**
通过name标签,得到其对象指针。
*/
virtual Node* getChildByName(const std::string& name) const;
/** Search the children of the receiving node to perform processing for nodes which share a name.
*
* @param name The name to search for, supports c++11 regular expression.
* Search syntax options:
* `//`: Can only be placed at the begin of the search string. This indicates that it will search recursively.
* `..`: The search should move up to the node's parent. Can only be placed at the end of string
* `/` : When placed anywhere but the start of the search string, this indicates that the search should move to the node's children.
*
* @code
* enumerateChildren("//MyName", ...): This searches the children recursively and matches any node with the name `MyName`.
* enumerateChildren("[[:alnum:]]+", ...): This search string matches every node of its children.
* enumerateChildren("A[[:digit:]]", ...): This searches the node's children and returns any child named `A0`, `A1`, ..., `A9`
* enumerateChildren("Abby/Normal", ...): This searches the node's grandchildren and returns any node whose name is `Normal`
* and whose parent is named `Abby`.
* enumerateChildren("//Abby/Normal", ...): This searches recursively and returns any node whose name is `Normal` and whose
* parent is named `Abby`.
* @endcode
*
* @warning Only support alpha or number for name, and not support unicode
*
* @param callback A callback function to execute on nodes that match the `name` parameter. The function takes the following arguments:
* `node`
* A node that matches the name
* And returns a boolean result. Your callback can return `true` to terminate the enumeration.
*
* @since v3.2
*/
/**
新增的函数功能,通过名字正则来搜索所有符合条件指针,cpp-test里面的demo貌似运行很卡。
*/
virtual void enumerateChildren(const std::string &name, std::function<bool(Node* node)> callback) const;
/**
上面说过会Node里面会有一个容器来保存添加进来的孩子对象指针,
使用的是cocos2dx自己封装的Vector容器。
*/
virtual Vector<Node*>& getChildren() { return _children; }
virtual const Vector<Node*>& getChildren() const { return _children; }
////// REMOVES //////
/**
* Removes this node itself from its parent node with a cleanup.
* If the node orphan, then nothing happens.
* @see `removeFromParentAndCleanup(bool)`
*/
/**
从其父结点中移除自己,并且cleanup,cleanup执行的是移除所有的和此node有关的任何操作,
像调试器,回调函数、正在运行的动作等等,此接口就是removeFromParentAndCleanup(true);
*/
virtual void removeFromParent();
/**
* Removes this node itself from its parent node.
* If the node orphan, then nothing happens.
* @param cleanup true if all actions and callbacks on this node should be removed, false otherwise.
* @js removeFromParent
* @lua removeFromParent
*/
virtual void removeFromParentAndCleanup(bool cleanup);
/**
移除容器中某一个孩子,cleanup为true,其操作和removeFromParent中一样,会移除掉所有和其相关的操作。
*/
virtual void removeChild(Node* child, bool cleanup = true);
/**
和上面一模一样,只不过是通过tag值来寻找要移除和孩子结点。
*/
virtual void removeChildByTag(int tag, bool cleanup = true);
/**
同上。
*/
virtual void removeChildByName(const std::string &name, bool cleanup = true);
/**
移除所有孩子结点,强行cleanup=true,相当于下面的removeAllChildrenWithCleanup(true)。
*/
virtual void removeAllChildren();
/**
* Removes all children from the container, and do a cleanup to all running actions depending on the cleanup parameter.
*
* @param cleanup true if all running actions on all children nodes should be cleanup, false oterwise.
* @js removeAllChildren
* @lua removeAllChildren
*/
virtual void removeAllChildrenWithCleanup(bool cleanup);
/**
* 停止所有正在运行的actions及调度器。
*/
virtual void cleanup();
/**
给其设置tag值,用来获取。
*/
virtual void setTag(int tag);
/**
可以用来设置自定义的数据,他为void* 意味着可以是任何类型的。
*/
virtual void setUserData(void *userData);
virtual void* getUserData() { return _userData; }
///////////////下面几个是OpenGL的知识,本吊目前不会,不敢造次
/// @{
/// @name GLProgram
/**
* Return the GLProgram (shader) currently used for this node
*
* @return The GLProgram (shader) currently used for this node
*/
GLProgram* getGLProgram() const;
CC_DEPRECATED_ATTRIBUTE GLProgram* getShaderProgram() const { return getGLProgram(); }
GLProgramState *getGLProgramState() const;
void setGLProgramState(GLProgramState *glProgramState);
/**
* Sets the shader program for this node
*
* Since v2.0, each rendering node must set its shader program.
