hdu2665 Kth number(主席树模板)
Problem Description
Give you a sequence and ask you the kth big number of a inteval.
Input
The first line is the number of the test cases.
For each test case, the first line contain two integer n and m (n, m <= 100000), indicates the number of integers in the sequence and the number of the quaere.
The second line contains n integers, describe the sequence.
Each of following m lines contains three integers s, t, k.
[s, t] indicates the interval and k indicates the kth big number in interval [s, t]
Output
For each test case, output m lines. Each line contains the kth big number.
Sample Input
1
10 1
1 4 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 0
1 3 2
Sample Output
2
分析:
主席树模板
这个blog讲的很好
主席树实际上就是一棵权值线段树
按照权值从小到大新建树
每个元素在树中按照原序列的顺序安置
这就能保证在x之前的且比x小的元素,都有记录
画个图模拟一下,加深印象
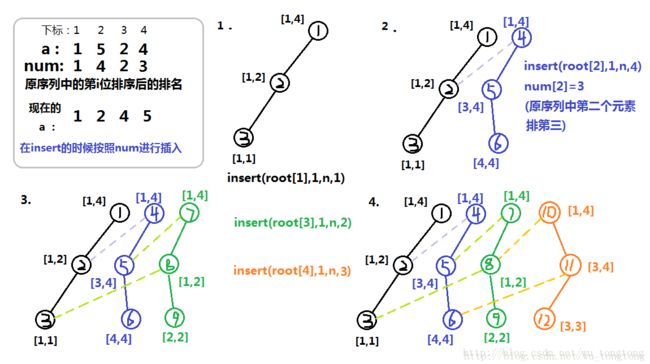
tip
询问区间第k小
空间不要开炸
主席树的空间一般是n*40
但是还要视情况而定
这道题n*40就MLE了,啊啊啊啊
hdu爆炸的情况挺严重。。。
这里写代码片
#includevoid insert(int &now,int l,int r,int pm)
{
top++;
tree[top]=tree[now];
now=top;
tree[now].sum++;
if (l==r)
return;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if (pm<=mid) insert(tree[now].l,l,mid,pm);
else insert(tree[now].r,mid+1,r,pm);
}
int ask(int x,int y,int l,int r,int k)
{
if (l==r)
return l; //返回的是在重排后的序列中的位置
int t=tree[tree[y].l].sum-tree[tree[x].l].sum;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if (t>=k) return ask(tree[x].l,tree[y].l,l,mid,k);
else return ask(tree[x].r,tree[y].r,mid+1,r,k-t);
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while (T--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i].v),a[i].bh=i;
sort(a+1,a+1+n,cmp);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) num[a[i].bh]=i;
//num[i]离散后排名是i的元素在原序列中的排名
//重复元素???
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) //按权值插入
{
root[i]=root[i-1];
insert(root[i],1,n,num[i]);
}
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x,y,k;
scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&k);
printf("%d\n",a[ask(root[x-1],root[y],1,n,k].v); //第k大
}
}
return 0;
}