大话设计模式 读书笔记
大话设计模式 读书笔记
程杰
- 着重从c#代码角度分析
学习心得: 学设计模式,不需要是否能立刻理解和记忆,无需着力
- 首先是UML图
- 再从设计模式到UML图
- 从UML图到代码
- 其次知道各种模式的应用场景即可
- 第三寻找到各种模式的经典应用实例
- 首先是UML图
设计模式心得
第29章 OOTV杯超级模式大赛–模式总结
Preface
- src code
- 菜鸟教程 C#
关于本书学习的疑问解答
作者谈了自己对design patterns学习理解,可供参考
- Ref
- GoF
- Java与模式,阎宏
第1章 代码无错就是优?——简单工厂模式
- C#
- solution(方案)可包括多个project(项目)
1.8 业务的封装
- 业务逻辑与界面逻辑相分离
1.10 简单工厂模式
为了简化程序,计算器程序采用 c# 多个button 对应同一消息处理方法
//各个button共用同一个事件处理函数
button1.click = new System.EventHandler(button_Click);
button2.click = new System.EventHandler(button_Click);
button3.click = new System.EventHandler(button_Click);
...
private void button_Click(objet sender ,EventArgs e)
{
Button btn =(Button)sender ; //实例化按钮,从而获取当前单击按钮的值
this.txtvalue.Text = btn.Text; //窗体中有txtvalue控件并给它赋值
}- 简单工厂模式
factory类:abstract product:concrete product
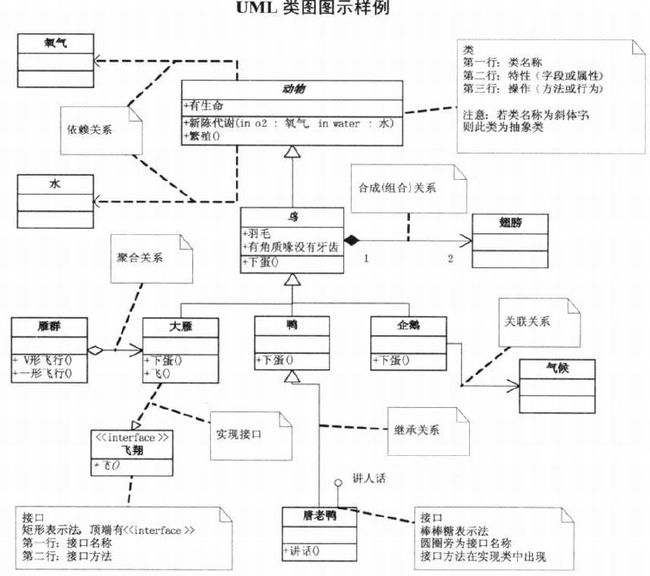
1.11 UML类图
- 类图: class
- 接口: interface
interface IFly
{
void Fly();
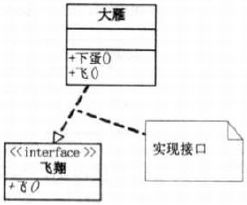
}- 继承
- 类继承
- 接口继承
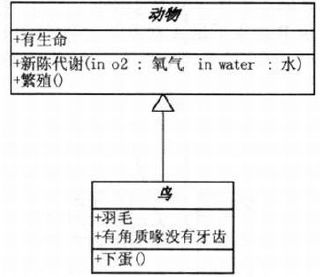
//类继承
class Bird : Animal
{}//接口继承
class WideGoose : IFly
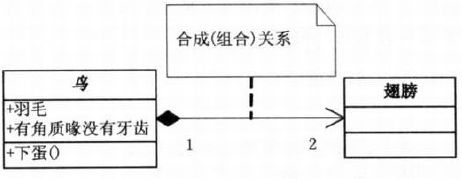
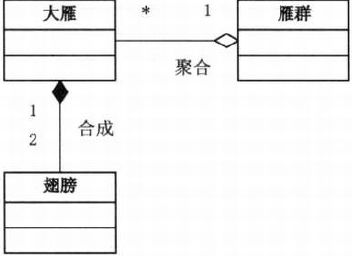
{}- 组合
- 关联 association
- 聚合 aggregation
- 合成 composition
//关联
class Penguin : Bird
{
private Climate climate;``
}`//聚合
class WideGooseAggregate
{
private WideGoose[] arrayWideGoose;
}//合成
class Bird
{
private Wing wing;
public Bird(){
wing = new Wing();
}
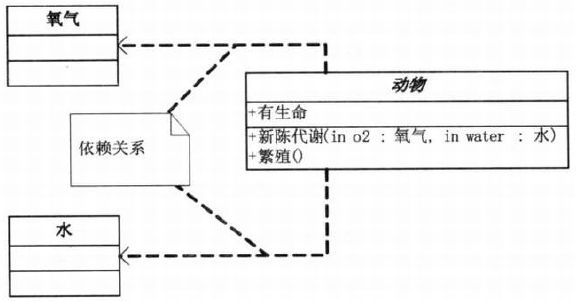
}- 依赖
//依赖
abstract class Animal
{
public Metabolism(Oxygen oxygen, Water water){}
}对比UML图,理解代码;或反之
- 工厂模式: 实例化具有共同父类的不同对象
- 应用: EJB,RMI,CORBA
- 可根据不同条件产生不同实例
switch-case或 反射
- 要素
- 工厂: 虚拟构造器
- 分类
- 简单工厂模式
- 工厂方法模式
- 抽象工厂模式
简单工厂模式的结构
工厂方法模式
- 深入浅出UML类图: 有价值,理解UML作用
第2章 商场促销——策略模式
2.1 商场收银软件
//初始化 Combox
cbxType.Items.AddRange(new object[] {"正常收费","打八折","打七折","打五折"});2.2 增加打折
2.3 简单工厂实现
2.4 策略模式
- strategy pattern: 定义算法族
- 封装变化点
- vs. 简单工厂
- 策略选择权在客户端
- 工厂模式相当于黑盒子,策略模式相当于白盒子
- 工厂模式:有一天你决定去吃披萨,一看菜单,哦,种类很多呀,就点了个培根披萨,过了二十分钟,你的披萨就来了就可以吃到了。但这个披萨是怎么做的,到底面粉放了多少,培根放了多少,佐料放了多少,有多少到工序,你是不需要管的,你需要的是一个美味培根披萨。
- 策略模式:同样还是在披萨店,你要一个培根披萨,老板说想吃自己去做吧。原料有培根、面粉、佐料。工序有1、2、3工序,你自己去做吧。然后你就需要自己去做,到底放多少培根,放多少面粉,放多少佐料,这都你自己来决定,工序1、2、3,你是怎么实现的,都你自己决定。最后你得到了披萨。
Strategy类和Context类为aggregate关系,即Strategy将作为构造函数的参数传递给`Context类
//抽象算法类
abstract class Strategy
{
//算法方法
public abstract void algorithmInterface();
}
//上下文
class Context
{
Strategy strategy;
public Context(Strategy strategyIn) {}
}2.5 策略模式实现
2.6 策略与简单工厂结合
Context类控制 ->switch-case选择,即具体策略的选择也交予Context类处理策略模式
Context
public CashContext(CashSuper csuper)
{
this.cs = csuper;
}- 策略+简单工厂
class CashContext
{
CashSuper cs = null;
//根据条件返回相应的对象
public CashContext(string type)
{
switch (type)
{
case "正常收费":
CashNormal cs0 = new CashNormal();
cs = cs0;
break;
...