* It should be set in initialize phase.
@code
node->setGLrProgram(GLProgramCache::getInstance()->getProgram(GLProgram::SHADER_NAME_POSITION_TEXTURE_COLOR));
@endcode
*
* @param shaderProgram The shader program
*/
void setGLProgram(GLProgram *glprogram);
CC_DEPRECATED_ATTRIBUTE void setShaderProgram(GLProgram *glprogram) { setGLProgram(glprogram); }
/// @} end of Shader Program
/**
* Override this method to draw your own node.
* The following GL states will be enabled by default:
* - `glEnableClientState(GL_VERTEX_ARRAY);`
* - `glEnableClientState(GL_COLOR_ARRAY);`
* - `glEnableClientState(GL_TEXTURE_COORD_ARRAY);`
* - `glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);`
* AND YOU SHOULD NOT DISABLE THEM AFTER DRAWING YOUR NODE
* But if you enable any other GL state, you should disable it after drawing your node.
*/
virtual void draw(Renderer *renderer, const Mat4& transform, uint32_t flags);
virtual void draw() final;
/**
* Visits this node's children and draw them recursively.
*/
virtual void visit(Renderer *renderer, const Mat4& parentTransform, uint32_t parentFlags);
virtual void visit() final;
/**
用来判断是否正在运行中,运行中node会接受各种回调,像更新帧update(),进入onEnter(),退出onExit()等。
*/
virtual bool isRunning() const;
/// @{
/// @name Event Callbacks
/**
* Event callback that is invoked every time when Node enters the 'stage'.
* If the Node enters the 'stage' with a transition, this event is called when the transition starts.
* During onEnter you can't access a "sister/brother" node.
* If you override onEnter, you shall call its parent's one, e.g., Node::onEnter().
* @js NA
* @lua NA
*/
virtual void onEnter();
/** Event callback that is invoked when the Node enters in the 'stage'.
* If the Node enters the 'stage' with a transition, this event is called when the transition finishes.
* If you override onEnterTransitionDidFinish, you shall call its parent's one, e.g. Node::onEnterTransitionDidFinish()
* @js NA
* @lua NA
*/
virtual void onEnterTransitionDidFinish();
/**
* Event callback that is invoked every time the Node leaves the 'stage'.
* If the Node leaves the 'stage' with a transition, this event is called when the transition finishes.
* During onExit you can't access a sibling node.
* If you override onExit, you shall call its parent's one, e.g., Node::onExit().
* @js NA
* @lua NA
*/
virtual void onExit();
/**
* Event callback that is called every time the Node leaves the 'stage'.
* If the Node leaves the 'stage' with a transition, this callback is called when the transition starts.
* @js NA
* @lua NA
*/
virtual void onExitTransitionDidStart();
Action* runAction(Action* action);
/**
停止和移除所有的actions从running actions列表中。
*/
void stopAllActions();
/**
* Stops and removes an action from the running action list.
*
* @param action The action object to be removed.
*/
void stopAction(Action* action);
/**
* Returns the numbers of actions that are running plus the ones that are schedule to run (actions in actionsToAdd and actions arrays).
*
* Composable actions are counted as 1 action. Example:
* If you are running 1 Sequence of 7 actions, it will return 1.
* If you are running 7 Sequences of 2 actions, it will return 7.
* @todo Rename to getNumberOfRunningActions()
*
* @return The number of actions that are running plus the ones that are schedule to run
*/
ssize_t getNumberOfRunningActions() const;
/// @} end of Actions
/// @{
/// @name Scheduler and Timer
/**
* Sets a Scheduler object that is used to schedule all "updates" and timers.
*
* @warning If you set a new Scheduler, then previously created timers/update are going to be removed.
* @param scheduler A Shdeduler object that is used to schedule all "update" and timers.
*/
virtual void setScheduler(Scheduler* scheduler);
/**
* Gets a Sheduler object.
