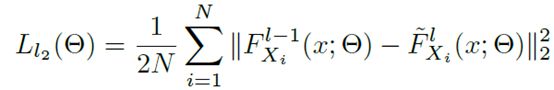论文解读《Almost Unsupervised Learning for Dense Crowd Counting》AAAI2019
Almost Unsupervised Learning for Dense Crowd Counting
Deepak Babu Sam, Neeraj N Sajjan, Himanshu Maurya, R. Venkatesh Babu
AAAI2019
摘要:
We present an unsupervised learning method for dense crowd count estimation.
we develop Grid Winner-Take-All (GWTA) autoencoder to learn several layers of useful filters from unlabeled crowd images. Our GWTA approach divides a convolution layer spatially into a grid of cells. Within each cell, only the maximally activated neuron is allowed to update the filter. Almost 99.9% of the parameters of the proposed model are trained without any labeled data while the rest 0.1% are tuned with supervision.
我们开发了Grid Winner-Take-All (GWTA)自动编码器,从未标记的人群图像中学习几个有用的过滤器层。我们的GWTA方法将卷积层在空间上划分为网格单元。在每个网格单元中,只有最大激活的神经元被允许更新过滤器。几乎99.9%的模型参数在没有任何标记数据的情况下进行了训练,而剩下的0.1%在监督下进行了调整。
引言:
贡献:
A stacked convolutional autoencoder model based on grid winner-take-all (GWTA) paradigm for large-scale unsupervised feature learning.
一种基于网格赢者通吃(GWTA)范式的层叠卷积自编码器模型,用于大规模的无监督特征学习。
The first crowd counting system that can train almost 99.9% of its parameters without any annotated data.
第一个人群计数系统,可以训练几乎99.9%的参数,没有任何注释的数据。
方法:
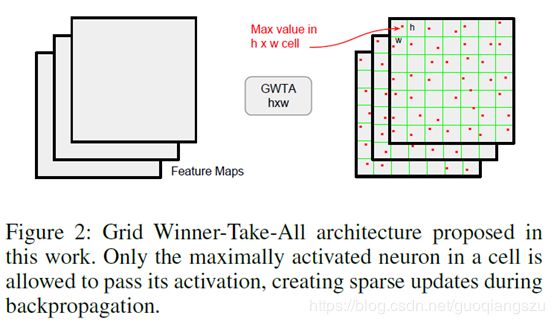
GWTA sparsity is applied independently over each channel. Any given feature map is divided into a grid of rectangular cells of pre-defined size hw. During forward propagation of the input, only the “winner” neuron in the h w cell is allowed to pass the activation. The “winner” neuron is the one having the maximum value of activation in the cell and activations of all other neurons in the h w cell are set to zero. Now the task of the decoder is to reconstruct the encoder input from such a sparse activation map, which is extremely hard. Hence, the encoder cannot simply learn near identity filters and get minimum reconstruction cost, but are forced to acquire useful features recurring frequently in the input data.
GWTA独立的应用到每一个通道中。任一给定的特征图都可以划分成预先设置好的h×w尺寸的网格图。在输入的前向传播中,只有h×w网格中的“赢家”神经元允许通过激活单元。“赢家”神经元是网格内激活值最大的神经元,而h× w网格内所有其他神经元的激活值均为零。现在解码器的任务是根据这样一个稀疏的激活图重建编码器的输入,这是非常困难的。因此,编码器不能简单地学习靠近的滤波器层的特征并获得最小的重建损失,而是要获得在输入数据中频繁出现的有用特性。
无监督学习分四个阶段,每个阶段都用L2损失,SGD优化。训练直到损失指标在验证集上不再有提升为止。
第一阶段训练完后,得到的参数固定,然后训练第二阶段,以此类推。
最后需要有监督学习过滤掉人群计数中不需要的信息。这一阶段也使用L2损失函数和SGD优化器。
Most common method is to blur the head annotation with a Gaussian of fixed variance summing to one. In this work, we use a sigma of 8.0 for generating ground truth density maps.
最常见的方法是用固定方差和为1的高斯函数模糊head注释。在这项工作中,我们使用8.0的sigma来生成地面真值密度图。
实验结果: