具体步骤看训练指南
( 一 )求解半平面交
Uyuw's Concert
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=40010;
const double EPS=1e-10;
struct Point
{
double x,y;
Point(double x=0,double y=0):x(x),y(y){}
};
typedef Point Vector;
Vector operator -(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y);
}
Vector operator+(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x+B.x,A.y+B.y);
}
double cross(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x;
}
Vector operator*(Vector A,double val)
{
return Vector(A.x*val,A.y*val);
}
struct Line
{
Point p;//直线上的任意一点
Vector v;//方向向量,它的左边是对应的半平面
double ang;//极角
Line(){}
Line(Point p,Vector v):p(p),v(v){ ang=atan2(v.y,v.x); }
bool operator<(const Line &l) const
{
return ang0;
}
Point getIntersection(Line a,Line b)//两直线交点,假定交点唯一存在
{
Vector u=a.p-b.p;
double t=cross(b.v,u)/cross(a.v,b.v);
return a.p+a.v*t;
}
Point p[MAXN];
Line q[MAXN];//双端队列
Line line[MAXN];
Point out[MAXN];
//半平面交的过程
int halfInter(Line *L,int n,Point *poly)
{
sort(L,L+n);
int first,last;
q[first=last=0]=L[0];
for(int i=1;i 类似的题目:
hdu 1632 Polygons
( 二 )求解多边形的核
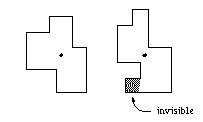
什么是多边形的内核?
它是平面简单多边形的核是该多边形内部的一个点集,该点集中任意一点与多边形边界上一点的连线都处于这个多边形
内部。就是一个在一个房子里面放一个摄像 头,能将所有的地方监视到的放摄像头的地点的集合即为多边形的核。
如上图,第一个图是有内核的,比如那个黑点,而第二个图就不存在内核了,无论点在哪里,总有地区是看不到的。
求解步骤:
只需要把多边形的边当做半平面来求即可
但是,判断点是否在直线的左边的时候,点在直线上的情况也是可以的
同时,在判断点在直线的位置时,还用注意下精度
Rotating Scoreboard
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=1010;
const double EPS=1e-10;
struct Point
{
double x,y;
Point(double x=0,double y=0):x(x),y(y){}
};
typedef Point Vector;
Vector operator-(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y);
}
Vector operator+(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x+B.x,A.y+B.y);
}
Vector operator *(Vector A,double val)
{
return Vector(A.x*val,A.y*val);
}
double cross(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x;
}
struct Line
{
Point p;
Vector v;
double ang;
Line(){}
Line(Point p,Vector v):p(p),v(v){ ang=atan2(v.y,v.x); }
bool operator<(const Line &l) const
{
return ang=0;
}
Point getIntersection(Line a,Line b)
{
Vector u=a.p-b.p;
double t=cross(b.v,u)/cross(a.v,b.v);
return a.p+a.v*t;
}
Line line[MAXN];
Line que[MAXN];
Point p[MAXN];
Point ans[MAXN];
Point point[MAXN];
int halfIntersection(Line *L,int n,Point *poly)
{
sort(L,L+n);
int first,last;
que[first=last=0]=L[0];
for(int i=1;i ( 三 )求解凸多边形的最大内切圆
凸多边形的最大内切圆半径?
等价于从凸多边形内部中找一个点,使得这个点到凸多边形边界的距离的最小值最大。
如何求?
二分半径加半平面交,将凸多边形的每条边向内部(垂直方向)收缩半径r,看每条边的半平面是否还会交出凸多边形。如果推进后的半平面交面积小于等于0,则说明距离太大,否则太小。
Most Distant Point from the Sea
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=1510;
const double EPS=1e-10;
struct Point
{
double x,y;
Point(double x=0,double y=0):x(x),y(y){}
};
typedef Point Vector;
Vector operator -(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y);
}
Vector operator +(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x+B.x,A.y+B.y);
}
Vector operator*(Vector A,double val)
{
return Vector(A.x*val,A.y*val);
}
double cross(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x;
}
struct Line
{
Point p;
Vector v;
double ang;
Line(){}
Line(Point p,Vector v):p(p),v(v){ ang=atan2(v.y,v.x); }
bool operator <(const Line &l)const
{
return ang0?1:-1;
}
bool onLeft(Line line,Point p)
{
return dcmp(cross(line.v,p-line.p))>=0;
}
Point getIntersection(Line a,Line b)
{
Vector u=a.p-b.p;
double t=cross(b.v,u)/cross(a.v,b.v);
return a.p+a.v*t;
}
Point p[MAXN];
Point point[MAXN];
Point change[MAXN];
Line que[MAXN];
Line line[MAXN];
Vector normal[MAXN];
bool halfIntersection(Line *L,int n)
{
sort(L,L+n);
int first,last;
que[first=last=0]=L[0];
for(int i=1;i Feng Shui
题意:
给定多边形和圆的半径r,在多边形内安排两个圆,使得两个圆覆盖的区域尽可能大(重合的部分只算一次),求两个圆的圆心坐标。
题解:
首先,我们应该先确定两个圆心的活动范围,怎么确定呢?
很简单,要使得圆在多边形内部,我们可以把多边形沿着边的垂直方向往内缩r个长度,然后形成的区域就是圆心的活动范围。这个可以用半平面交来求。
怎么才能使得圆覆盖的区域尽可能大?
根据常识,两个圆越远他们的重合区域越少,即覆盖面积越大,也就是求区域最远的两点,所以就变成了凸包的直径问题。
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=1510;
const double EPS=1e-10;
int dcmp(double val)
{
if(abs(val)0?1:-1;
}
struct Point
{
double x,y;
Point(double x=0,double y=0):x(x),y(y){}
};
typedef Point Vector;
Vector operator -(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y);
}
Vector operator +(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x+B.x,A.y+B.y);
}
Vector operator*(Vector A,double val)
{
return Vector(A.x*val,A.y*val);
}
double cross(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x;
}
struct Line
{
Point p;
Vector v;
double ang;
Line(){}
Line(Point p,Vector v):p(p),v(v){ ang=atan2(v.y,v.x); }
bool operator <(const Line &l)const
{
return ang=0;
}
Point getIntersection(Line a,Line b)
{
Vector u=a.p-b.p;
double t=cross(b.v,u)/cross(a.v,b.v);
return a.p+a.v*t;
}
Point p1,p2;
Point p[MAXN];
Point point[MAXN];
Point ans[MAXN];
Line que[MAXN];
Line line[MAXN];
int halfIntersection(Line *L,int n,Point *poly)
{
sort(L,L+n);
int first,last;
que[first=last=0]=L[0];
for(int i=1;icross(ch[i]-ch[i-1],ch[up]-ch[i-1])) up=(up+1)%n;
len=length(ch[up+1]-ch[i]);
if(dcmp(len-res)>=0)
{
p1=ch[up+1];
p2=ch[i];
res=len;
}
len=length(ch[up]-ch[i-1]);
if(dcmp(len-res)>=0)
{
p1=ch[i-1];
p2=ch[up];
res=len;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n,mid;
double x,y,r,maxr,d;
while(scanf("%d%lf",&n,&r)!=EOF)
{
maxr=0.0;
for(int i=0;i