机器学习算法与Python实践之(一)k近邻(KNN)
机器学习算法与Python实践之(一)k近邻(KNN)
http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09
机器学习算法与Python实践这个系列主要是参考《机器学习实战》这本书。因为自己想学习Python,然后也想对一些机器学习算法加深下了解,所以就想通过Python来实现几个比较常用的机器学习算法。恰好遇见这本同样定位的书籍,所以就参考这本书的过程来学习了。
一、kNN算法分析
K最近邻(k-Nearest Neighbor,KNN)分类算法可以说是最简单的机器学习算法了。它采用测量不同特征值之间的距离方法进行分类。它的思想很简单:如果一个样本在特征空间中的k个最相似(即特征空间中最邻近)的样本中的大多数属于某一个类别,则该样本也属于这个类别。
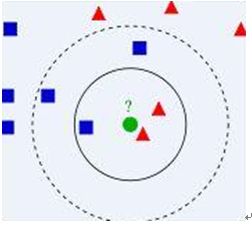
比如上面这个图,我们有两类数据,分别是蓝色方块和红色三角形,他们分布在一个上图的二维中间中。那么假如我们有一个绿色圆圈这个数据,需要判断这个数据是属于蓝色方块这一类,还是与红色三角形同类。怎么做呢?我们先把离这个绿色圆圈最近的几个点找到,因为我们觉得离绿色圆圈最近的才对它的类别有判断的帮助。那到底要用多少个来判断呢?这个个数就是k了。如果k=3,就表示我们选择离绿色圆圈最近的3个点来判断,由于红色三角形所占比例为2/3,所以我们认为绿色圆是和红色三角形同类。如果k=5,由于蓝色四方形比例为3/5,因此绿色圆被赋予蓝色四方形类。从这里可以看到,k的值还是很重要的。
KNN算法中,所选择的邻居都是已经正确分类的对象。该方法在定类决策上只依据最邻近的一个或者几个样本的类别来决定待分样本所属的类别。由于KNN方法主要靠周围有限的邻近的样本,而不是靠判别类域的方法来确定所属类别的,因此对于类域的交叉或重叠较多的待分样本集来说,KNN方法较其他方法更为适合。
该算法在分类时有个主要的不足是,当样本不平衡时,如一个类的样本容量很大,而其他类样本容量很小时,有可能导致当输入一个新样本时,该样本的K个邻居中大容量类的样本占多数。因此可以采用权值的方法(和该样本距离小的邻居权值大)来改进。该方法的另一个不足之处是计算量较大,因为对每一个待分类的文本都要计算它到全体已知样本的距离,才能求得它的K个最近邻点。目前常用的解决方法是事先对已知样本点进行剪辑,事先去除对分类作用不大的样本。该算法比较适用于样本容量比较大的类域的自动分类,而那些样本容量较小的类域采用这种算法比较容易产生误分[参考机器学习十大算法]。
总的来说就是我们已经存在了一个带标签的数据库,然后输入没有标签的新数据后,将新数据的每个特征与样本集中数据对应的特征进行比较,然后算法提取样本集中特征最相似(最近邻)的分类标签。一般来说,只选择样本数据库中前k个最相似的数据。最后,选择k个最相似数据中出现次数最多的分类。其算法描述如下:
1)计算已知类别数据集中的点与当前点之间的距离;
2)按照距离递增次序排序;
3)选取与当前点距离最小的k个点;
4)确定前k个点所在类别的出现频率;
5)返回前k个点出现频率最高的类别作为当前点的预测分类。
二、Python实现
对于机器学习而已,Python需要额外安装三件宝,分别是Numpy,scipy和Matplotlib。前两者用于数值计算,后者用于画图。安装很简单,直接到各自的官网下载回来安装即可。安装程序会自动搜索我们的python版本和目录,然后安装到python支持的搜索路径下。反正就python和这三个插件都默认安装就没问题了。
另外,如果我们需要添加我们的脚本目录进Python的目录(这样Python的命令行就可以直接import),可以在系统环境变量中添加:PYTHONPATH环境变量,值为我们的路径,例如:E:\Python\Machine Learning in Action
2.1、kNN基础实践
一般实现一个算法后,我们需要先用一个很小的数据库来测试它的正确性,否则一下子给个大数据给它,它也很难消化,而且还不利于我们分析代码的有效性。
首先,我们新建一个kNN.py脚本文件,文件里面包含两个函数,一个用来生成小数据库,一个实现kNN分类算法。代码如下:
- #########################################
- # kNN: k Nearest Neighbors
- # Input: newInput: vector to compare to existing dataset (1xN)
- # dataSet: size m data set of known vectors (NxM)
- # labels: data set labels (1xM vector)
- # k: number of neighbors to use for comparison
- # Output: the most popular class label
- #########################################
- from numpy import *
- import operator
- # create a dataset which contains 4 samples with 2 classes
- def createDataSet():
- # create a matrix: each row as a sample
- group = array([[1.0, 0.9], [1.0, 1.0], [0.1, 0.2], [0.0, 0.1]])
- labels = ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B'] # four samples and two classes
- return group, labels
- # classify using kNN
- def kNNClassify(newInput, dataSet, labels, k):
- numSamples = dataSet.shape[0] # shape[0] stands for the num of row
- ## step 1: calculate Euclidean distance
- # tile(A, reps): Construct an array by repeating A reps times
- # the following copy numSamples rows for dataSet
- diff = tile(newInput, (numSamples, 1)) - dataSet # Subtract element-wise
- squaredDiff = diff ** 2 # squared for the subtract
- squaredDist = sum(squaredDiff, axis = 1) # sum is performed by row
- distance = squaredDist ** 0.5
- ## step 2: sort the distance
- # argsort() returns the indices that would sort an array in a ascending order
- sortedDistIndices = argsort(distance)
- classCount = {} # define a dictionary (can be append element)
- for i in xrange(k):
- ## step 3: choose the min k distance
- voteLabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]]
- ## step 4: count the times labels occur
