深度学习入门---Numpy图像处理
在Python的学习过程中,我们实际上有各种图像处理库可以使用,比如opencv,Matplotlib,Scipy等等,这里我们使用Numpy来实现图像处理算法,以此来加深Numpy和图像算法的学习。
我们使用Matplotlib来读取和显示图像,如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as img
im = img.imread("data/test/2.bmp")#图像读取
print(im.shape)
plt.imshow(im)#图像显示
img.imsave(“data/test/save.jpg”,im)#图像保存有了图像读取、显示、保存之后,可以开始numpy图像处理编程了(本文只为了解numpy的使用和图像处理的一些算法,并无其他目的)。
1.图像裁剪
#图像裁剪
def imgCrop(im, x, y, w, h):
"""
image crop function.
im: source image
x: x of crop position
y: y of crop position
w: width of crop
h: height of crop
Return cropped image.
"""
img = im[x:np.clip(x+w,0,im.shape[0]),y:np.clip(y+h,0,im.shape[1])]
return img
#test
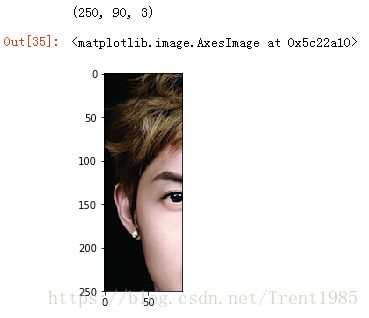
im = img.imread("data/test/6.bmp")
im = imgCrop(im,20,10,250,90)
print(im.shape)
plt.imshow(im)2.图像灰度化
def imgGray(im):
"""
image gray
im: source image
Return gray image.
"""
imgarray = np.array(im)
rows = im.shape[0]
cols = im.shape[1]
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
imgarray[i, j, :] = (imgarray[i, j, 0] * 0.299 + imgarray[i, j, 1] * 0.587 + imgarray[i, j, 2] * 0.114)
return imgarray
#test
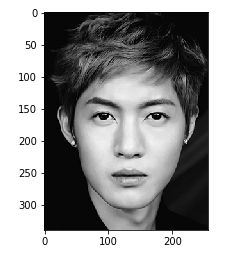
im = img.imread("data/test/6.bmp")
im = imgGray(im)
plt.imshow(im)
plt.show()3.图像二值化
def imgThreshold(im, threshold):
"""
im: source image
threshold: 0-255
Return blackwhite image.
"""
imgarray = np.array(im)
rows = im.shape[0]
cols = im.shape[1]
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
gray = (imgarray[i, j, 0] * 0.299 + imgarray[i, j, 1] * 0.587 + imgarray[i, j, 2] * 0.114)
if gray <= threshold :
imgarray[i,j,:] = 0
else:
imgarray[i,j,:] = 255
return imgarray
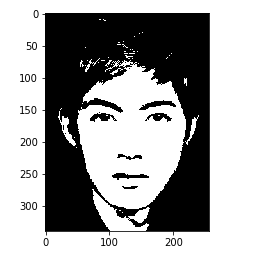
#test
im = img.imread("data/test/6.bmp")
im = imgThreshold(im, 128)
plt.imshow(im)
plt.show()4.图像高斯模糊
def gausskernel(radius, sigma):
length = 2 * radius + 1
kernel = np.zeros(length)
print("kernel size: ", str(kernel.shape))
sum = 0.0
for i in range(length):
kernel[i] = float(np.exp(-(i - radius) * (i - radius) / (2.0 * sigma * sigma)))
sum += kernel[i]
for i in range(length):
kernel[i] = kernel[i] / sum
return kernel
def imgGaussFilter(im, sigma):
"""
Gauss filter.
"""
imarray = np.array(im)
res = np.array(im)
radius = sigma
kernel = gausskernel(radius, sigma*3.0)
print(str(kernel))
tempb = 0.0
tempg = 0.0
tempr = 0.0
rem = 0.0
t = 0.0
v = 0.0
K = 0.0
rows = im.shape[0]
cols = im.shape[1]
for y in range(rows):
for x in range(cols):
tempb = 0.0
tempg = 0.0
tempr = 0.0
for k in range(-radius, radius + 1):
rem = np.abs(x + k) % cols
K = kernel[k+radius]
tempr = tempr + imarray[y,rem,0] * K
tempg = tempg + imarray[y,rem,1] * K
tempb = tempb + imarray[y,rem,2] * K
res[y,x,0] = tempr
res[y,x,1] = tempg
res[y,x,2] = tempb
for x in range(cols):
for y in range(rows):
tempb = 0.0
tempg = 0.0
tempr = 0.0
for k in range(-radius, radius + 1):
rem = np.abs(y + k) % rows
K = kernel[k+radius]
tempr = tempr + res[rem,x,0] * K
tempg = tempg + res[rem,x,1] * K
tempb = tempb + res[rem,x,2] * K
imarray[y,x,0] = tempr
imarray[y,x,1] = tempg
imarray[y,x,2] = tempb
return imarray
#test
im = img.imread("data/test/6.bmp")
im = imgGaussFilter(im, 3)
plt.imshow(im)
plt.show()上面就是使用Numpy进行图像处理的一些简单示例,关于具体的算法原理,可以参考本人博客图像处理基础。