*
* @see setScheduler(Scheduler*)
* @return A Scheduler object.
*/
virtual Scheduler* getScheduler() { return _scheduler; }
virtual const Scheduler* getScheduler() const { return _scheduler; }
/**
* Checks whether a selector is scheduled.
*
* @param selector A function selector
* @return Whether the funcion selector is scheduled.
* @js NA
* @lua NA
*/
bool isScheduled(SEL_SCHEDULE selector);
/**
* Schedules the "update" method.
*
* It will use the order number 0. This method will be called every frame.
* Scheduled methods with a lower order value will be called before the ones that have a higher order value.
* Only one "update" method could be scheduled per node.
* @js NA
* @lua NA
*/
void scheduleUpdate(void);
/**
* Schedules the "update" method with a custom priority.
*
* This selector will be called every frame.
* Scheduled methods with a lower priority will be called before the ones that have a higher value.
* Only one "update" selector could be scheduled per node (You can't have 2 'update' selectors).
* @js NA
* @lua NA
*/
void scheduleUpdateWithPriority(int priority);
/*
* Unschedules the "update" method.
* @see scheduleUpdate();
*/
void unscheduleUpdate(void);
/**
* Schedules a custom selector.
*
* If the selector is already scheduled, then the interval parameter will be updated without scheduling it again.
@code
// firstly, implement a schedule function
void MyNode::TickMe(float dt);
// wrap this function into a selector via schedule_selector marco.
this->schedule(schedule_selector(MyNode::TickMe), 0, 0, 0);
@endcode
*
* @param selector The SEL_SCHEDULE selector to be scheduled.
* @param interval Tick interval in seconds. 0 means tick every frame. If interval = 0, it's recommended to use scheduleUpdate() instead.
* @param repeat The selector will be excuted (repeat + 1) times, you can use kRepeatForever for tick infinitely.
* @param delay The amount of time that the first tick will wait before execution.
* @lua NA
*/
void schedule(SEL_SCHEDULE selector, float interval, unsigned int repeat, float delay);
/**
* Schedules a custom selector with an interval time in seconds.
* @see `schedule(SEL_SCHEDULE, float, unsigned int, float)`
*
* @param selector The SEL_SCHEDULE selector to be scheduled.
* @param interval Callback interval time in seconds. 0 means tick every frame,
* @lua NA
*/
void schedule(SEL_SCHEDULE selector, float interval);
/**
* Schedules a selector that runs only once, with a delay of 0 or larger
* @see `schedule(SEL_SCHEDULE, float, unsigned int, float)`
*
* @param selector The SEL_SCHEDULE selector to be scheduled.
* @param delay The amount of time that the first tick will wait before execution.
* @lua NA
*/
void scheduleOnce(SEL_SCHEDULE selector, float delay);
/**
* Schedules a custom selector, the scheduled selector will be ticked every frame
* @see schedule(SEL_SCHEDULE, float, unsigned int, float)
*
* @param selector A function wrapped as a selector
* @lua NA
*/
void schedule(SEL_SCHEDULE selector);
/**
* Unschedules a custom selector.
* @see `schedule(SEL_SCHEDULE, float, unsigned int, float)`
*
* @param selector A function wrapped as a selector
* @lua NA
*/
void unschedule(SEL_SCHEDULE selector);
/**
* Unschedule all scheduled selectors: custom selectors, and the 'update' selector.
* Actions are not affected by this method.
* @lua NA
*/
void unscheduleAllSelectors(void);
/**
* Resumes all scheduled selectors, actions and event listeners.
* This method is called internally by onEnter
*/
void resume(void);
/**
* Pauses all scheduled selectors, actions and event listeners..
* This method is called internally by onExit
*/
void pause(void);
/**
* Resumes all scheduled selectors, actions and event listeners.
* This method is called internally by onEnter
*/
CC_DEPRECATED_ATTRIBUTE void resumeSchedulerAndActions();
/**
* Pauses all scheduled selectors, actions and event listeners..
* This method is called internally by onExit
*/
CC_DEPRECATED_ATTRIBUTE void pauseSchedulerAndActions();
/*
* Update method will be called automatically every frame if "scheduleUpdate" is called, and the node is "live"
*/
virtual void update(float delta);
/// @} end of Scheduler and Timer
/// @{
/// @name Coordinate Converters
/**
* Converts a Vec2 to node (local) space coordinates. The result is in Points.
