UVa 10173 - Smallest Bounding Rectangle
题目:求包裹平面上已知点的最小面积矩形。
分析:计算几何、凸包、旋转卡壳。最小面积矩形一定存在一条边与凸包共线。(不共线时,可以通过旋转变得更小)
根据以上结论,直接枚举底边,然后利用旋转卡壳确定其余三个顶点即可。
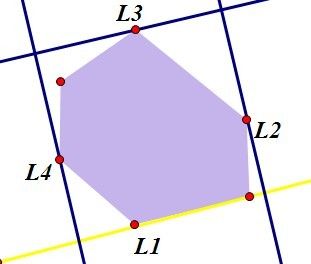
如图:L1为底边,初始化确定四个边界点,然后利用向量,控制L2,L3,L4与L1的角度即可。
注意:1.输入点可以小于3个,可能是点或者线段;
2.精度问题,之前用点到直线距离公式WA了N久,换成向量计算就AC了。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define esp 1e-6
using namespace std;
//点结构
typedef struct pnode
{
double x,y,d;
pnode( double a, double b ){x = a;y = b;}
pnode(){}
}point;
point P[ 1005 ];
//直线结构
typedef struct lnode
{
double x,y,dx,dy;
lnode( point a, point b ){x = a.x;y = a.y;dx = b.x-a.x;dy = b.y-a.y;}
lnode(){}
}line;
//叉乘ab*ac
double crossproduct( point a, point b, point c )
{
return (b.x-a.x)*(c.y-a.y)-(c.x-a.x)*(b.y-a.y);
}
//点到点距离
double dist( point a, point b )
{
return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y));
}
//点到直线距离
double dist( point p, point a, point b )
{
return fabs(crossproduct( p, a, b )/dist( a, b ));
}
//坐标排序
bool cmp1( point a, point b )
{
return (a.x == b.x)?(a.y < b.y):(a.x < b.x);
}
//级角排序
bool cmp2( point a, point b )
{
double cp = crossproduct( P[0], a, b );
if ( cp == 0 ) return a.d < b.d;
else return cp > 0;
}
//叉乘判断平行
double judge1( point a, point b, point c, point d )
{
return crossproduct( a, b, point( a.x+d.x-c.x, a.y+d.y-c.y ) );
}
//点乘判断垂直
double judge2( point a, point b, point c, point d )
{
return ((b.x-a.x)*(d.x-c.x)+(b.y-a.y)*(d.y-c.y));
}
double Graham( int n )
{
if ( n < 3 ) return 0.0;
sort( P+0, P+n, cmp1 );
for ( int i = 1 ; i < n ; ++ i )
P[i].d = dist( P[0], P[i] );
sort( P+1, P+n, cmp2 );
//计算凸包
int top = 1;
for ( int i = 2 ; i < n ; ++ i ) {
while ( top > 0 && crossproduct( P[top-1], P[top], P[i] ) < esp ) -- top;
P[++ top] = P[i];
}
P[++ top] = P[0];
if ( top < 3 ) return 0.0;
//旋转卡壳
int L2 = 0,L3 = 0,L4 = 0;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < top ; ++ i ) {
if ( P[i].y <= P[L2].y ) L2 = i;
if ( P[i].x >= P[L3].x ) L3 = i;
if ( P[i].y >= P[L4].y ) L4 = i;
}
double Min = (P[0].x-P[L3].x)*(P[L2].y-P[L4].y);
for ( int L1 = 0 ; L1 < top ; ++ L1 ) {
//旋转平行边
while ( judge1( P[L1], P[L1+1], P[L3], P[L3+1] ) > esp )
L3 = (L3+1)%top;
//旋转垂直边
while ( L2 != L3 && judge2( P[L1], P[L1+1], P[L2], P[L2+1] ) > esp )
L2 = (L2+1)%top;
while ( L4 != L1 && judge2( P[L1+1], P[L1], P[L4], P[L4+1] ) > esp )
L4 = (L4+1)%top;
double D = dist( P[L3], P[L1], P[L1+1] );
double L = dist( P[L2], P[L4], point( P[L4].x-P[L1+1].y+P[L1].y, P[L4].y+P[L1+1].x-P[L1].x ) );
if ( Min > D*L ) Min = D*L;
}
return Min;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while ( ~scanf("%d",&n) && n ) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i )
scanf("%lf%lf",&P[i].x,&P[i].y);
printf("%.4lf\n",Graham( n ));
}
return 0;
}