}
}- 反射
- 依赖注入(Dependency Injection)
- 不管工厂模式,还是策略模式,
switch-case依然去不掉。原因在哪里?
Assembly.Load("程序集名称").CreateInstance("名称空间.类名称")
?
2.7 策略模式解析
- 反射(reflect)
第3章 拍摄UFO–单一职责原则
3.1 新手机
3.2 拍摄
3.3 没用的东西
3.4 单一职责原则
单一职责原则(SRP:Single responsibility principle)
案例
- 六大原则之SRP笔记
3.5 方块游戏的设计
3.6 手机职责过多吗?
第4章 考研求职两不误–开放-封闭原则
4.1 考研失败
4.2 开放-封闭原则
4.3 何时应对变化
- 抽象 -> 隔离 -> 变化
4.4 两手准备,并全力以赴
第5章 会修电脑不会修收音机?–依赖倒转原则
5.1 MM请求修电脑
5.2 电话遥控修电脑
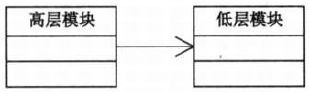
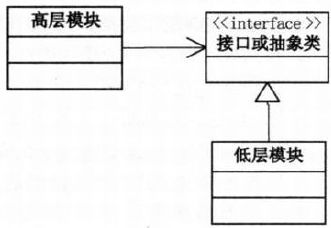
5.3 依赖倒转原则
- error: 高层模块 依赖于 低层模块
- solution: 抽象 -> 接口
5.4 里氏代换原则
子类型可替换性
- 依赖倒转 IOC
5.5 修收音机
第6章 穿什么有这么重要?–装饰模式
6.1 穿什么有这么重要?
6.2 小菜扮靓第一版
6.3 小菜扮靓第二版
- aim: 所需功能按照正确顺序串联执行,
有点像pipeline?
- GOF: 动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说,Decorator模式相比生成子类更为灵活。
6.4 装饰模式
Componentclass
abstract class Component{
public abstract void Operation();
}ConcreteComponentclass
class ConcreteComponent : Component{
public override void Operation(){
Console.WriteLine("具体对象操作");
}
}Decoratorclass
abstract class Decorator : Component{
protected Component component;
public void setComponent(Component component) {
this.component = component; //设置Component
}
//
public override void Operation(){
if(component != NULL){ component.Operation();}
}
}ConcreteDecoratorAclass
class ConcreteDecoratorA : Decorator {
private string addState;
public override void Operation(){
base.Operation();
...
}
}ConcreteDecoratorBclassClientcode
static void Main(stringp[] args){
ConcreteComponent c = new ConcreteComponent();
ConcreteDecoratorA d1 = new ConcreteDecoratorA();
ConcreteDecoratorB d2 = new ConcreteDecoratorB();
//Pipeline?
d1.setComponent(c);
d2.setComponent(d1);
d2.Operation();
}我认为客户端代码就是
pipeline
6.5 小菜扮靓第三版
6.6 装饰模式总结
- 装饰模式的装饰顺序重要!
Example: 加密数据和过滤词汇是数据处理模块的装饰功能,若先加密再过滤,则不妥!
- 装饰模式 vs. 桥接模式
?? - vs. 责任链模式
- 责任链: 表示上下级审批权限
- 装饰: pipeline
- 实际应用:
Java IO流是典型的装饰模式
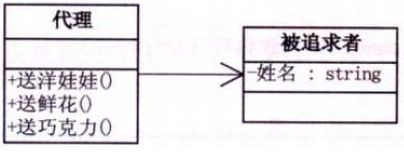
第7章 为别人做嫁衣–代理模式
7.1 为别人做嫁衣!
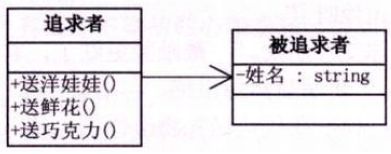
7.2 没有代理的代码
//追求者类
class Pursuit
{
SchoolGirl mm;
public Pursuit(SchoolGirl mm) {this.mm = mm; }
public void GiveDolls() {}
public void GiveFlows() {}
public void GiveChocolate() {}
}
//被追求者类
class SchoolGirl
{
private string name;
public string Name
{
get {return name; }
set {name = value; }
}
}
//客户端调用代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
SchoolGirl mm = new SchoolGirl();
mm.name = "妹妹";
Pursuit zhuojiayi = new Pursuit(mm);
zhuojiayi.GiveDolls();
...
}
7.3 只有代理的代码
7.4 符合实际的代码
//代理接口
interface IGiveGift {
public void GiveDolls();
public void GiveFlows();
public void GiveChocolate();
}
//追求者类
class Pursuit : IGiveGift
{
SchoolGirl mm;
public Pursuit(SchoolGirl mm) {this.mm = mm; }
public void GiveDolls() {}
public void GiveFlows() {}
public void GiveChocolate() {}
}
//代理类
class Proxy : IGiveGift
{
private Pursuit gg; //被代理者
public Proxy(SchoolGirl mm) {gg = new Pursuit(mm); }
public void GiveDolls() { gg.GiveDolls(); }
public void GiveFlows() { gg.GiveFlows(); }
public void GiveChocolate() { gg.GiveChocolate(); }
}
//客户端
static void Main(String[] args)
{
SchoolGirl jiaojiao = new SchoolGirl();
//代理
Proxy daili = new Proxy(jiaojiao);
daili.GiveDolls();
...
}
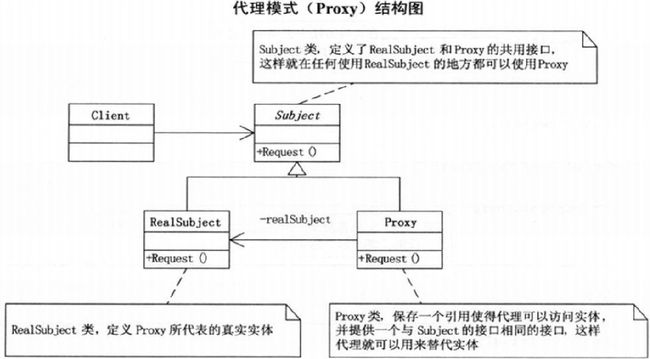
7.5 代理模式
代理模式原理及实例讲解
代理模式角色分为 4 种:
- 主题接口:定义代理类和真实主题的公共对外方法,也是代理类代理真实主题的方法;
- 真实主题:真正实现业务逻辑的类;
- 代理类:用来代理和封装真实主题;
- Main:客户端,使用代理类和主题接口完成一些工作。
Subject类: 定义RealSubject和Proxy的公用接口
abstract class Subject
{
public abstract void Request();
}RealSubject类: 定义Proxy所代表的真正实体
class RealSubject : Subject
{
public override void Request(){}
}Proxy类:
class Proxy : Subject
{
RealSubject real;
public override void Request(){
if(real == NULL) real = new RealSubject();
}
}- 客户端代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Proxy proxy = new Proxy(); //代理
proxy.Request();
}7.6 代理模式应用
- 远程代理
- 虚拟代理
- 安全代理
7.7 秀才让小六代其求婚
第8章 雷锋依然在人间–工厂方法模式
8.1 再现活雷锋
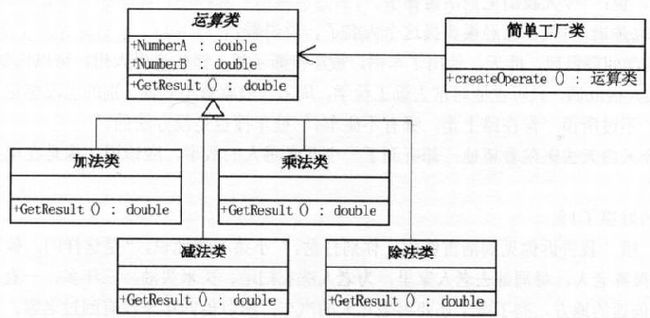
8.2 简单工厂模式实现
class OperationFactory{
public static Operation createOperate(String operate){
Operation oper = NULL;
switch(operate){
case "+":
oper = new OperationAdd();
break;
case "-":
oper = new OperationSub();
break;
case "*":
oper = new OperationMul();
break;
case "/":
oper = new OperationDiv();
break;
}
return oper;
}
}客户端
Operation oper;
oper = OperarionFactory.createOperate("+");
oper.NumberA=1;
oper.NumberB=2;
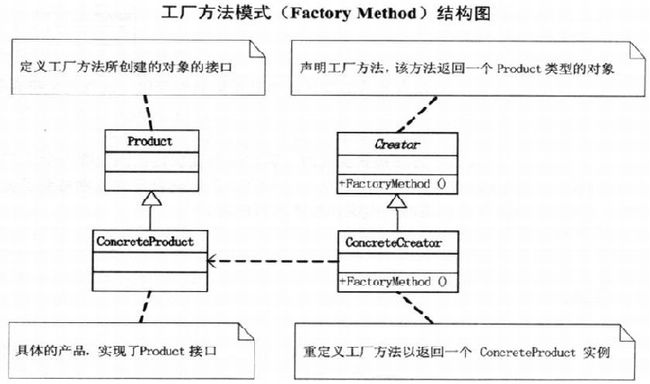
double result = oper.GetResult();8.3 工厂方法模式实现
工厂接口
interface IFactory{
Operator CreateOperation();
}具体工厂类
//加法工厂
Class AddFactory : IFactory{
public Operation CreateOperation{
return new OperationAdd();
}
}
...
//除法工厂
Class DivFactory : IFactory{
public Operation CreateOperation{
return new OperationDiv();
}
}客户端
IFactory operFactory = new AddFactory();
Operation oper = operFactory.CreateOperation();
Operation oper;
oper = OperarionFactory.createOperate("+");
oper.NumberA=1;
oper.NumberB=2;
double result = oper.GetResult();8.4 简单工厂vs.工厂方法
- 工厂方法模式:
- 创建对象的接口,让子类去决定具体实例化的对象,把简单的内部逻辑判断移到了客户端代码。(延迟实例化)
- 只需修改客户端即可: Open-Close Principle
8.5 雷锋工厂
- 反射
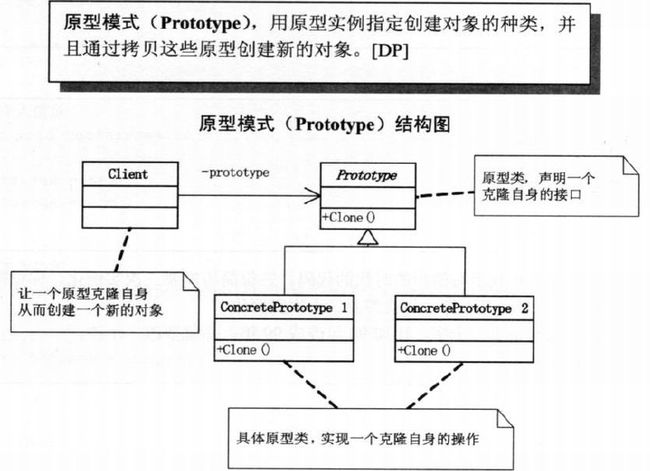
第9章 简历复印–原型模式
9.1 夸张的简历
9.2 简历代码初步实现
- 传值 vs 传引用
- clone
9.3 原型模式
原型类
abstract class Prototype{
private string id;
public Prototype(string id) {this.id = id;}
public string Id {
get {return id;}
}
//抽象类的关键
public abstract Prototype Clone();
}`具体原型类
class ConcretePrototype : Prototype{
pulic ConcretePrototype(string id) : base(id) {}
public override Prototype Clone(){
//创建当前对象的浅表副本
return (Prototype) this.MemberwiseClone();
}
}客户端
MemberWiseClone: 浅clone方法,通过创建一个新对象,并把所有当前对象中非静态域复制到新对象中,从而创建一个浅拷贝。对于值类型的域,进行的是按位拷贝。对于引用类型的域,引用会被赋值而引用的对象则不会。因此,原始对象及其克隆都会引用同一个对象。注意,这种方法对派生类都是有效的,也就是说,你只需在基类中定义一次Clone方法。
static void Main(string[] args){
ConcretePrototype p1 = new ConcretePrototype("I");
ConcretePrototype c1.p1.Clone();
...
