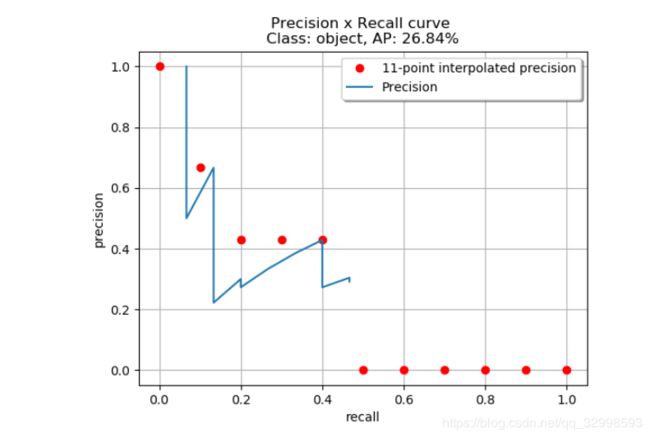
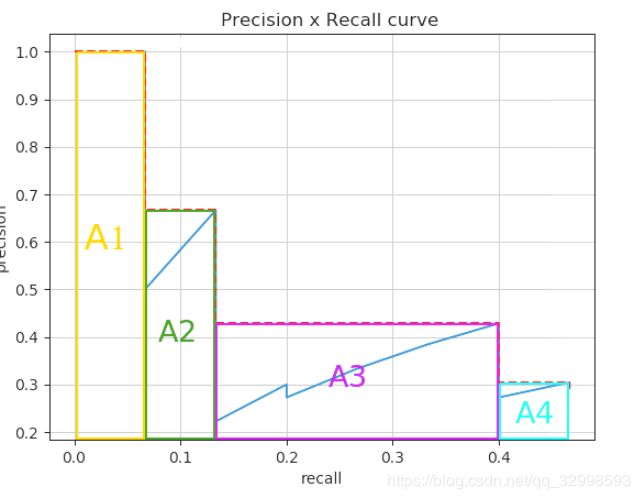
- Python多张图片存入PDF:一步步教你实现
木头左
python办公自动化python钉钉自动化
哈喽,大家好,我是木头左!引言在当今的数字时代,经常需要将多张图片整合成一个PDF文件。无论是为了分享、备份还是打印,PDF都是一个理想的格式。在这篇文章中,我将详细介绍如何使用Python将多张图片存入PDF。准备工作在开始之前,需要确保已经安装了以下库:Pillow:一个强大的图像处理库,用于打开、操作和保存各种图像文件格式。ReportLab:一个用于创建PDF文件的库。你可以通过以下命令安
- 点云从入门到精通技术详解100篇-基于卷积和注意力机制的3D点云特征提取
格图素书
3d
目录知识储备点云获取技术分类一、图像衍生点云二、LiDAR三、RGB-D深度图像传感器基于3D激光slam的点云特征提取为什么要进行点云特征提取特征提取理论与代码编写点云特征提取主体类sample_and_groupfarthest_point_samplequery_ball_pointindex_points前言国内外研究现状卷积神经网络三维卷积神经网络稀疏卷积[21]基于3D点云数据的目标分
- AI学习指南Ollama篇-Ollama简介
俞兆鹏
AI学习指南人工智能ollama
一、定义大语言模型(LLM)是一种基于深度学习的自然语言处理模型,能够生成文本、回答问题、翻译语言、撰写代码等。这些模型通过海量的文本数据进行训练,学习语言的模式和结构,从而能够生成自然流畅的文本内容。随着技术的不断进步,大语言模型在各个领域都展现出了巨大的潜力。二、应用场景大语言模型的应用场景非常广泛,以下是一些常见的例子:聊天机器人:通过自然语言理解与生成,为用户提供智能对话服务。内容创作:帮
- 图像处理算法研究的程序框架
mickey0380
系统调用图像处理算法程序框架Windows
目录1程序框架简介2C#图像读取、显示、保存模块3C动态库图像算法模块4C#调用C动态库5演示Demo5.1开发环境5.2功能介绍5.3下载地址参考1程序框架简介一个图像处理算法研究的常用程序逻辑框架,如下图所示在该框架中,将图像处理算法产品分为上层模块和底层模块两个部分。底层模块使用C/C++实现算法API,提供给上层模块调用;上层模块执行调用API和一些界面功能的实现,最后得到不同平台的软件产
- 图像处理之颜色空间小结
AI洲抿嘴的薯片
opencv算法专题图像处理人工智能
1.介绍在图像处理中,我们会遇到各式各样的颜色空间,比如RGB、HLS、HSV、HSB、YCrCb、CIEXYZ、CIELab,那么它们的区别和应用场所又在哪里呢?1)RGB是生活中最常见的颜色空间,其中,R代表红色通道,G代表绿色通道,B代表蓝色通道,它们之间的相互搭配组合256*256*256,几乎可以包括人类视力所能感知的所有颜色。应用场所:一般的彩色图片都是用RGB三通道来表示,另外,在深
- 深度ResUnet与ResUnet++:新一代的语义分割神器
倪澄莹George
深度ResUnet与ResUnet++:新一代的语义分割神器去发现同类优质开源项目:https://gitcode.com/在这个数据驱动的时代,深度学习模型在图像处理领域展现出了强大的潜力,尤其是在语义分割任务中。今天,我们向您推荐一个基于PyTorch实现的开源项目——DeepResUnet和ResUnet++。这两个模型源自于学术界的最新研究,旨在提高图像分割的准确性和效率。项目介绍这个开源
- 医学类 使用TransUNet、UNet、DeepLabV3+、HRNet、PSPNet 模型对息肉分割数据集进行训练、评估和可视化 EDD2020息肉数据集分割数据集
计算机C9硕士_算法工程师
数据集语义分割医学类数据集语义分割息肉TransUNetUNet
息肉数据集/息肉瘤分割项目解决(已处理好:EDD2020数据集(EndoscopyDiseaseDetectionandSegmentationChallenge)该息肉分割数据集主要包含人体生长的(肠胃)息肉用于器官内部息肉瘤分割,息肉目标检测,息肉定位任务息肉分割是一个重要的医学影像分析任务,特别是在内窥镜检查中。EDD2020数据集是一个很好的起点。我们将使用几种流行的深度学习模型(如Tra
- L8打卡学习笔记
无涯学徒1998
学习笔记支持向量机
本文为365天深度学习训练营中的学习记录博客原作者:K同学啊SVM与集成学习SVMSVM线性模型SVM非线性模型SVM常用参数集成学习随机森林导入数据查看数据信息数据分析随机森林模型预测结果结果分析个人总结SVM超平面:SVM在特征空间中寻找一个能够最大化类别间隔的超平面,称为最大间隔超平面。这个超平面就是将数据集分成不同类别的边界。支持向量:支持向量是离分隔超平面最近的样本点,它们决定了超平面的
- P5学习笔记
无涯学徒1998
pythonpytorch
本文为365天深度学习训练营中的学习记录博客原作者:K同学啊运动鞋品牌识别设置GPU导入数据构建CNN模型编写训练函数编写测试函数设置动态学习率等间隔动态调整自定义调整多间隔调整余弦退火正式训练结果可视化使用模型进行预测个人总结设置GPUimporttorchimporttorch.nnasnnimporttorchvision.transformsastransformsimporttorchv
- 【学习笔记】昇思25天学习打卡(D14)CV05-SSD目标检测.ipynb
UnseenMe
昇思学习笔记目标检测
SSD目标检测模型简介SSD,全称SingleShotMultiBoxDetector,是WeiLiu在ECCV2016上提出的一种目标检测算法。使用NvidiaTitanX在VOC2007测试集上,SSD对于输入尺寸300x300的网络,达到74.3%mAP(meanAveragePrecision)以及59FPS;对于512x512的网络,达到了76.9%mAP,超越当时最强的FasterRC
- 基于STM32开发的智能交通灯控制系统
STM32发烧友
stm32嵌入式硬件单片机
目录引言环境准备工作硬件准备软件安装与配置系统设计系统架构硬件连接代码实现系统初始化红绿灯控制逻辑车辆与行人检测信号灯控制与调度OLED显示与状态提示Wi-Fi通信与远程监控应用场景城市交通管理智能交通系统的研发与测试常见问题及解决方案常见问题解决方案结论1.引言随着城市化的加速,交通管理成为现代城市中亟待解决的问题。智能交通灯控制系统通过实时检测交通状况,根据实际车流量调整信号灯的切换时间,提高
- 深度学习中高斯噪声:为什么以及如何使用
小白学视觉
深度学习人工智能
点击上方“小白学视觉”,选择加"星标"或“置顶”重磅干货,第一时间送达来源:DeepHubIMBA本文约1800字,建议阅读8分钟高斯噪声是深度学习中用于为输入数据或权重添加随机性的一种技术。在数学上,高斯噪声是一种通过向输入数据添加均值为零和标准差(σ)的正态分布随机值而产生的噪声。正态分布,也称为高斯分布,是一种连续概率分布,由其概率密度函数(PDF)定义:pdf(x)=(1/(σ*sqrt(
- OpenCV中添加高斯噪声到彩色图像和点云
LpmShell
opencv人工智能计算机视觉点云