*/
Vec2 convertToNodeSpace(const Vec2& worldPoint) const;
/**
* Converts a Vec2 to world space coordinates. The result is in Points.
*/
Vec2 convertToWorldSpace(const Vec2& nodePoint) const;
/**
* Converts a Vec2 to node (local) space coordinates. The result is in Points.
* treating the returned/received node point as anchor relative.
*/
Vec2 convertToNodeSpaceAR(const Vec2& worldPoint) const;
/**
* Converts a local Vec2 to world space coordinates.The result is in Points.
* treating the returned/received node point as anchor relative.
*/
Vec2 convertToWorldSpaceAR(const Vec2& nodePoint) const;
/**
* convenience methods which take a Touch instead of Vec2
*/
Vec2 convertTouchToNodeSpace(Touch * touch) const;
/**
* converts a Touch (world coordinates) into a local coordinate. This method is AR (Anchor Relative).
*/
Vec2 convertTouchToNodeSpaceAR(Touch * touch) const;
#if CC_USE_PHYSICS
/**
* set the PhysicsBody that let the sprite effect with physics
* @note This method will set anchor point to Vec2::ANCHOR_MIDDLE if body not null, and you cann't change anchor point if node has a physics body.
*/
void setPhysicsBody(PhysicsBody* body);
/**
* get the PhysicsBody the sprite have
*/
PhysicsBody* getPhysicsBody() const;
};
我们用的最多的,最容易出现崩溃的无非是removChild之类的和addChild等等,前者要弄明白到底里面做了些什么操作,操作之后有哪些改变,后者要明白里面是否调用了retain(),保存了指针等等。用得多,看得多,自然就明白的多了。
二、NodeTest
cpp-tests样例中讲了很多关于Node的例子,大家可以去看,我只列举几个说明一下。
1、CameraTest1
这例子主要讲解了orbitCamera这个球形运动轨迹的效果:
void CameraTest1::onEnter()
{
TestCocosNodeDemo::onEnter();
_preProjection = Director::getInstance()->getProjection();
//设置其为3D效果;
Director::getInstance()->setProjection(Director::Projection::_3D);
Director::getInstance()->setDepthTest(true);
}
void CameraTest1::onExit()
{
Director::getInstance()->setProjection(_preProjection);
Director::getInstance()->setDepthTest(false);
TestCocosNodeDemo::onExit();
}
CameraTest1::CameraTest1()
{
auto s = Director::getInstance()->getWinSize();
_sprite1 = MySprite::create(s_back3);
addChild( _sprite1 );
_sprite1->setPosition( Vec2(1*s.width/4, s.height/2) );
_sprite1->setScale(0.5);
_sprite2 = Sprite::create(s_back3);
addChild( _sprite2 );
_sprite2->setPosition( Vec2(3*s.width/4, s.height/2) );
_sprite2->setScale(0.5);
/********************************************************
????这个效果的参数实在难理解,他是一个3D球形轨迹,但是看效果貌似可
以实现翻盘效果,具体设置什么参数有什么样子的效果,我也不清楚,下面看
其参数:
*creates a OrbitCamera action with radius, delta-radius, z, deltaZ, x, deltaX
*static OrbitCamera* create(float t, float radius, float deltaRadius, float angleZ,
float deltaAngleZ, float angleX, float deltaAngleX);
就字面意思:
t: 旋转时间,这个无庸置疑;
radius: 起始半径;
deltaRadius:半径差;
angleZ: 起始Z角;
deltaAngleZ:旋转Z角差;
angleX: 起始X角;
deltaAngleX:旋转X角差;
*********************************************************/
auto camera = OrbitCamera::create(10, 10, 1, 0, 360, 0, 90);
_sprite1->runAction( camera );
_sprite2->runAction( camera->clone() );
}
目前我依然不是特别能体会到orbitCamera里面参数的含义,但是以后用到了,一点点试应该理解的更快。
2、CameraCenterTest
用来让人感受3D效果的。
//3D效果,5个小方块,他们其实完全一样的,速度、变化角度等等;
//但是看效果感觉他们速度不一,那正是符合常理情况,camera是视野在正中间;
//就像我们人站在他们正中间,左边的翻转45度后,我们就能看到另一面,而右边的要翻转135度;
//我才能看到他的另一面。这是视野位置不同引起的。
CameraCenterTest::CameraCenterTest()
{
auto s = Director::getInstance()->getWinSize();
Sprite *sprite;
OrbitCamera *orbit;
// LEFT-BOTTOM
sprite = Sprite::create("Images/white-512x512.png");
addChild( sprite, 0);
sprite->setPosition(Vec2(s.width/5*1, s.height/5*1));
//我一直不知道精灵还可以为其着色?因为我的理解精灵就是一张图片
//图片都是固定好了的,怎么给其着色了?下面开眼了。
sprite->setColor(Color3B::RED);
sprite->setTextureRect(Rect(0, 0, 120, 150));
orbit = OrbitCamera::create(10, 1, 0, 0, 360, 0, 0);
sprite->runAction(RepeatForever::create( orbit ));
// [sprite setAnchorPoint: Vec2(0,1));
// LEFT-TOP
//这种重复使用同一临时变量sprite来存储不同的对象是很危险的;
//因为下面重新生成一个新对象时,旧对象指针就丢失了,成了野指针;
//这里之所以敢这么用是因为有addChild(), 他里面其实是使用了一个
//容器Vector<Node*> _children把每一个指针对象添加进去了,这样
//指针就没有丢失,也就不会成为野指针,建议大家这样使用时要谨慎;
sprite = Sprite::create("Images/white-512x512.png");
addChild( sprite, 0, 40);
sprite->setPosition(Vec2(s.width/5*1, s.height/5*4));
sprite->setColor(Color3B::BLUE);
sprite->setTextureRect(Rect(0, 0, 120, 50));
orbit = OrbitCamera::create(10, 1, 0, 0, 360, 0, 0);
sprite->runAction(RepeatForever::create( orbit ));
// RIGHT-BOTTOM
sprite = Sprite::create("Images/white-512x512.png");
addChild( sprite, 0);
sprite->setPosition(Vec2(s.width/5*4, s.height/5*1));
sprite->setColor(Color3B::YELLOW);
sprite->setTextureRect(Rect(0, 0, 120, 50));
orbit = OrbitCamera::create(10, 1, 0, 0, 360, 0, 0);
sprite->runAction(RepeatForever::create( orbit) );
// RIGHT-TOP
sprite = Sprite::create("Images/white-512x512.png");
addChild( sprite, 0, 40);
sprite->setPosition(Vec2(s.width/5*4, s.height/5*4));
sprite->setColor(Color3B::GREEN);
sprite->setTextureRect(Rect(0, 0, 120, 50));