}Clone 分浅拷贝和深拷贝
- 两者区别:当有引用类型成员时,浅拷贝复制的是成员的引用,深拷贝复制的是成员对象。
ICloneable接口
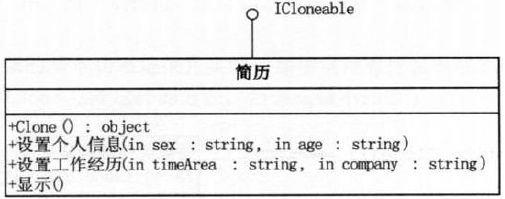
9.4 简历的原型实现
简历类
class Resume : ICloneable{
public Object Clone(){
return (Object) this.MemberwiseClone();
}
}9.5 浅复制与深复制

- MemberwiseClone: 复制时,对于类中的值类型会创建新的变量,而对于引用变量来说,会指向原来的引用并不创建新的引用变量
9.6 简历的深复制实现
//也实现ICloneable接口
class WorkExperience : ICloneable {
public Object Clone(){
return (Object) this.MemberwiseClone();
}
}简历类
class Resume : IClonealbe{
...
private Resume(WorkExprience work){
this.work = (WorkExprience) work.Clone();
}
...
public Object Clone(){
Resume obj = new Resume(this.work);
}
}9.7 复制简历vs.手写求职信
第10章 考题抄错会做也白搭–模板方法模式
10.1 选择题不会做,蒙呗!
10.2 重复=易错+难改
- 继承 -> template
- 虚方法
virtual
- 虚方法
10.3 提炼代码
10.4 模板方法模式
抽象类AbstractClass
abstract class AbstractClass{
public abstract void PrimitiveOperation1();
public abstract void PrimitiveOperation2();
public void templateMethod(){
PrimitiveOperation1();
PrimitiveOperation1();
Console.WriteLine("");
}
}ConcreteClass
class ConcreteClassA : AbstractClass{
public override void PrimitiveOperation1(){
Console.WriteLine("具体A类方法 1 实现");
}
public abstract void PrimitiveOperation2(){
Console.WriteLine("具体A类方法 2 实现");
}
}10.5 模板方法模式特点
10.6 主观题,看你怎么蒙
- 对比C#模板
- C#设计模式总结
第11章 无熟人难办事?–迪米特法则
11.1 第一天上班
11.2 无熟人难办事
- 方法: 通过引入一个合理的第三者来降低现有对象之间的耦合度
11.3 迪米特法则
迪米特法则(Law of Demeter): 又叫作最少知识原则(Least Knowledge Principle, LKP),就是说一个对象应当对其他对象有尽可能少的了解,不和陌生人说话。英文简写为: LoD.
talk only to your immediate friends
设计模式的门面模式(Facade)和中介模式(Mediator),都是迪米特法则应用的例子
第12章 牛市股票还会亏钱?–外观模式
12.1 牛市股票还会亏钱?
12.2 股民炒股代码
12.3 投资基金代码
12.4 外观模式
12.5 何时使用外观模式
- 分层设计
- 业务层与数据访问层解耦合
- 增加 Facade 以提供一个简单接口
Facade相当于增加一个接口层,向client提供简洁API接口,同时屏蔽低层复杂的遗留代码
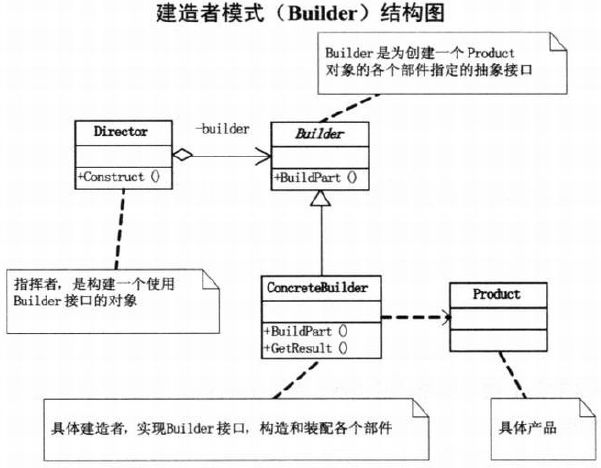
第13章 好菜每回味不同–建造者模式
13.1 炒面没放盐
- essence
- 抽象流程不变
- 流程中各组件的具体实现细节则是经常变化
example
- 建筑流程是确定,往往建筑一座楼房包括下面步骤:(1)打桩,建立基础(2)建立框架等。建造者模式的本质和建造楼房是一致的:即流程不变,但每个流程实现的具体细节则是经常变化。
- 建造者模式的好处就是保证流程不会变化,流程即不会增加、也不会遗漏或者产生流程次序错误,这是非常重要的。
- check list 实现么?