在计算机视觉和图像处理中,噪声是一种常见的现象,可以对图像和点云数据产生不良影响。高斯噪声是一种常见的噪声类型,它具有正态分布的特点。在本文中,我们将使用OpenCV库来添加高斯噪声到彩色图像和点云数据,并提供相应的源代码示例。添加高斯噪声到彩色图像首先,我们将介绍如何使用OpenCV库向彩色图像添加高斯噪声。以下是添加高斯噪声的步骤:步骤1:导入必要的库importnumpyasnpimport
- 基于Canny边缘检测和轮廓检测
如若123
opencv人工智能计算机视觉
这段代码实现了基于Canny边缘检测和轮廓检测,从图像中筛选出面积较大的矩形,并使用OpenCV和Matplotlib显示结果。主要流程如下:步骤详解:读取图像:img=cv2.imread('U:/1.png')使用cv2.imread()加载图像。转换为灰度图像:gray=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)使用cv2.cvtColor()将图像从BGR色彩
- 深度学习|表示学习|卷积神经网络|由参数共享引出的特征图|08
漂亮_大男孩
表示学习深度学习学习cnn
如是我闻:FeatureMap(特征图)的概念与ParameterSharing(参数共享)密切相关。换句话说,参数共享是生成FeatureMap的基础。FeatureMap是卷积操作的核心产物,而卷积操作的高效性正是由参数共享带来的。下面我们详细看一下FeatureMap和ParameterSharing之间的关系:1.什么是FeatureMap?定义:FeatureMap是卷积操作生成的输出结
- 探秘FreeMovie:一个开源的电影推荐系统
孟振优Harvester
探秘FreeMovie:一个开源的电影推荐系统去发现同类优质开源项目:https://gitcode.com/项目简介是一个基于深度学习的开源电影推荐系统,由pojiezhiyuanjun开发并维护。该项目的目标是为用户提供个性化的电影推荐服务,通过机器学习算法理解用户的观影偏好,并据此进行智能推荐。技术分析FreeMovie的核心架构包括以下关键组件:数据处理-项目采用Hadoop进行大数据预处
- Topaz Video AI——视频修复
爱研究的小牛
AIGC—视频AIGC
一、TopazVideoAI介绍及使用TopazVideoAI是一款基于人工智能的视频增强和修复软件,主要用于提升视频质量、去噪、插帧和分辨率提升。它利用深度学习技术对视频进行智能化处理,使得视频看起来更加清晰和流畅。TopazVideoAI特别适合那些需要修复旧视频、提升低分辨率视频质量的用户。二、TopazVideoAI的主要功能视频去噪:通过AI模型去除视频中的噪点,使画面更加干净。分辨率提
- 流媒体直播实时视频延迟时间排查和剖析:gop关键帧间隔导致延迟,流媒体和播放器缓存,B帧等导致的延迟
eguid_1
#1.4.3版本)直播延迟视频延迟直播平台播放延迟网络延迟
本章是流媒体直播实时视频延迟时间排查和剖析javaCV系列文章:javacv开发详解之1:调用本机摄像头视频javaCV开发详解之2:推流器实现,推本地摄像头视频到流媒体服务器以及摄像头录制视频功能实现(基于javaCV-FFMPEG、javaCV-openCV)javaCV开发详解之3:收流器实现,录制流媒体服务器的rtsp/rtmp视频文件(基于javaCV-FFMPEG)
- 分形、大自然的分形几何、数据可视化、Python绘图
timedot-hj
python绘图指南-分形与数据可视化可视化python几何学算法
分形、大自然的分形几何、数据可视化、Python绘图中国传统中的『分形』大自然的分形几何数据可视化本系列采用turtle、matplotlib、numpy这三个Python工具,以分形与计算机图像处理的经典算法为实例,通过程序和图像,来帮助读者一步步掌握Python绘图和数据可视化的方法和技巧,并且让读者感受到“龙枝屈曲竞分形,瑰丽绮错千万状”的分形魅力。本系列共有八章,分别为海岸线有多长,基因与
- 细节增强注意力模型DEAB详解及代码复现
清风AI
深度学习算法详解及代码复现深度学习人工智能神经网络python计算机视觉机器学习conda
基本原理DEAB模型的基本原理是通过细节增强卷积(DEConv)和内容引导注意力(CGA)机制的协同工作来实现细节增强注意力功能。这种设计使得模型能够在处理图像时更好地保留细节信息,同时关注图像中的重要内容。DEAB模型的核心组件包括:细节增强卷积(DEConv):DEConv是一种创新的卷积层设计,通过并行部署普通卷积和差分卷积来增强特征提取能力。差分卷积包括中心差分卷积(CDC)、角差分卷积(
- 【深度学习|变化检测孪生网络】基于共享权重的双流 U-Net 变化检测网络架构,附代码(一)
努力学习的大大
深度学习基础深度学习网络架构人工智能python
【深度学习|变化检测孪生网络】基于共享权重的双流U-Net变化检测网络架构,附代码(一)【深度学习|变化检测孪生网络】基于共享权重的双流U-Net变化检测网络架构,附代码(一)文章目录【深度学习|变化检测孪生网络】基于共享权重的双流U-Net变化检测网络架构,附代码(一)基于共享权重的双流U-Net变化检测网络架构1.双流网络(SiameseNetwork)概述2.双流网络的应用——变化检测3.U
- 【深度学习|迁移学习】Wasserstein距离度量和跨域原型一致性损失(CPC Loss)如何计算?以及Wasserstein距离和CPC Loss结合的对抗训练示例,附代码(二)
努力学习的大大
深度学习基础深度学习迁移学习人工智能python
【深度学习|迁移学习】Wasserstein距离度量和跨域原型一致性损失(CPCLoss)如何计算?以及Wasserstein距离和CPCLoss结合的对抗训练示例,附代码(二)【深度学习|迁移学习】Wasserstein距离度量和跨域原型一致性损失(CPCLoss)如何计算?以及Wasserstein距离和CPCLoss结合的对抗训练示例,附代码(二)文章目录【深度学习|迁移学习】Wassers
- 2023-简单点-非极大值抑制NMS
万物琴弦光锥之外
目标跟踪人工智能计算机视觉
非极大值抑制(Non-MaximumSuppression,NMS)是一种在目标检测中常用的后处理技术。NMS能够抑制那些与真实目标重叠较大的冗余检测框,留下最好的一个。非极大值抑制(Non-MaximumSuppression,NMS)的原理是:在目标检测中,对于检测到的冗余框,保留置信度最高的那个,抑制其他与它有较大重叠的冗余框。其基本原理是先在图像中找到所有可能包含目标物体的矩形区域,并按照
- 2025数学建模美赛B题完整建模思路——管理可持续旅游业
鹿鹿数模
数学建模
2025MCM问题B:管理可持续旅游业以下是我们对该题目的赛题分析,由于完整内容过长,因此在此处放出部分内容,欢迎从文末小卡片处加群获取。赛题分析以下内容包括三个主要部分:(1)题目的中文翻译(2)对题目的整体分析与思路综述(3)对题目要求的逐项详细分析与求解思路。本文的撰写将综合运用多元的数学模型、算法以及机器学习/深度学习的方法,并在必要时给出题外假设与可行的创新性思路,以期为参赛者提供较为系
- 使用YOLOv8训练一个无人机(UAV)检测模型,深度学习目标检测中_并开发一个完整的系统 yolov8来训练无人机数据集并检测无人机
QQ_767172261
无人及视角YOLO无人机深度学习
使用YOLOv8训练一个无人机(UAV)检测模型,深度学习目标检测中_并开发一个完整的系统yolov8来训练无人机数据集并检测无人机无人机数据集,yolo格式种类为uav,一共近5w张图片,如何用yolov8代码训练无人机检测数据集文章目录以下文章及内容仅供参考。1.环境部署2.数据预处理数据集准备划分数据集3.模型定义4.训练模型5.评估模型6.结果分析与可视化7.集成与部署PyQt6GUI(`