orbit = OrbitCamera::create(10, 1, 0, 0, 360, 0, 0);
sprite->runAction( RepeatForever::create( orbit ) );
// CENTER
sprite = Sprite::create("Images/white-512x512.png");
addChild( sprite, 0, 40);
sprite->setPosition(Vec2(s.width/2, s.height/2));
sprite->setColor(Color3B::WHITE);
sprite->setTextureRect(Rect(0, 0, 120, 50));
orbit = OrbitCamera::create(10, 1, 0, 0, 360, 0, 0);
sprite->runAction(RepeatForever::create( orbit ) );
}
这里面也用到了orbitCamera,不过貌似可以尝试用下FlipX3D和FlipY3D,但是FlipX3D或FlipY3D时效果不是特别好,他翻转时会有左右或上下的移动偏差,然后在翻转完后瞬间又回到原来位置,貌似像bug,我没有去看他的源码,我们还是用orbitCamera吧。
效果图:
3、Test2
锚点与孩子。
//------------------------------------------------------------------
//
// Test2 测试锚点Anchor,及父亲对孩子的影响;
//
//------------------------------------------------------------------
void Test2::onEnter()
{
TestCocosNodeDemo::onEnter();
auto s = Director::getInstance()->getWinSize();
auto sp1 = Sprite::create(s_pathSister1);
auto sp2 = Sprite::create(s_pathSister2);
auto sp3 = Sprite::create(s_pathSister1);
auto sp4 = Sprite::create(s_pathSister2);
sp1->setPosition(Vec2(100, s.height /2 ));
sp2->setPosition(Vec2(380, s.height /2 ));
addChild(sp1);
addChild(sp2);
sp3->setScale(0.25f);
sp4->setScale(0.25f);
sp1->addChild(sp3);
sp2->addChild(sp4);
auto a1 = RotateBy::create(2, 360);
auto a2 = ScaleBy::create(2, 2);
auto action1 = RepeatForever::create( Sequence::create(a1, a2, a2->reverse(), nullptr) );
auto action2 = RepeatForever::create( Sequence::create(
a1->clone(),
a2->clone(),
a2->reverse(),
nullptr)
);
//改变了sp2的锚点,但是sp1默认锚点是(0.5,0.5);
//所以sp2是以左下角为定点作旋转,sp1是中心点作旋转;
//父亲的actions对孩子是有传递性的,上篇例子中有讲到;
sp2->setAnchorPoint(Vec2(0,0));
sp1->runAction(action1);
sp2->runAction(action2);
}
效果图:
4、Test6
简简单单测试Node中的removeChild系列的功能,这个样例非常好,让我们一目了然的体会了removeChild系列的动作细节。
//------------------------------------------------------------------
//
// Test6 测试父子影响,对父亲删除操作,会递归的把所有儿子都操作一遍;
// 也就是对父亲的动作,同样会传递给儿子。除非人为的设置为不传递;
// 如果父亲和儿子都作同一动作,儿子要和父亲同步,那样儿子运动就会变快;
// 类似于公转与自转等;
//------------------------------------------------------------------
Test6::Test6()
{
auto sp1 = Sprite::create(s_pathSister1);
auto sp11 = Sprite::create(s_pathSister1);
auto sp2 = Sprite::create(s_pathSister2);
auto sp21 = Sprite::create(s_pathSister2);
sp1->setPosition(Vec2(100,160));
sp2->setPosition(Vec2(380,160));
auto rot = RotateBy::create(2, 360);
auto rot_back = rot->reverse();
