树
普通树
树的实现:将每个节点的所有儿子都放在树节点的链表中.下面是典型的声明
typedef struct TreeNode *PtrToNode;
struct TreeNode
{
ElementType Element;
PtrToNode FirstChild;
PtrToNode nextSibling;
}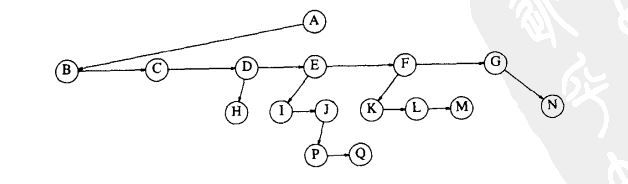
图中向下的箭头是指向FirstChild(第一个儿子)的指针.从左到右的箭头是指向NextSibling(下一兄弟)的指针.因为空指针太多.所以没有把它们画出.节点E有一个指针指向兄弟(F),另一个指针指向儿子(I),而有的节点这两种指针都没有.
树有很多应用.流行的用法之一是包括UNIX, VAX/VMS和DOS在内的许多常用操作系统中的目录结构.
二叉树
二叉树是一棵树,其中每个节点都不能有多于两个的儿子.
二叉树查找树
二叉树的一个重要的应用是它们在查找中的使用.
性质:对于树中的每个节点X,它的左子树中所有关键字值小于X的关键字值,而它的右子树中所有关键字值大于X的关键字值.
AVL树
一颗AVL树是其每个节点的左子树和右子树的高度最多差1的二叉查找树.当向AVL树种插入一个节点时,可能会破坏AVL树的平衡,这时我们需要通过单旋转或双旋转来保持树的平衡
伸展树(splay tree)
它能在O(log n)内完成插入、查找和删除操作.splay tree是一种自调整形式的二叉查找树,了使整个查找时间更小,被查频率高的那些条目就应当经常处于靠近树根的位置。于是想到设计一个简单方法, 在每次查找之后对树进行重构,它会沿着从某个节点到树根之间的路径,通过一系列的旋转把这个节点搬移到树根去。
B-tree
多路搜索树,并不是二叉的。使用B-tree结构可以显著减少定位记录时所经历的中间过程,从而加快存取速度。按照翻译,B 通常认为是Balance的简称。这个数据结构一般用于数据库的索引,综合效率较高。
对于一棵m阶B-tree,每个结点至多可以拥有m个子结点。各结点的关键字和可以拥有的子结点数都有限制,规定m阶B-tree中,根结点至少有2个子结点,除非根结点为叶子节点,相应的,根结点中关键字的个数为1~m-1;非根结点至少有[m/2]([],向上取整)个子结点,相应的,关键字个数为[m/2]-1~m-1。
B-tree中,每个结点包含:
1、本结点所含关键字的个数;
2、指向父结点的指针;
3、关键字;
4、指向子结点的指针;
二叉查找树ADT
public class BinarySearchTree {
// 树的根结点
private TreeNode root = null;
// 遍历结点列表
private List<TreeNode> nodelist = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
//二叉查找树类
private class TreeNode {
private int key;
private TreeNode leftChild;
private TreeNode rightChild;
private TreeNode parent;
public TreeNode(int key, TreeNode leftChild, TreeNode rightChild,
TreeNode parent) {
this.key = key;
this.leftChild = leftChild;
this.rightChild = rightChild;
this.parent = parent;
}
public int getKey() {
return key;
}
public String toString() {
String leftkey = (leftChild == null ? "" : String
.valueOf(leftChild.key));
String rightkey = (rightChild == null ? "" : String
.valueOf(rightChild.key));
return "(" + leftkey + " , " + key + " , " + rightkey + ")";
}
}
/** * search: 在二叉查找树中查询给定关键字 * * @param key * 给定关键字 * @return 匹配给定关键字的树结点 */
public TreeNode search(int key) {
TreeNode pNode = root;
while (pNode != null && pNode.key != key) {
if (key < pNode.key) {
pNode = pNode.leftChild;
} else {
pNode = pNode.rightChild;
}
}
return pNode;
}
/** * insert: 将给定关键字插入到二叉查找树中 * * @param key * 给定关键字 */
public void insert(int key) {
TreeNode parentNode = null;
TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(key, null, null, null);
TreeNode pNode = root;
if (root == null) {
root = newNode;
return;
}
while (pNode != null) { //找到父节点
parentNode = pNode;
if (key < pNode.key) {
pNode = pNode.leftChild;
} else if (key > pNode.key) {
pNode = pNode.rightChild;
} else {
// 树中已存在匹配给定关键字的结点,则什么都不做直接返回
return;
}
}
if (key < parentNode.key) {
parentNode.leftChild = newNode;
newNode.parent = parentNode;
} else {
parentNode.rightChild = newNode;
newNode.parent = parentNode;
}
}
/** * insert: 从二叉查找树中删除匹配给定关键字相应的树结点 * * @param key * 给定关键字 */
public void delete(int key) throws Exception {
TreeNode pNode = search(key);
if (pNode == null) {
throw new Exception("树中不存在要删除的关键字!");
}
delete(pNode);
}
/** * delete: 从二叉查找树中删除给定的结点. * * @param pNode * 要删除的结点 * * 前置条件: 给定结点在二叉查找树中已经存在 * @throws Exception */
private void delete(TreeNode pNode) throws Exception {
if (pNode == null) {
return;
}
if (pNode.leftChild == null && pNode.rightChild == null) { // 该结点既无左孩子结点,也无右孩子结点
TreeNode parentNode = pNode.parent;
if (pNode == parentNode.leftChild) {
parentNode.leftChild = null;
} else {
parentNode.rightChild = null;
}
return;
}