13.2 建造小人一
- 复杂对象的组装与创建——建造者模式
13.3 建造小人二
13.4 建造者模式
13.5 建造者模式解析
- Director: 控制流程
- Builder: 抽象服务
- ConcreteBuilder: 具体服务
- Product: 产品
13.6 建造者模式基本代码
Product: 产品类,由多个部件组成
class Product {
IList<string> parts = new IList<string>();
//添加产品部件
public void Add(string part) {
parts.Add(part);
}
}Builder: 抽象建造者类,确定产品组成: PartA与PartB,并返回结果。
abstract class Builder{
public abstract void BuilderPartA();
public abstract void BuilderPartB();
public abstract Product GetResult();
}- 注意: Builder只生产,不规定流程次序;而Dirctor强调规定流程次序
ConcreteBuilder:
注意: ConcreteBuilder与Product为关联关系
class ConcreteBuilder1 : Builder {
private Product product = new Product();
public override void BuildPartA() {}
...
}Director: 指挥者类,规定流程次序!
class Director{
public void Construct(Builder builder) {
//生产次序,important
builder.BuildPartA();
builder.BuildPartB();
}
}客户端
static void Main(string[] args){
Director director = new Director();
Builder b1 = new ConcreteBuilder1();
director.Constructor(b1);
Product p1 = b1.GetResult();
...
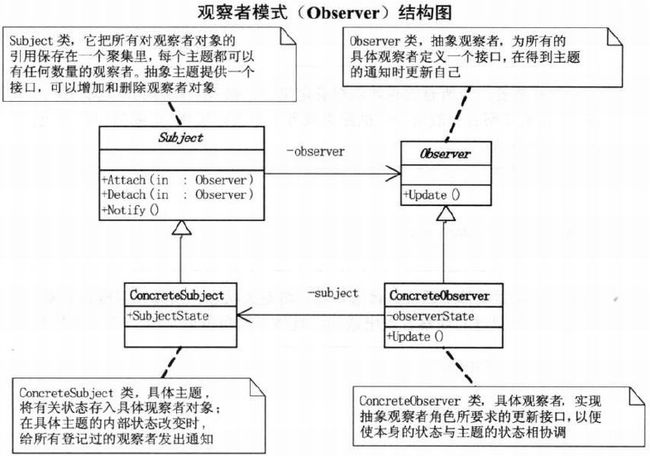
}第14章 老板回来,我不知道–观察者模式
14.1 老板回来?我不知道!
14.2 双向耦合的代码
- 观察者模式
前台秘书类
class Secretary
{
//同事列表
private IList investors = new List;
//添加成员
public void Attach(Investor invest) { investors.Add(invest); }
//发送通知
public void Notify()
{ foreach( Investor i in investors ) i.Update(); }
//前台状态
public string SecretaryAction {
get { return action; }
set { action = value; }
}
} 看股票同事类
class Investor {
private string name;
private Secretary sub;
public Investor(string name, Secretary sub){...}
public Update() {}
}客户端代码
static void Main(string[] args){
Secretary mm = new Secretary(); //前台小姐mm
//看股票的同事
Investor one = new Investor("One",mm);
Investor two = new Investor("Two",mm);
//前台记录下两个待通知的同事
mm.Attach(one);
mm.Attach(two);
mm.Notify(); //通知同事
}14.3 解耦实践一
- 增加抽象的观察者
abstract class Observer {
protected string name;
protected Secretary sub;
public Observer(string name, Secretary sub) {}
}- 增加两个具体观察者
//看股票
class StockObserver : Observer {
public StockObserver(string name, Secretary sub) : base(name,sub) {}
public override void Update() {}
}
//看NBA
class NBAObserver : Observer {
public NBAObserver(string name, Secretary sub) : base(name,sub) {}
public override void Update() {}
}- 前台秘书类
class Secretary {
//同事列表
private IList observers = new List();
private string action;
//增加 -> 针对抽象接口编程
public void Attach(Observer observer) { observer.Add(observer); }
//减少
public void Detach(Observer observer) { observer.Remove(observer); }
//通知
public void Notify() {
foreach(Observer o in observers)
o.Update();
}
//前台状态
public string SecretaryAction {
get { return action; }
set { action = value; }
}
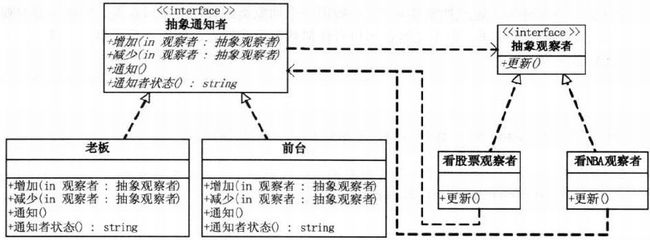
} 14.4 解耦实践二
- 增加抽象通知者接口
interface Subject {
void Attach(Observer observer);
void Detach(Observer observer);
void Notify();
string SubjectState {
get;
set;
}
}- 具体通知者: 老板(boss) 或秘书
class Boss : Subject {
//同事列表
private IList observers = new List();
private string action;
...
} - 抽象观察者
abstract class Observer {
protected string name;
protected Subject sub;
//原来“前台” -> 现改为"抽象通知者"
public Observer(string name, Subject sub) {...}
}- 客户端代码
//老板
Boss dog = new Boss();
//看股票的同事
StockObserver one = new StockObserver("one",dog);
//看NBA的同事
StockObserver two = new StockObserver("two",dog);
dog.Attach(one);
dog.Attach(two);
dog.Detach(one);
dog.SubjectState = "Boss来了";
dog.Notify(); //发送通知14.5 观察者模式
abstract class Subject {
private IList observers = new List();
//增加观察者
public void Attach(Observer observer) { observers.Add(observer); }
//移除观察者
public void Detach(Observer observer) { observers.Remove(observer); }
//通知
public void Notify(){
foreach(Observer o in observers) { o.Update(); }
}
} Observer类: 抽象观察者
abstract class Observer{
public abstract void Update();
}ConcreteSubject类: 具体通知者
class ConcreteSubject : Subject {
private string subjectState; //状态
public string SubjectState {
get { return subjectState; }
set { subjectState = value; }
}
}ConcreteObserver类: 具体观察者- 客户端代码
14.6 观察者模式特点
- 维护对象之间的一致性
- 观察者模式:在对象之间定义一对多的依赖,这样一来,当一个对象改变状态,依赖它的对象都会收到通知,并自动更新。
- java回调机制 vs. 观察者模式:
- I thinkL java回调机制近似于观察者模式一个特例(一对一)
- java回调机制 vs. 观察者模式:
14.7 观察者模式的不足
14.8 事件委托实现
14.9 事件委托说明
14.10 石守吉失手机后的委托
第15章 就不能不换DB吗?–抽象工厂模式
15.1 就不能不换DB吗?
