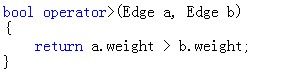优先队列
C++ Priority Queue(优先队列)
C++优先队列类似队列,但是在这个数据结构中的元素按照一定的断言排列有序。它的头文件为<queue>。由于适配器不支持迭代,一个 priority_queue 将有没有关联的迭代器。
函数列表:
empty() 如果优先队列为空,则返回真
pop() 删除第一个元素
push() 加入一个元素
size() 返回优先队列中拥有的元素的个数
top() 返回优先队列中有最高优先级的元素
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
构造函数
explicit priority_queue(const Pred& pr = Pred(),
const allocator_type& al = allocator_type());
priority_queue(const value_type *first, const value_type *last,
const Pred& pr = Pred(), const allocator_type& al = allocator_type());
empty
语法:
bool empty();
empty()函数返回真(true)如果优先队列为空,否则返回假(false)。
pop
语法:
void pop();
pop()函数删除优先队列中的第一个元素。
push
语法:
void push( const TYPE &val );
push()函数添加一个元素到优先队列中,值为val。
size
语法:
size_type size();
size()函数返回优先队列中存储的元素个数。
top
语法:
TYPE &top();
top()返回一个引用,指向优先队列中有最高优先级的元素。注意只有pop()函数删除一个元素。
示例1:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
#if _MSC_VER > 1020 // if VC++ version is > 4.2
using namespace std; // std c++ libs implemented in std
#endif
// Using priority_queue with deque
// Use of function greater sorts the items in ascending order
typedef deque<int, allocator<int> > INTDQU;
typedef priority_queue<int,INTDQU, greater<int> > INTPRQUE;
// Using priority_queue with vector
// Use of function less sorts the items in descending order
typedef vector<char, allocator<char> > CHVECTOR;
typedef priority_queue<char,CHVECTOR,less<char> > CHPRQUE;
void main(void)
{
int size_q;
INTPRQUE q;
CHPRQUE p;
// Insert items in the priority_queue(uses deque)
q.push(42);
q.push(100);
q.push(49);
q.push(201);
// Output the item at the top using top()
cout << q.top() << endl;
// Output the size of priority_queue
size_q = q.size();
cout << "size of q is:" << size_q << endl;
// Output items in priority_queue using top()
// and use pop() to get to next item until
// priority_queue is empty
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.top() << endl;
q.pop();
}
// Insert items in the priority_queue(uses vector)
p.push('c');
p.push('a');
p.push('d');
p.push('m');
p.push('h');
// Output the item at the top using top()
cout << p.top() << endl;
// Output the size of priority_queue
size_q = p.size();
cout << "size of p is:" << size_q << endl;
// Output items in priority_queue using top()
// and use pop() to get to next item until
// priority_queue is empty
while (!p.empty())
{
cout << p.top() << endl;
p.pop();
}
}
输出结果:
42
size of q is:4
42
49
100
201
m
size of p is:5
m
h
d
c
a
示例2:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(const int &a,const int &b)
{
return a<b;//按升序排序
}
};
typedef priority_queue< int, vector<int>, cmp > qu;
void main()
{
qu p;
p.push(42);
p.push(100);
p.push(49);
p.push(201);
while (!p.empty())
{
cout << p.top() << endl;
p.pop();
}
}
输出结果:
201
100
49
42
示例3(用priority_queue实现哈夫曼树):
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int weight;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(int w, Node* l, Node* r): weight(w), left(l), right(r) {}
Node(int w): weight(w), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class cmp //用于priority_queue的仿函数类
{
public :
bool operator()(Node* a,Node* b)
{
return a->weight>=b->weight;
}
};
//传入的是指针,如果用对象去实现,你就不知道左右指针的指向了
//中序遍历
void InOrder(Node* p)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
InOrder(p->left);
cout<<p->weight<<'\t';
InOrder(p->right);
}
}
void freeTree(Node* p)//销毁二叉树
{
if(p->left!=NULL)
freeTree(p->left);
if(p->right!=NULL)
freeTree(p->right);
delete(p);
}
int main()
{
Node* m1,*m2;
priority_queue<Node*,vector<Node*>,cmp> q;
for(int i=0;i<6;++i)//6个节点
{
int n=rand()%100;
q.push(new Node(n));//权值随机产生
cout<<n<<'\t';
}
cout<<endl;
for(int j=1;j<6;++j)//合并5次
{
m1=q.top(); q.pop();
m2=q.top(); q.pop();
int w=m1->weight+m2->weight;
q.push(new Node(w,m1,m2));
}
Node* root=q.top();
InOrder(root);
cout<<endl;
freeTree(root);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
输出结果:
41 67 34 0 69 24
41 99 0 24 24 58 34 235 67 136
69
最近用近似算法实现旅行商问题,需要首先求解最小生成树,用Prim算法求解最小生成树,需要找割的最小边。于是想到了使用priority_queue,现在把priority_queue用法总结一下,不废话了,总结完了,快点求解TSP。
在STL中它的源码如下:
class priority_queue
{
protected:
_Sequence c; ///容器
_Compare comp; ///比较准则
public:
bool empty() const
{ return c.empty(); }
size_type size() const
{ return c.size(); }
const_reference top() const
{
__glibcxx_requires_nonempty();
return c.front();
}
void push(const value_type& __x)
{
try
{
c.push_back(__x);
std::push_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
}
catch(...)
{
c.clear();
__throw_exception_again;
}
}
void pop()
{
__glibcxx_requires_nonempty();
try
{
std::pop_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
c.pop_back();
}
catch(...)
{
c.clear();
__throw_exception_again;
}
}
}
用法:
C++头文件 #include <queue>
template<typename _Tp,
typename _Sequence = vector<_Tp>,
typename _Compare = less<typename _Sequence::value_type> >
第一个参数 _Tp: 指定存储的类型名称;
第二个参数 _Sequence: 指定存储的数据结构,该结果必须支持随机存取迭代器;
第三个参数 _Compare : 比较函数,对于自定义类型有两种方法实现大小顶堆,第一个是重载操作符,第二个是写一个结构实现比较。
各个数据类型算法讲解如下:
1. 对于一般的基本数据类型,比如 int,double等。
1). 默认是大顶堆,测试代码如下
其中省略了比较泛型函数less<int>
输出结果如下:
![]()
2). 小顶堆实现如下:
其中加上了存储的数据结构,和比较函数大小。
输出结果如下:
![]()
2. 对于自定义类型,必须实现比较函数。
自定义类型如下:
实现小顶堆:
自定义比较函数,这里选择实现比较结构:
测试代码为:
运行结果如下:
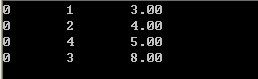
等价的重载大于号实现:
测试代码:
运行结果:
总结大顶堆于小于号有关,小顶堆与大于号有关,这样关联起来就不会忘了。