- ubuntu电脑调用摄像头拍摄照片
山山而川_R
Drugsopencv计算机视觉人工智能
一、1、先装环境condacreate-ntextpython==3.8-ycondaactivatetext2、pipinstallopencv-python-ihttps://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple1、连接摄像头拍摄收集数据集capture_image5.pyimportcv2ascvimportosimportdatetimeimportnumpya
- 【树莓派入门系列】opencv安装
^Mark_Zhang^
pythonopencv人工智能
树莓派入门之Opencv库安装提示:本文树莓派4B所搭载的系统是Raspi11本教程不需要任何换源,直接用树莓派自带的源就行文章目录一、树莓派版本查看二、Opencv库安装1.扩大系统文件(常规操作)2.安装aptitude软件包3.CMake工具安装4.基础库安装5.opencv-python库5.注意点一、树莓派版本查看代码如下:uanme-a或lsb_release-a二、Opencv库安装
- 图像分类与识别的自组织特征映射网络实践
无声远望
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:自组织特征映射网络(SOFM)是一种无监督学习模型,适用于图像处理中的预处理、特征提取和分类识别。通过在MATLAB中实现SOFM,可以进行数据预处理、特征提取、网络训练、分类与识别以及优化评估。本内容涵盖了SOFM网络的应用步骤、训练过程、参数调整和性能评估,旨在提供图像处理问题的解决方案。1.自组织特征映射网络简介1.1自组织特征映射网络概述自组织特征映射
- AlphaFold2的思路总结(十五)
xiaofengzihhh
蛋白质结构预测深度学习人工智能神经网络
2021SC@SDUSC这学期的代码分析工作接近尾声了,我想简单总结一下AlphaFold2的总体思路 具体来看,AlphaFold2主要利用多序列比对(MSA),把蛋白质的结构和生物信息整合到了深度学习算法中。它主要包括两个部分:神经网络EvoFormer和结构模块(Structuremodule)。一、EvoFormer 在EvoFormer中,主要是将图网络(Graphnetworks)
- python机器学习
方安乐
pythonpython机器学习人工智能
Python机器学习是当前最为热门的机器学习领域之一,其简洁、易用、高效的特点,让越来越多的开发者开始探索其应用。本文将从以下几个方面介绍Python机器学习的基础知识和实践案例,帮助读者更好地理解和应用机器学习技术。前提Python机器学习的应用领域A.图像识别和计算机视觉B.自然语言处理和文本分析C.数据挖掘和推荐系统深度学习A.神经网络的基本原理B.常用的深度学习框架和算法C.深度学习在图像
- 多线程编程之存钱与取钱
周凡杨
javathread多线程存钱取钱
生活费问题是这样的:学生每月都需要生活费,家长一次预存一段时间的生活费,家长和学生使用统一的一个帐号,在学生每次取帐号中一部分钱,直到帐号中没钱时 通知家长存钱,而家长看到帐户还有钱则不存钱,直到帐户没钱时才存钱。
问题分析:首先问题中有三个实体,学生、家长、银行账户,所以设计程序时就要设计三个类。其中银行账户只有一个,学生和家长操作的是同一个银行账户,学生的行为是
- java中数组与List相互转换的方法
征客丶
JavaScriptjavajsonp
