空间直角坐标转换成大地坐标matlab代码(附精度)
在实际生产中,通常需要进行空间直角坐标和大地坐标之间的相互转换。精度估计是大地测量数据处理的一项内容,而目前使用的的坐标转换软件中一般都没有提供空间直角坐标与大地坐标之间转换的精度。其中,空间直角坐标至大地坐标的转换常用的迭代法可以表示为:
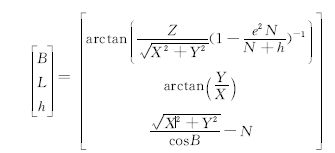
在文章《空间直角坐标与大地坐标的精度关系式_徐思达》中,作者论通过误差传播律推导了由空间直角坐标转到大地坐标的精度,分析了严密公式和简便公式的精度转换结果的差异,发现两者只有微小差异,所以可以用简便公式。根据其提供的公式,用matlab编写程序实现。
function [llh, sigmallh ] = xyz2llh222(xyz,sigmaxyz)
%
% ... Transform from x,y,z to lat,lon,h
% 精度公式为 《空间直角坐标与大地坐标的精度关系式_徐思达》一文中的简便公式
%
deg2rad = pi/180;
a = 6378137;
f = 1/298.257223563;%扁率
e2 = 2*f - f*f;%第一偏心率
rou=180*3600/pi;
[junk,num] = size(xyz);
for i = 1:num,
p = sqrt(xyz(1:2,i)'*xyz(1:2,i));
r = sqrt(xyz(:,i)'*xyz(:,i));
lon = atan2(xyz(2,i),xyz(1,i));
%
% ... First iteration on lat and h
% - assumes h = 0
%
lat = atan2(xyz(3,i)/p,(1-e2));
n = a/sqrt((1 - e2*sin(lat)^2));
m = (a*(1-e2))/sqrt((1 - e2*sin(lat)^2));
h = p/cos(lat) - n;
%%%以下公式为参考文献中的简便公式
jian1 = (m+h)^2;
jian2 = ((n+h)*cos(lat))^2;
sigx2 = sigmaxyz(1,i)^2;
sigy2 = sigmaxyz(2,i)^2;
sigz2 = sigmaxyz(3,i)^2;
siglat =(sin(lat)*cos(lon))^2/jian1*sigx2+(sin(lat)*sin(lon))^2/jian1*sigy2+cos(lat)^2/jian1*sigz2;
sigmalat=rou*sqrt(siglat);
siglon=sin(lon)^2/jian2*sigx2+cos(lon)^2/jian2*sigy2;
sigmalon=rou*sqrt(siglon);
sigh=(cos(lat)*cos(lon))^2*sigx2+(cos(lat)*sin(lon))^2*sigy2+sin(lat)^2*sigz2;
sigmah=sqrt(sigh);
%
% ... Iterate until h converges (should be quick since h << n)
%
oldh = -1e9;
iter = 0;
num = xyz(3,i)/p;
while abs(h - oldh) > 0.0001,
iter = iter + 1;
oldh = h;
den = 1 - e2*n/(n+h);
lat = atan2(num,den);
n = a/sqrt((1 - e2*sin(lat)^2));
h = p/cos(lat) - n;
end
%
llh(1,i) = lat/deg2rad;
llh(2,i) = lon/deg2rad;
llh(3,i) = h;
sigmallh(1,i) = sigmalat;
sigmallh(2,i) = sigmalon;
sigmallh(3,i) = sigmah;
end
可以用下面的代码实现读取时间序列文件,完成转换,并将转换后的经纬度级精度写入指定路径下的新文件中:
clear
file='..\data_xyz\XCNG.xyz';
fid = fopen(file, 'r'); %以只读的方式打开文件
if (fid == -1 )
disp(strcat('Error opening file ', file));
else
c = textscan(fid, '%f %f %f %f %f %f %f %f %f %f %f %f'); % 读取文件
fclose(fid);
yr=c{1}; %第一列为年份
mt=c{2}; %第二列为月份
dy=c{3}; %第三列为天数
tm=decyear(yr,mt,dy);
timeseries.time = tm;
timeseries.year = yr;
timeseries.month= mt;
timeseries.day = dy;
ndates = length(timeseries.time);
t_init = timeseries.time(1);
timeseries.xyz = zeros(3,ndates);
timeseries.xyz(1,:) = c{4}';%4 5 6列为xyz坐标
timeseries.xyz(2,:) = c{5}';
timeseries.xyz(3,:) = c{6}';
timeseries.sigmaxyz(1,:) = c{7}'; %7 8 9列为精度
timeseries.sigmaxyz(2,:) = c{8}';
timeseries.sigmaxyz(3,:) = c{9}';
[timeseries.llh,timeseries.sigmallh] = xyz2llh222(timeseries.xyz,timeseries.sigmaxyz);% 把xyz转化成经纬度
timeseries.llh=timeseries.llh';
timeseries.sigmallh=timeseries.sigmallh';
%生成llh文件
path_file=file(1:3);
site=file(13:16);%根据前面的file路径来 如果前面变动 则此处也需要变动
paths=[path_file 'llhfile\'];
pathfile=[paths site];
name=[pathfile '.llh'];
fid = fopen(name, 'wt');
for i = 1:ndates
fprintf(fid,'%f %f %f %f %f %f %f\n',timeseries.time(i),timeseries.llh(i,1),...
timeseries.llh(i,2),timeseries.llh(i,3),timeseries.sigmallh(i,1),...
timeseries.sigmallh(i,2),timeseries.sigmallh(i,3));
end
fclose(fid);
end
参考文献:徐思达, 贾国宪, 王丽红,等. 空间直角坐标与大地坐标的精度关系式[J]. 北京测绘, 2018.