if (pNode.leftChild == null && pNode.rightChild != null) { // 该结点左孩子结点为空,右孩子结点非空
TreeNode parentNode = pNode.parent;
if (pNode == parentNode.leftChild) {
parentNode.leftChild = pNode.rightChild;
pNode.rightChild.parent = parentNode;
} else {
parentNode.rightChild = pNode.rightChild;
pNode.rightChild.parent = parentNode;
}
return;
}
if (pNode.leftChild != null && pNode.rightChild == null) { // 该结点左孩子结点非空,右孩子结点为空
TreeNode parentNode = pNode.parent;
if (pNode == parentNode.leftChild) {
parentNode.leftChild = pNode.leftChild;
pNode.rightChild.parent = parentNode;
} else {
parentNode.rightChild = pNode.leftChild;
pNode.rightChild.parent = parentNode;
}
return;
}
// 该结点左右孩子结点均非空,则删除该结点的后继结点,并用该后继结点取代该结点
TreeNode successorNode = successor(pNode);
delete(successorNode);
pNode.key = successorNode.key;
}
/** * successor: 获取给定结点在中序遍历顺序下的后继结点 * * @param node * 给定树中的结点 * @return 若该结点存在中序遍历顺序下的后继结点,则返回其后继结点;否则返回 null * @throws Exception */
public TreeNode successor(TreeNode node) throws Exception {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
// 若该结点的右子树不为空,则其后继结点就是右子树中的最小关键字结点
if (node.rightChild != null) {
return minElemNode(node.rightChild);
}
// 若该结点右子树为空 (中序遍历下的后继结点)
TreeNode parentNode = node.parent;
while (parentNode != null && node == parentNode.rightChild) {
node = parentNode;
parentNode = parentNode.parent;
}
if (node.rightChild == null && node.leftChild != null)
{
return node.leftChild;
}
return parentNode;
}
/** * minElemNode: 获取二叉查找树中的最小关键字结点 * * @return 二叉查找树的最小关键字结点 * @throws Exception * 若树为空,则抛出异常 */
public TreeNode minElemNode(TreeNode node) throws Exception {
if (node == null) {
throw new Exception("树为空!");
}
TreeNode pNode = node;
while (pNode.leftChild != null) {
pNode = pNode.leftChild;
}
return pNode;
}
/** * maxElemNode: 获取二叉查找树中的最大关键字结点 * * @return 二叉查找树的最大关键字结点 * @throws Exception * 若树为空,则抛出异常 */
public TreeNode maxElemNode(TreeNode node) throws Exception {
if (node == null) {
throw new Exception("树为空!");
}
TreeNode pNode = node;
while (pNode.rightChild != null) {
pNode = pNode.rightChild;
}
return pNode;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (root == null) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/** * precessor: 获取给定结点在中序遍历顺序下的前趋结点 * * @param node * 给定树中的结点 * @return 若该结点存在中序遍历顺序下的前趋结点,则返回其前趋结点;否则返回 null * @throws Exception */
public TreeNode precessor(TreeNode node) throws Exception {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
// 若该结点的左子树不为空,则其前趋结点就是左子树中的最大关键字结点
if (node.leftChild != null) {
return maxElemNode(node.leftChild);
}
// 若该结点左子树为空
TreeNode parentNode = node.parent;
while (parentNode != null && node == parentNode.leftChild) {
node = parentNode;
parentNode = parentNode.parent;
}
return parentNode;
}
/** * inOrderTraverse: 对给定二叉查找树进行中序遍历 * * @param root * 给定二叉查找树的根结点 */
private void inOrderTraverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
nodelist.add(root);
inOrderTraverse(root.leftChild);
inOrderTraverse(root.rightChild);
}
}
public TreeNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree();
System.out.println("查找树是否为空? " + (bst.isEmpty() ? "是" : "否"));
int[] keys = new int[] { 15, 6, 18, 3, 7, 13, 20, 2, 9, 4 };
for (int key : keys) {
bst.insert(key);
}
System.out.println("查找树是否为空? " + (bst.isEmpty() ? "是" : "否"));
bst.inOrderTraverse(bst.getRoot());
System.out.println(bst.getRoot().getKey());
if(bst.nodelist != null)
{
for (TreeNode value : bst.nodelist)
{
System.out.println(value.getKey());
}
}
}
}