1.List转换成为数组。(这里的List是实体是ArrayList)
调用ArrayList的toArray方法。
toArray
public T[] toArray(T[] a)返回一个按照正确的顺序包含此列表中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型就是指定数组的运行时类型。如果列表能放入指定的数组,则返回放入此列表元素的数组。否则,将根据指定数组的运行时类型和此列表的大小分
- Shell 流程控制
daizj
流程控制if elsewhilecaseshell
Shell 流程控制
和Java、PHP等语言不一样,sh的流程控制不可为空,如(以下为PHP流程控制写法):
<?php
if(isset($_GET["q"])){
search(q);}else{// 不做任何事情}
在sh/bash里可不能这么写,如果else分支没有语句执行,就不要写这个else,就像这样 if else if
if 语句语
- Linux服务器新手操作之二
周凡杨
Linux 简单 操作
1.利用关键字搜寻Man Pages man -k keyword 其中-k 是选项,keyword是要搜寻的关键字 如果现在想使用whoami命令,但是只记住了前3个字符who,就可以使用 man -k who来搜寻关键字who的man命令 [haself@HA5-DZ26 ~]$ man -k
- socket聊天室之服务器搭建
朱辉辉33
socket
因为我们做的是聊天室,所以会有多个客户端,每个客户端我们用一个线程去实现,通过搭建一个服务器来实现从每个客户端来读取信息和发送信息。
我们先写客户端的线程。
public class ChatSocket extends Thread{
Socket socket;
public ChatSocket(Socket socket){
this.sock
- 利用finereport建设保险公司决策分析系统的思路和方法
老A不折腾
finereport金融保险分析系统报表系统项目开发
决策分析系统呈现的是数据页面,也就是俗称的报表,报表与报表间、数据与数据间都按照一定的逻辑设定,是业务人员查看、分析数据的平台,更是辅助领导们运营决策的平台。底层数据决定上层分析,所以建设决策分析系统一般包括数据层处理(数据仓库建设)。
项目背景介绍
通常,保险公司信息化程度很高,基本上都有业务处理系统(像集团业务处理系统、老业务处理系统、个人代理人系统等)、数据服务系统(通过
- 始终要页面在ifream的最顶层
林鹤霄
index.jsp中有ifream,但是session消失后要让login.jsp始终显示到ifream的最顶层。。。始终没搞定,后来反复琢磨之后,得到了解决办法,在这儿给大家分享下。。
index.jsp--->主要是加了颜色的那一句
<html>
<iframe name="top" ></iframe>
<ifram
- MySQL binlog恢复数据
aigo
mysql
1,先确保my.ini已经配置了binlog:
# binlog
log_bin = D:/mysql-5.6.21-winx64/log/binlog/mysql-bin.log
log_bin_index = D:/mysql-5.6.21-winx64/log/binlog/mysql-bin.index
log_error = D:/mysql-5.6.21-win
- OCX打成CBA包并实现自动安装与自动升级
alxw4616
ocxcab
近来手上有个项目,需要使用ocx控件
(ocx是什么?
http://baike.baidu.com/view/393671.htm)
在生产过程中我遇到了如下问题.