auto forever1 = RepeatForever::create(Sequence::create(rot, rot_back, nullptr));
auto forever11 = forever1->clone();
auto forever2 = forever1->clone();
auto forever21 = forever1->clone();
addChild(sp1, 0, kTagSprite1);
sp1->addChild(sp11);
addChild(sp2, 0, kTagSprite2);
sp2->addChild(sp21);
sp1->runAction(forever1);
sp11->runAction(forever11);
sp2->runAction(forever2);
sp21->runAction(forever21);
schedule( schedule_selector(Test6::addAndRemove), 12.0f);
}
void Test6::addAndRemove(float dt)
{
auto sp1 = getChildByTag(kTagSprite1);
auto sp2 = getChildByTag(kTagSprite2);
//手动retain一次以免被构造掉;
sp1->retain();
sp2->retain();
//sp1的调试器和动作都还在;
removeChild(sp1, false);
//sp2彻底清除了;
removeChild(sp2, true);
//所以通过下面的重新添加后,sp1依然保持着他原有的动作,而sp2却没有任何动作了;
addChild(sp1, 0, kTagSprite1);
addChild(sp2, 0, kTagSprite2);
//配套的,有retain就要有release
sp1->release();
sp2->release();
}
效果图:
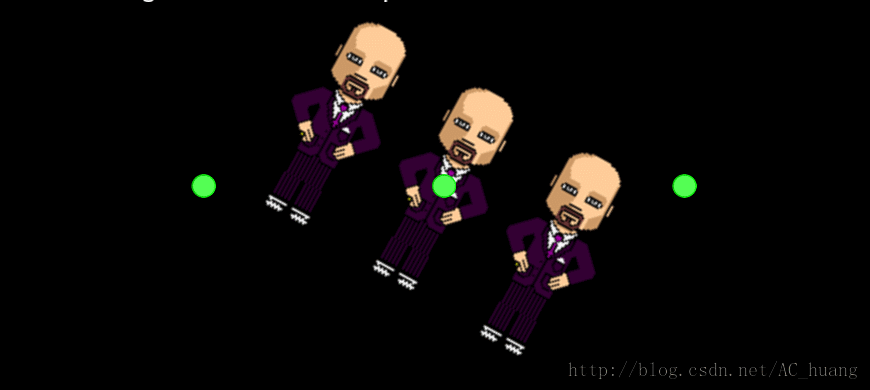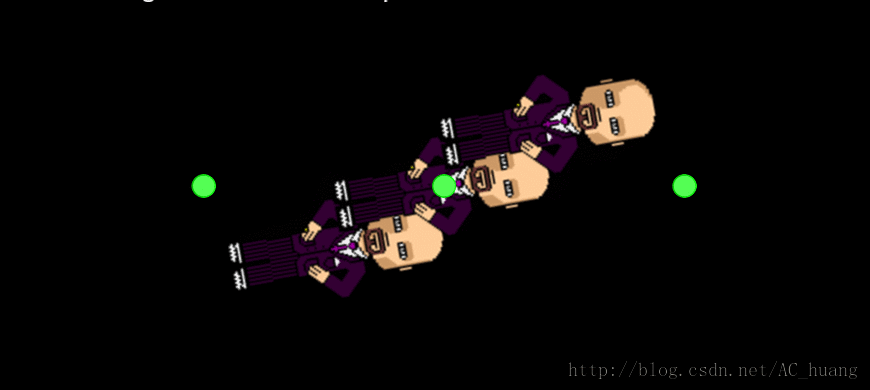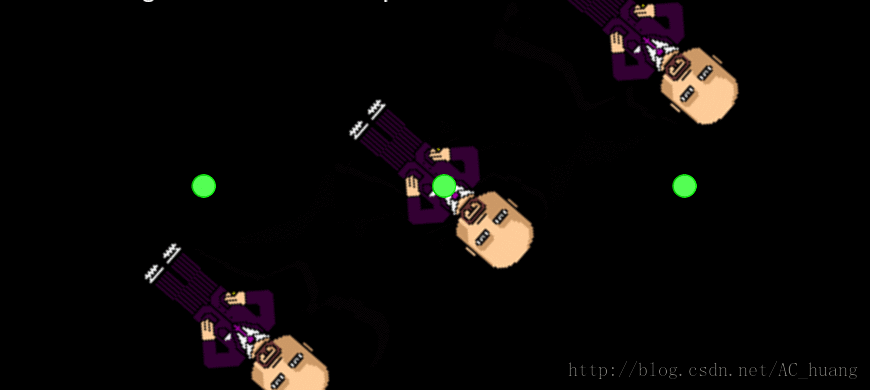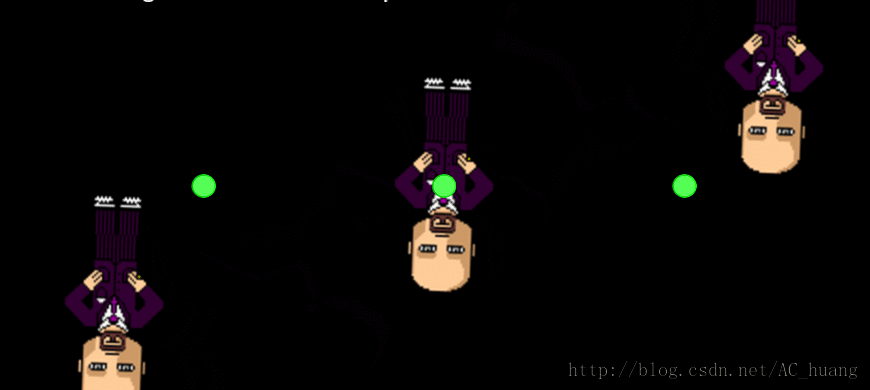
5、ConvertToNode
这个也是通过改变父亲的锚点来看旋转中心及打印在不同锚点下的相同坐标值的是不同的。
//------------------------------------------------------------------
//
// 对于不同的锚点AnchorPoint, 旋转的中心是不一样的;
//
//------------------------------------------------------------------
ConvertToNode::ConvertToNode()
{
auto listener = EventListenerTouchAllAtOnce::create();
listener->onTouchesEnded = CC_CALLBACK_2(ConvertToNode::onTouchesEnded, this);
_eventDispatcher->addEventListenerWithSceneGraphPriority(listener, this);
auto s = Director::getInstance()->getWinSize();
auto rotate = RotateBy::create(10, 360);
auto action = RepeatForever::create(rotate);
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
auto sprite = Sprite::create("Images/grossini.png");
sprite->setPosition(Vec2( s.width/4*(i+1), s.height/2));
auto point = Sprite::create("Images/r1.png");
point->setScale(0.25f);
point->setPosition(sprite->getPosition());
addChild(point, 10, 100 + i);
switch(i)
{
case 0:
sprite->setAnchorPoint(Vec2::ZERO);
break;
case 1:
sprite->setAnchorPoint(Vec2(0.5f, 0.5f));
break;
case 2:
sprite->setAnchorPoint(Vec2(1,1));
break;
}
point->setPosition(sprite->getPosition());
sprite->runAction( action->clone() );
addChild(sprite, i);
}
}
void ConvertToNode::onTouchesEnded(const std::vector<Touch*>& touches, Event *event)
{
for( auto& touch : touches)
{
auto location = touch->getLocation();