- 数据库选型
- e.g., SQL Server, Acess
15.2 最基本的数据访问程序
class User{
private int _id;
public int ID {
get {return _id; }
set { _id = value; }
}
private string _name;
public string Name{
get { return _name; }
set { _name = value; }
}
}SQL
class SqlserverUser{
public void insert(User user) {
Console.WriteLine("SQL Server insert a record");
}
}15.3 用了工厂方法模式的数据访问程序
IUser 接口
interface IUser{
void Insert(User user);
User GetUser(int id);
}SqlserverUser类:访问SQL Server的User
class SqlserverUser : IUser{
public void Insert(User user){
Console.WriteLine("insert a record into SQL Server Database");
}
public User GetUser(int id){
Console.WriteLine("get User's a record from SQL Server according to ID");
return null;
}
}AccessUser类: 用于访问Acess的User
class AccessUser : IUser{
public void Insert(User user){
Console.WriteLine("insert a record into Access Database");
}
public User GetUser(int id){
Console.WriteLine("get User's a record from Access according to ID");
return null;
}
}IFactory接口: 定义访问User的抽象工厂接口
interface IFactory{
IUser CreateUser();
}SqlServerFactory类: 实现IFactory接口
class SqlServerFactory{
public IUser CreateUser(){
return new SqlserverUser();
}
}AccessFactory类: 实现IFactory接口
class AccessFactory{
public IUser CreateUser(){
return new AccessUser();
}
}客户端
static void Main(string args){
User user = new User();
IFactory factory = new SqlServerFactory();
IUser iu = factory.CreateUser();
iu.Insert(user);
iu.GetUser(1);
Console.Read();
}15.4 用了抽象工厂模式的数据访问程序
增加了部门表Department的处理
interface IDepaerment{
void insert(Department department);
Department GetDepartment(int i);
}SqlserverDepartment类: 用于访问SQL Server的Department
class SqlserverDepartment : IDepartment{
...
}修改IFactory类,增加了访问Department表的抽象工厂接口
interface IFactory{
IUser CreateUser();
IDepartment CreateDepartment(); //增加新接口
} SqlServerFactory类: 实现IFactory接口
class SqlServerFactory : IFactory{
public IUser CreateUser(){
return new SqlserverUser();
}
public IDepartment CreateDepartment() {
return new SqlserverDepartment();
}
}客户端
static void Main(string[] args)
{
User user = new User();
Department dept = new Department();
//AbstractFactory factory = new SqlServerFactory();
IFactory factory = new AccessFactory();
IUser iu = factory.CreateUser();
iu.Insert(user);
iu.GetUser(1);
IDepartment id = factory.CreateDepartment();
id.Insert(dept);
id.GetDepartment(1);
Console.Read();
}15.5 抽象工厂模式
- 抽象工厂: 可理解为 抽象工厂生产抽象产品
- 具体工厂生产具体产品
15.6 抽象工厂模式的优点与缺点
15.7 用简单工厂来改进抽象工厂
class DataAccess
{
private static readonly string db = "Sqlserver";
//private static readonly string db = "Access";
public static IUser CreateUser()
{
IUser result = null;
switch (db)
{
case "Sqlserver":
result = new SqlserverUser();
break;
case "Access":
result = new AccessUser();
break;
}
return result;
}
public static IDepartment CreateDepartment()
{
IDepartment result = null;
switch (db)
{
case "Sqlserver":
result = new SqlserverDepartment();
break;
case "Access":
result = new AccessDepartment();
break;
}
return result;
}
}客户端
static void Main(string[] args)
{
User user = new User();
Department dept = new Department();
IUser iu = DataAccess.CreateUser();
iu.Insert(user);
iu.GetUser(1);
IDepartment id = DataAccess.CreateDepartment();
id.Insert(dept);
id.GetDepartment(1);
Console.Read();
}15.8 用反射+抽象工厂的数据访问程序
- 依赖注入(Dependency Injection)
- IoC
- C# 反射技术:
Assembly.Load(AssemblyName).CreateInstance(className);
using System.Reflection;
class DataAccess
{
private static readonly string AssemblyName = "抽象工厂模式";
private static readonly string db = "Sqlserver";
//private static readonly string db = "Access";
public static IUser CreateUser()
{
string className = AssemblyName + "." + db + "User";
return (IUser)Assembly.Load(AssemblyName).CreateInstance(className);
}
public static IDepartment CreateDepartment()
{
string className = AssemblyName + "." + db + "Department";
return (IDepartment)Assembly.Load(AssemblyName).CreateInstance(className);
}
}- new issue: 更换数据库访问时,还需改变
db
15.9 用反射+配置文件实现数据访问程序
- solution: 添加
app.config
- 通过配置文件来解决
<configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="DB" value="Sqlserver"/>
appSettings>
configuration>C#读取配置文件
private static readonly string db = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["DB"];15.10 无痴迷,不成功
- Application: 反射 应用于 WCF,比如
app.config
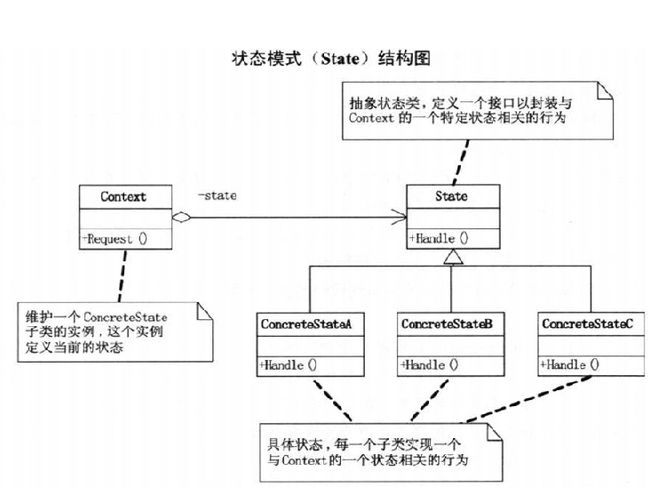
第16章 无尽加班何时休–状态模式
16.1 加班,又是加班!
16.2 工作状态-函数版
- 面向对象
- 程序 -> 类 + 方法
- 面向过程
16.3 工作状态-分类版
16.4 方法过长是坏味道
- Martin Flow: Long Method -> 坏味道
- 过多判断,过多分支 -> 责任分解不到位
16.5 状态模式
State类: 抽象状态类
abstract class State {
public abstract void Handle(Context context);
}ConcreteState类: 具体状态,每一子类实现与一个Context的状态相关行为
class ConcreteStateA : State {
public override void Handle(Context context) {
//下一状态为ConcretexStateB
//自动机状态 -> 变迁
context.State = new ConcretexStateB();
}
}
class ConcreteStateB : State {
public override void Handle(Context context) {
//下一状态为ConcretexStateA
//自动机状态 -> 变迁
context.State = new ConcretexStateA();
}
}Context类: 维护一个ConcreteState子类的实例,该实例定义当前状态
class Context {
private State state;
public Context(State state) {this.state = state;}
public State State {
get {return state;}
set {
state = value;
...
}
}
public void Request() {state.Handle(this);}
}16.6 状态模式好处与用处
16.7 工作状态-状态模式版
- 注意 uml图中虚线箭头的含义,对照代码
//工作
public class Work {
private State state;
...
public void WriteProgram() {current.WriteProgram(this);}
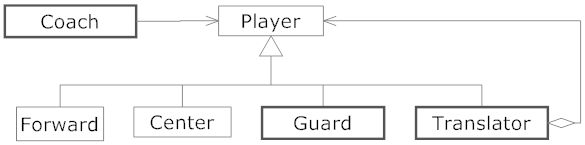
}第17章 在NBA我需要翻译–适配器模式
17.1 在NBA我需要翻译!
- Adapter
17.2 适配器模式
- 类适配器
- 通过多重继承,实现接口间匹配
- C#,Java不支持多重继承,仅C++支持
- 对象适配器
Target: 客户端适配接口
class Target {
public virtual void Request() {}
}Adaptee: 待适配类
class Adaptee {
public virtual void SpecificRequest() {}
}Adapter: 实际适配类,内部包装一个Adaptee对象,实现接口转换
class Adapter : Target {
//包装
private Adaptee adaptee = new Adaptee();
public virtual void Request() {
adaptee.SpecificRequest(); //转换
}
}客户端代码
static void Main(string[] args){
Target target = new Adapter();
target.Request();
}17.3 何时使用适配器模式
17.4 篮球翻译适配器
我认为本节示例有不合理成分,比如外籍中锋为中锋的子类,又比如有外籍后卫呢?
17.5 适配器模式的.NET应用
- .NET: DataAdapter
17.6 扁鹊的医术
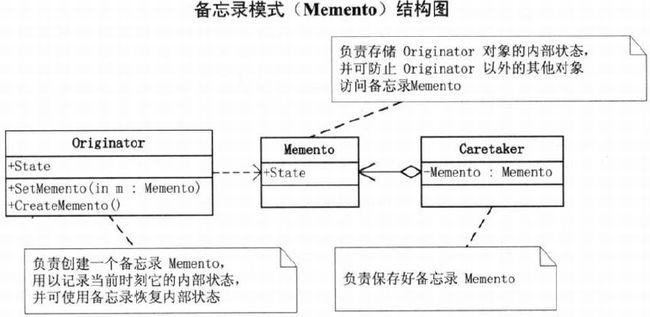
第18章 如果再回到从前–备忘录模式
18.1 如果再给我一次机会……
18.2 游戏存进度
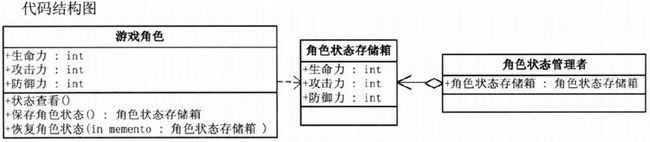
18.3 备忘录模式
- Originator: 负责创建备忘录,以记录其内部当前时刻状态
- Memento: 备忘录,负责存储Originator对象内部状态
- Caretaker: 负责保存好备忘录
18.4 备忘录模式基本代码
发起者(Originator)
class Originator {
private string state;
public string State {
get {return state;}
set {state = value;}
}
public Memento CreateMemeto() {
return Memetor(state);
}
public void SetMemento(Memento memento){
state = memento.State;
}
public void Show(){
Console.WriteLine("State=" + state);
}
}备忘录(Memento)类
class Memento {
private string state;
public Memento(string state) {this.state = state;}
public string State {
get {return state;}
}
}管理者(Caretaker):
class Caretaker {
private Memento memento;
public Memento Memento {
get {return memento;}
set {memento = value;}
}
}18.5 游戏进度备忘
- JAVA与模式 博文
博文写得很好,还有时序图,比书上介绍的更清楚!
本书作者 程杰 示意图 没有引入 Client行为时序图,很难表现 Design pattern使用方式!
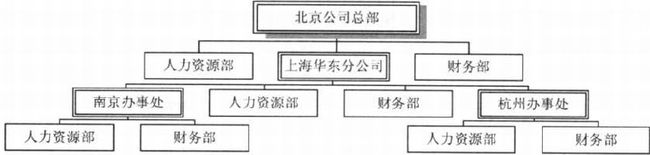
第19章 分公司=一部门–组合模式
19.1 分公司不就是一部门吗?
