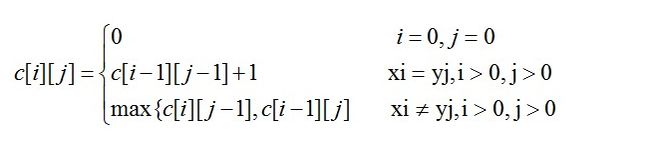最长公共子序列问题
问题描述:字符序列的子序列是指从给定字符序列中随意地(不一定连续)去掉若干个字符(可能一个也不去掉)后所形成的字符序列。令给定的字符序列X=“x0,x1,…,xm-1”,序列Y=“y0,y1,…,yk-1”是X的子序列,存在X的一个严格递增下标序列<i0,i1,…,ik-1>,使得对所有的j=0,1,…,k-1,有xij=yj。例如,X=“ABCBDAB”,Y=“BCDB”是X的一个子序列。
解决方法:
1、穷举法:针对序列x中所有的子序列(共2^m个),在Y序列中寻列是否存在相同序列,并找出其中最大的序列。这种方法的时间复杂度为O(2^m*2^n)。
2、动态规划法:引进一个二维数组c[][],用c[i][j]记录X[i]与Y[j] 的LCS 的长度,b[i][j]记录c[i][j]是通过哪一个子问题的值求得的,以决定搜索的方向。可以通过以下公式来计算从c[i][j]的值。
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度:O(m*n);
空间复杂度:O(m*n);
代码:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#define MAXLEN 100
using namespace std;
void GetLCSLen(string str1, string str2,int m,int n,int c[][MAXLEN],int b[][MAXLEN])
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i <= m; i++)
c[i][0] = 0;
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
c[0][j] = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (str1[i - 1] == str2[j - 1])
{
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
b[i][j] = 0;
}
else
{
if (c[i - 1][j] >= c[i][j - 1])
{
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j];
b[i][j] = 1;
}
else
{
c[i][j] = c[i][j - 1];
b[i][j] = 2;
}
}
}
}
}
void PrintLCS(int b[][MAXLEN], string x, int i, int j) //递归回溯最长子序列
{
if (i == 0 || j == 0)
return;
if (b[i][j] == 0)
{
PrintLCS(b, x, i - 1, j - 1);
cout<<x[i-1];
}
else if (b[i][j] == 1)
PrintLCS(b, x, i - 1, j);
else
PrintLCS(b, x, i, j - 1);
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
string s1 = "ABCBDAB";
string s2 = "BDCABA";
int strlen1 = s1.size();
int strlen2 = s2.size();
int b[MAXLEN][MAXLEN];
int c[MAXLEN][MAXLEN];
GetLCSLen(s1,s2,strlen1,strlen2,c,b);
cout << c[strlen1][strlen2] << endl; //输出最长子序列长度
PrintLCS(b,s1,strlen1,strlen2);
return 0;
}