1. 如何让 ocx 自动安装?
a) 如何签名?
b) 如何打包?
c) 如何安装到指定目录?
2.
- Hashmap队列和PriorityQueue队列的应用
百合不是茶
Hashmap队列PriorityQueue队列
HashMap队列已经是学过了的,但是最近在用的时候不是很熟悉,刚刚重新看以一次,
HashMap是K,v键 ,值
put()添加元素
//下面试HashMap去掉重复的
package com.hashMapandPriorityQueue;
import java.util.H
- JDK1.5 returnvalue实例
bijian1013
javathreadjava多线程returnvalue
Callable接口:
返回结果并且可能抛出异常的任务。实现者定义了一个不带任何参数的叫做 call 的方法。
Callable 接口类似于 Runnable,两者都是为那些其实例可能被另一个线程执行的类设计的。但是 Runnable 不会返回结果,并且无法抛出经过检查的异常。
ExecutorService接口方
- angularjs指令中动态编译的方法(适用于有异步请求的情况) 内嵌指令无效
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJS
在directive的link中有一个$http请求,当请求完成后根据返回的值动态做element.append('......');这个操作,能显示没问题,可问题是我动态组的HTML里面有ng-click,发现显示出来的内容根本不执行ng-click绑定的方法!
- 【Java范型二】Java范型详解之extend限定范型参数的类型
bit1129
extend
在第一篇中,定义范型类时,使用如下的方式:
public class Generics<M, S, N> {
//M,S,N是范型参数
}
这种方式定义的范型类有两个基本的问题:
1. 范型参数定义的实例字段,如private M m = null;由于M的类型在运行时才能确定,那么我们在类的方法中,无法使用m,这跟定义pri
- 【HBase十三】HBase知识点总结
bit1129
hbase
1. 数据从MemStore flush到磁盘的触发条件有哪些?
a.显式调用flush,比如flush 'mytable'
b.MemStore中的数据容量超过flush的指定容量,hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size,默认值是64M 2. Region的构成是怎么样?
1个Region由若干个Store组成
- 服务器被DDOS攻击防御的SHELL脚本
ronin47
mkdir /root/bin
vi /root/bin/dropip.sh
#!/bin/bash/bin/netstat -na|grep ESTABLISHED|awk ‘{print $5}’|awk -F:‘{print $1}’|sort|uniq -c|sort -rn|head -10|grep -v -E ’192.168|127.0′|awk ‘{if($2!=null&a
- java程序员生存手册-craps 游戏-一个简单的游戏
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.Random;
public class CrapsGame {
/**
*
*一个简单的赌*博游戏,游戏规则如下:
*玩家掷两个骰子,点数为1到6,如果第一次点数和为7或11,则玩家胜,
*如果点数和为2、3或12,则玩家输,
*如果和为其它点数,则记录第一次的点数和,然后继续掷骰,直至点数和等于第一次掷出的点
- TOMCAT启动提示NB: JAVA_HOME should point to a JDK not a JRE解决
开窍的石头
JAVA_HOME
当tomcat是解压的时候,用eclipse启动正常,点击startup.bat的时候启动报错;
报错如下:
The JAVA_HOME environment variable is not defined correctly
This environment variable is needed to run this program
NB: JAVA_HOME shou
- [操作系统内核]操作系统与互联网
comsci
操作系统
我首先申明:我这里所说的问题并不是针对哪个厂商的,仅仅是描述我对操作系统技术的一些看法
操作系统是一种与硬件层关系非常密切的系统软件,按理说,这种系统软件应该是由设计CPU和硬件板卡的厂商开发的,和软件公司没有直接的关系,也就是说,操作系统应该由做硬件的厂商来设计和开发
- 富文本框ckeditor_4.4.7 文本框的简单使用 支持IE11
cuityang
富文本框
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<title>知识库内容编辑</tit
- Property null not found
darrenzhu
datagridFlexAdvancedpropery null
When you got error message like "Property null not found ***", try to fix it by the following way:
1)if you are using AdvancedDatagrid, make sure you only update the data in the data prov
- MySQl数据库字符串替换函数使用
dcj3sjt126com
mysql函数替换
需求:需要将数据表中一个字段的值里面的所有的 . 替换成 _
原来的数据是 site.title site.keywords ....