for( int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
auto node = getChildByTag(100+i);
Vec2 p1, p2;
p1 = node->convertToNodeSpaceAR(location);
p2 = node->convertToNodeSpace(location);
CCLOG("AR: x=%.2f, y=%.2f -- Not AR: x=%.2f, y=%.2f", p1.x, p1.y, p2.x, p2.y);
}
}
}
效果:
6、NodeNormalizedPositionTest2
Node结点的归一化。
//------------------------------------------------------------------
//
// NodeNormalizedPositionTest2 坐标归一化;
//
//------------------------------------------------------------------
NodeNormalizedPositionTest2::NodeNormalizedPositionTest2()
: _accum(0)
{
Sprite *sprites[5];
Vec2 positions[5];
positions[0] = Vec2(0,0);
positions[1] = Vec2(0,1);
positions[2] = Vec2(0.5,0.5);
positions[3] = Vec2(1,0);
positions[4] = Vec2(1,1);
std::vector<Color3B>cc;
cc.push_back(Color3B::RED);
cc.push_back(Color3B::GREEN);
cc.push_back(Color3B::GRAY);
cc.push_back(Color3B::BLUE);
cc.push_back(Color3B::WHITE);
Sprite *bg = Sprite::create("Images/background3.png");
bg->setPosition(Director::getInstance()->getWinSize().width*0.5,Director::getInstance()->getWinSize().height*0.5);
addChild(bg,-1,1);
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
sprites[i] = Sprite::create("Images/grossini.png");
//用该方法可以使用0-1之间的值设置节点position(x,y)。当节点有父节点时才可以使用该方法;
//所以setNormalizedPosition()是相对于父亲结点的位置,如果父亲结点变化了,相应的儿子
//也会改变位置,这样就造成了儿子在运动一样,下面的效果就是利用这点实现的。
sprites[i]->setNormalizedPosition(positions[i]);
if( i != 2 )
{
sprites[i]->setColor(cc.at(i));
}
addChild(sprites[i]);
}
scheduleUpdate();
setContentSize( Director::getInstance()->getWinSize());
_copyContentSize = getContentSize();
// setAnchorPoint(Vec2(0.5,0.5));
// setNormalizedPosition(Vec2(0.5,0.5));
}
std::string NodeNormalizedPositionTest2::title() const
{
return "setNormalizedPositon() #2";
}
std::string NodeNormalizedPositionTest2::subtitle() const
{
return "5 sprites: One in the center, the others on the corners of its parents";
}
void NodeNormalizedPositionTest2::update(float dt)
{
_accum += dt;
// for 5 seconds
// sinf()里面参数为弧度,注意这个函数的曲线图;
float norm = sinf(_accum);
Size s = Size(_copyContentSize.width*norm, _copyContentSize.height*norm);
//通过改变父亲的Size大小来影响孩子在其上面的坐标,从而达到像孩子在运动一样;
//最开始我以为是通过使用MoveBy或者MoveTo之类的直线移动来达到的效果,看完代码后还是为其惊叹;
//虽然使用MoveBy或者MoveTo能很容易的达到目的,但是用归一化的方法很有创造力;
setContentSize(s);
CCLOG("s: %f,%f,%f,%f",_accum, norm, s.width, s.height);
}
效果图:
更多的NodeTest样例请去看cpp-tests