- # when the key voteLabel is not in dictionary classCount, get()
- # will return 0
- classCount[voteLabel] = classCount.get(voteLabel, 0) + 1
- ## step 5: the max voted class will return
- maxCount = 0
- for key, value in classCount.items():
- if value > maxCount:
- maxCount = value
- maxIndex = key
- return maxIndex
#########################################
# kNN: k Nearest Neighbors
# Input: newInput: vector to compare to existing dataset (1xN)
# dataSet: size m data set of known vectors (NxM)
# labels: data set labels (1xM vector)
# k: number of neighbors to use for comparison
# Output: the most popular class label
#########################################
from numpy import *
import operator
# create a dataset which contains 4 samples with 2 classes
def createDataSet():
# create a matrix: each row as a sample
group = array([[1.0, 0.9], [1.0, 1.0], [0.1, 0.2], [0.0, 0.1]])
labels = ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B'] # four samples and two classes
return group, labels
# classify using kNN
def kNNClassify(newInput, dataSet, labels, k):
numSamples = dataSet.shape[0] # shape[0] stands for the num of row
## step 1: calculate Euclidean distance
# tile(A, reps): Construct an array by repeating A reps times
# the following copy numSamples rows for dataSet
diff = tile(newInput, (numSamples, 1)) - dataSet # Subtract element-wise
squaredDiff = diff ** 2 # squared for the subtract
squaredDist = sum(squaredDiff, axis = 1) # sum is performed by row
distance = squaredDist ** 0.5
## step 2: sort the distance
# argsort() returns the indices that would sort an array in a ascending order
sortedDistIndices = argsort(distance)
classCount = {} # define a dictionary (can be append element)
for i in xrange(k):
## step 3: choose the min k distance
voteLabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]]
## step 4: count the times labels occur
# when the key voteLabel is not in dictionary classCount, get()
# will return 0
classCount[voteLabel] = classCount.get(voteLabel, 0) + 1
## step 5: the max voted class will return
maxCount = 0
for key, value in classCount.items():
if value > maxCount:
maxCount = value
maxIndex = key
return maxIndex
然后我们在命令行中这样测试即可:
- import kNN
- from numpy import *
- dataSet, labels = kNN.createDataSet()
- testX = array([1.2, 1.0])
- k = 3
- outputLabel = kNN.kNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, 3)
- print "Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class: ", outputLabel
- testX = array([0.1, 0.3])
- outputLabel = kNN.kNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, 3)
- print "Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class: ", outputLabel
import kNN from numpy import * dataSet, labels = kNN.createDataSet() testX = array([1.2, 1.0]) k = 3 outputLabel = kNN.kNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, 3) print "Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class: ", outputLabel testX = array([0.1, 0.3]) outputLabel = kNN.kNNClassify(testX, dataSet, labels, 3) print "Your input is:", testX, "and classified to class: ", outputLabel
这时候会输出:
- Your input is: [ 1.2 1.0] and classified to class: A
- Your input is: [ 0.1 0.3] and classified to class: B
Your input is: [ 1.2 1.0] and classified to class: A Your input is: [ 0.1 0.3] and classified to class: B
2.2、kNN进阶
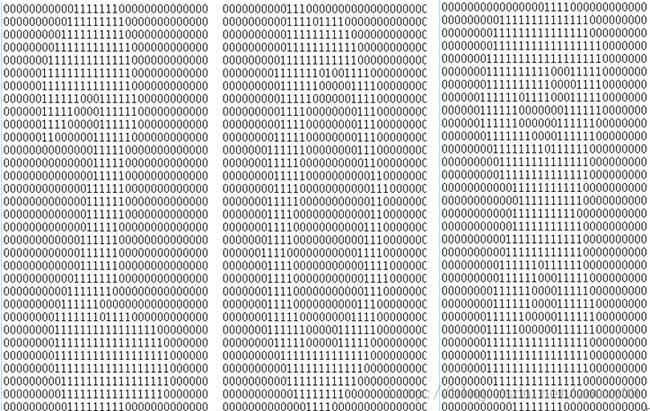
这里我们用kNN来分类一个大点的数据库,包括数据维度比较大和样本数比较多的数据库。这里我们用到一个手写数字的数据库,可以到这里下载。这个数据库包括数字0-9的手写体。每个数字大约有200个样本。每个样本保持在一个txt文件中。手写体图像本身的大小是32x32的二值图,转换到txt文件保存后,内容也是32x32个数字,0或者1,如下:
数据库解压后有两个目录:目录trainingDigits存放的是大约2000个训练数据,testDigits存放大约900个测试数据。
这里我们还是新建一个kNN.py脚本文件,文件里面包含四个函数,一个用来生成将每个样本的txt文件转换为对应的一个向量,一个用来加载整个数据库,一个实现kNN分类算法。最后就是实现这个加载,测试的函数。
- #########################################
- # kNN: k Nearest Neighbors
- # Input: inX: vector to compare to existing dataset (1xN)
- # dataSet: size m data set of known vectors (NxM)
- # labels: data set labels (1xM vector)
- # k: number of neighbors to use for comparison
- # Output: the most popular class label
- #########################################
- from numpy import *
- import operator
- import os
- # classify using kNN
- def kNNClassify(newInput, dataSet, labels, k):
- numSamples = dataSet.shape[0] # shape[0] stands for the num of row
- ## step 1: calculate Euclidean distance
- # tile(A, reps): Construct an array by repeating A reps times
- # the following copy numSamples rows for dataSet
- diff = tile(newInput, (numSamples, 1)) - dataSet # Subtract element-wise
- squaredDiff = diff ** 2 # squared for the subtract
- squaredDist = sum(squaredDiff, axis = 1) # sum is performed by row
- distance = squaredDist ** 0.5
- ## step 2: sort the distance
- # argsort() returns the indices that would sort an array in a ascending order
- sortedDistIndices = argsort(distance)
- classCount = {} # define a dictionary (can be append element)
- for i in xrange(k):
- ## step 3: choose the min k distance
- voteLabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]]
- ## step 4: count the times labels occur
- # when the key voteLabel is not in dictionary classCount, get()
- # will return 0
- classCount[voteLabel] = classCount.get(voteLabel, 0) + 1
- ## step 5: the max voted class will return
- maxCount = 0
- for key, value in classCount.items():
- if value > maxCount:
- maxCount = value
- maxIndex = key
- return maxIndex
- # convert image to vector
- def img2vector(filename):
- rows = 32
- cols = 32
- imgVector = zeros((1, rows * cols))
- fileIn = open(filename)
- for row in xrange(rows):
- lineStr = fileIn.readline()
- for col in xrange(cols):
- imgVector[0, row * 32 + col] = int(lineStr[col])
- return imgVector
- # load dataSet
- def loadDataSet():
- ## step 1: Getting training set
- print "---Getting training set..."
- dataSetDir = 'E:/Python/Machine Learning in Action/'
- trainingFileList = os.listdir(dataSetDir + 'trainingDigits') # load the training set
- numSamples = len(trainingFileList)
- train_x = zeros((numSamples, 1024))
- train_y = []
- for i in xrange(numSamples):
- filename = trainingFileList[i]
- # get train_x
- train_x[i, :] = img2vector(dataSetDir + 'trainingDigits/%s' % filename)
- # get label from file name such as "1_18.txt"
- label = int(filename.split('_')[0]) # return 1
- train_y.append(label)
- ## step 2: Getting testing set
- print "---Getting testing set..."
- testingFileList = os.listdir(dataSetDir + 'testDigits') # load the testing set
- numSamples = len(testingFileList)
- test_x = zeros((numSamples, 1024))
- test_y = []
- for i in xrange(numSamples):
- filename = testingFileList[i]
- # get train_x
- test_x[i, :] = img2vector(dataSetDir + 'testDigits/%s' % filename)
- # get label from file name such as "1_18.txt"
- label = int(filename.split('_')[0]) # return 1
- test_y.append(label)
- return train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y
- # test hand writing class
- def testHandWritingClass():
- ## step 1: load data
- print "step 1: load data..."
- train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y = loadDataSet()
- ## step 2: training...
- print "step 2: training..."
- pass
- ## step 3: testing
- print "step 3: testing..."
- numTestSamples = test_x.shape[0]
- matchCount = 0
- for i in xrange(numTestSamples):
- predict = kNNClassify(test_x[i], train_x, train_y, 3)
- if predict == test_y[i]:
- matchCount += 1
- accuracy = float(matchCount) / numTestSamples
- ## step 4: show the result
- print "step 4: show the result..."
- print 'The classify accuracy is: %.2f%%' % (accuracy * 100)
#########################################
# kNN: k Nearest Neighbors
# Input: inX: vector to compare to existing dataset (1xN)
# dataSet: size m data set of known vectors (NxM)
# labels: data set labels (1xM vector)
# k: number of neighbors to use for comparison
# Output: the most popular class label
#########################################
from numpy import *
import operator
import os
# classify using kNN
def kNNClassify(newInput, dataSet, labels, k):
numSamples = dataSet.shape[0] # shape[0] stands for the num of row
## step 1: calculate Euclidean distance
# tile(A, reps): Construct an array by repeating A reps times
# the following copy numSamples rows for dataSet
diff = tile(newInput, (numSamples, 1)) - dataSet # Subtract element-wise
squaredDiff = diff ** 2 # squared for the subtract
squaredDist = sum(squaredDiff, axis = 1) # sum is performed by row
distance = squaredDist ** 0.5
## step 2: sort the distance
# argsort() returns the indices that would sort an array in a ascending order
sortedDistIndices = argsort(distance)
classCount = {} # define a dictionary (can be append element)
for i in xrange(k):
## step 3: choose the min k distance
voteLabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]]
## step 4: count the times labels occur
# when the key voteLabel is not in dictionary classCount, get()
# will return 0
classCount[voteLabel] = classCount.get(voteLabel, 0) + 1
## step 5: the max voted class will return
maxCount = 0
for key, value in classCount.items():
if value > maxCount:
maxCount = value
maxIndex = key
return maxIndex
# convert image to vector
def img2vector(filename):
rows = 32
cols = 32
imgVector = zeros((1, rows * cols))
fileIn = open(filename)
for row in xrange(rows):
lineStr = fileIn.readline()
for col in xrange(cols):
imgVector[0, row * 32 + col] = int(lineStr[col])
return imgVector
# load dataSet
def loadDataSet():
## step 1: Getting training set
print "---Getting training set..."
dataSetDir = 'E:/Python/Machine Learning in Action/'
trainingFileList = os.listdir(dataSetDir + 'trainingDigits') # load the training set
numSamples = len(trainingFileList)
train_x = zeros((numSamples, 1024))
train_y = []
for i in xrange(numSamples):
filename = trainingFileList[i]
# get train_x
train_x[i, :] = img2vector(dataSetDir + 'trainingDigits/%s' % filename)
# get label from file name such as "1_18.txt"
label = int(filename.split('_')[0]) # return 1
train_y.append(label)
## step 2: Getting testing set
print "---Getting testing set..."
testingFileList = os.listdir(dataSetDir + 'testDigits') # load the testing set
numSamples = len(testingFileList)
test_x = zeros((numSamples, 1024))
test_y = []
for i in xrange(numSamples):
filename = testingFileList[i]
# get train_x
test_x[i, :] = img2vector(dataSetDir + 'testDigits/%s' % filename)
# get label from file name such as "1_18.txt"
label = int(filename.split('_')[0]) # return 1
test_y.append(label)
return train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y
# test hand writing class
def testHandWritingClass():
## step 1: load data
print "step 1: load data..."
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y = loadDataSet()
## step 2: training...
print "step 2: training..."
pass
## step 3: testing
print "step 3: testing..."
numTestSamples = test_x.shape[0]
matchCount = 0
for i in xrange(numTestSamples):
predict = kNNClassify(test_x[i], train_x, train_y, 3)
if predict == test_y[i]:
matchCount += 1
accuracy = float(matchCount) / numTestSamples
## step 4: show the result
print "step 4: show the result..."
print 'The classify accuracy is: %.2f%%' % (accuracy * 100)
测试非常简单,只需要在命令行中输入:
- import kNN
- kNN.testHandWritingClass()
import kNN kNN.testHandWritingClass()
输出结果如下:
- step 1: load data...
- ---Getting training set...
- ---Getting testing set...
- step 2: training...
- step 3: testing...
- step 4: show the result...
- The classify accuracy is: 98.84%