替换后要为 site_title site_keywords
使用的SQL语句如下:
updat
- mac上终端起动MySQL的方法
dcj3sjt126com
mysqlmac
首先去官网下载: http://www.mysql.com/downloads/
我下载了5.6.11的dmg然后安装,安装完成之后..如果要用终端去玩SQL.那么一开始要输入很长的:/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql
这不方便啊,好想像windows下的cmd里面一样输入mysql -uroot -p1这样...上网查了下..可以实现滴.
打开终端,输入:
1
- Gson使用一(Gson)
eksliang
jsongson
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2175401 一.概述
从结构上看Json,所有的数据(data)最终都可以分解成三种类型:
第一种类型是标量(scalar),也就是一个单独的字符串(string)或数字(numbers),比如"ickes"这个字符串。
第二种类型是序列(sequence),又叫做数组(array)
- android点滴4
gundumw100
android
Android 47个小知识
http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1422676091314.html
Android实用代码七段(一)
http://www.cnblogs.com/over140/archive/2012/09/26/2611999.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/over140/arch
- JavaWeb之JSP基本语法
ihuning
javaweb
目录
JSP模版元素
JSP表达式
JSP脚本片断
EL表达式
JSP注释
特殊字符序列的转义处理
如何查找JSP页面中的错误
JSP模版元素
JSP页面中的静态HTML内容称之为JSP模版元素,在静态的HTML内容之中可以嵌套JSP
- App Extension编程指南(iOS8/OS X v10.10)中文版
啸笑天
ext
当iOS 8.0和OS X v10.10发布后,一个全新的概念出现在我们眼前,那就是应用扩展。顾名思义,应用扩展允许开发者扩展应用的自定义功能和内容,能够让用户在使用其他app时使用该项功能。你可以开发一个应用扩展来执行某些特定的任务,用户使用该扩展后就可以在多个上下文环境中执行该任务。比如说,你提供了一个能让用户把内容分
- SQLServer实现无限级树结构
macroli
oraclesqlSQL Server
表结构如下:
数据库id path titlesort 排序 1 0 首页 0 2 0,1 新闻 1 3 0,2 JAVA 2 4 0,3 JSP 3 5 0,2,3 业界动态 2 6 0,2,3 国内新闻 1
创建一个存储过程来实现,如果要在页面上使用可以设置一个返回变量将至传过去
create procedure test
as
begin
decla
- Css居中div,Css居中img,Css居中文本,Css垂直居中div
qiaolevip
众观千象学习永无止境每天进步一点点css
/**********Css居中Div**********/
div.center {
width: 100px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
/**********Css居中img**********/
img.center {
display: block;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
}
- Oracle 常用操作(实用)
吃猫的鱼
oracle
SQL>select text from all_source where owner=user and name=upper('&plsql_name');
SQL>select * from user_ind_columns where index_name=upper('&index_name'); 将表记录恢复到指定时间段以前
- iOS中使用RSA对数据进行加密解密
witcheryne
iosrsaiPhoneobjective c
RSA算法是一种非对称加密算法,常被用于加密数据传输.如果配合上数字摘要算法, 也可以用于文件签名.
本文将讨论如何在iOS中使用RSA传输加密数据. 本文环境
mac os
openssl-1.0.1j, openssl需要使用1.x版本, 推荐使用[homebrew](http://brew.sh/)安装.
Java 8
RSA基本原理
RS