- 树结构 -> 层次化
- 整体 vs 部分
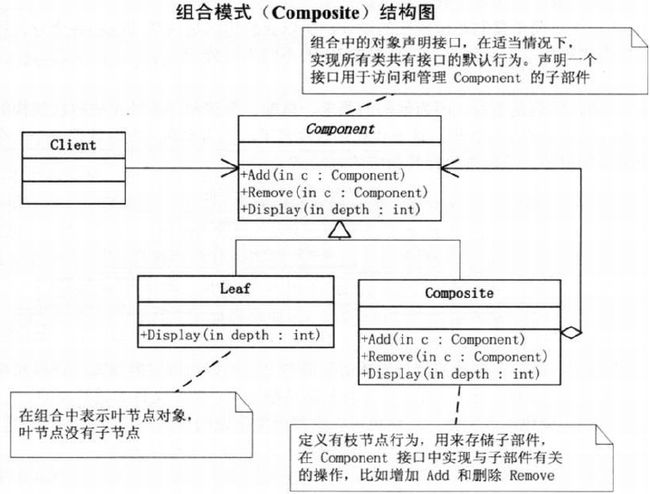
19.2 组合模式
Component: 组合中对象声明接口
abstract class Component {
protected string name;
public Component(string name) {this.name = name;}
public abstract void Add(Component c);
public abstract void Remove(Component c);
public abstract void Display(Component c);
}Leaf: 表示组合中叶节点 -> 无子节点
class Leaf : Component {
pulic Leaf(string name) : base(name) {}
...
}Composite: 表示枝节点,有子节点
class Composite : Component {
//保存下属的枝/叶节点
private List children = new List();
} 19.3 透明方式与安全方式
19.4 何时使用组合模式
- ASP.net: TreeView控件
19.5 公司管理系统
![]()
19.6 组合模式好处
第20章 想走?可以!先买票–迭代器模式
20.1 乘车买票,不管你是谁!
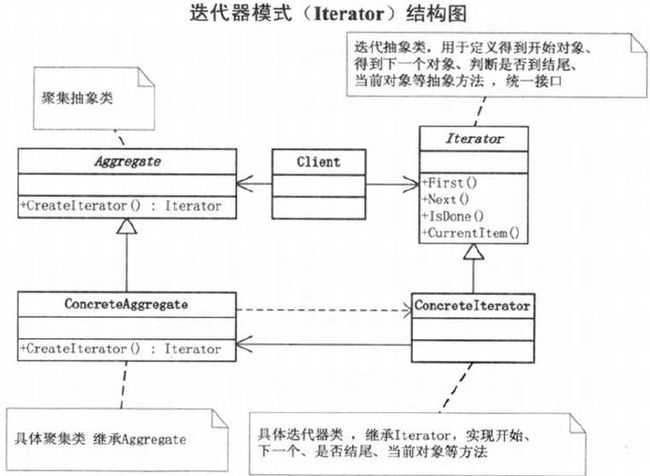
20.2 迭代器模式
Iterator -> 遍历
20.3 迭代器实现
Iterator迭代器抽象类
abstract class Iterator {
public abstract object First();
public abstract object Next();
public abstract bool IsDone();
public abstract object CurrentItem();
}Aggregate聚焦抽象类
abstract class aggregate {
public abstract Iterator createIterator(); //创建迭代器
}ConcreteIterator: 具体迭代器类
class ConcreteIterator : Iterator {
private ConcreteAggregate aggregate;
private int current = 0;
public ConcreteIterator(ConcreteAggregate aggregate) {
this.aggregate = aggregate;
}
public override Object First(){
return aggregate[0];
}
public override Object Next(){
Object ret = null;
current++;
if(current < aggregate.Count)
ret = aggregate[current];
return ret;
}
public override bool IsDone(){
return current >= aggregate.Count? true : false;
}
public override object CurrentItem(){
return aggregate[current];
}
}ConcreteAggregate: 具体聚集类
class Concreteaggregate : Aggregate {
private IList<object> items = new List客户端代码
20.4 .NET的迭代器实现
- 实现
foreach必须要实现IEnumerable和IEnumerator接口
IEumerator: 支持对非泛型集合的简单迭代
public interface IEumerator {
object Current {get;}
bool MoveNext();
void Reset();
}IEnumerable: 该枚举数支持在非泛型集合上进行简单的迭代
- IEnumerable的用法
public interface IEnumerable{
IEumerator GetEnumerator();
}foreach in实际通过IEnumerable和IEumerator接口实现的
20.5 迭代高手
第21章 有些类也需计划生育–单例模式
21.1 类也需要计划生育
21.2 判断对象是否是null
- 实例化
21.3 生还是不生是自己的责任
GetInstance()
public partial class FormToolBox : Form
{
private static FormToolBox ftb = null;//Static var
//构造函数私有化,外部代码不能直接new来实例化
private FormToolBox(){
InitializeComponent();
}
public static FormToolBox GetInstance(){
if(ftb == null | ftb.IsDisposed){
ftb = new FormToolBox();
ftb.MdiParent = Form.
}
}
}form==null: 是把该窗体对象设置为空,但该form仍存在内存里
21.4 单例模式
Singleton类
class Singleton
{
private static Singleton inst;
private Singleton(){}
public static Singleton GetInstance()
{
if(inst == null)
inst = new Singleton();
return inst;
}
}客户端代码
static Main(string[] args)
{
Singleton s1 = Singleton.GetInstance();
Singleton s2 = Singleton.GetInstance();
if(s1 == s2)
Console.WriteLine("s1's address is as same as s2");
Console.Read();
}21.5 多线程时的单例
- 多线程并发 ->
lock()
21.6 双重锁定
if(instance == null){
lock(obj){
if(instance == null){instance = new Object();}
}
}- 第一个判断null: 为了尽量减少进入锁的线程数;
- 第二个判断null: 防止重复实例化
21.7 静态初始化
public sealed class Singleton
{
private static readonly Singleton inst = new Singleton();
private Singleton(){}
public static Singleton GetInstance()
{ return inst; }
}sealed?readonly?
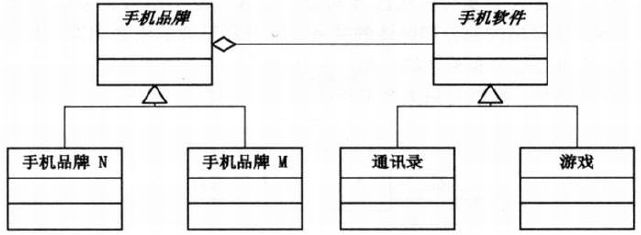
第22章 手机软件何时统一–桥接模式
22.1 凭什么你的游戏我不能玩
22.2 紧耦合的程序演化
22.3 合成/聚合复用原则
DP: 尽量用合成/聚合,尽量不用类继承
- Composition
- Aggregation
手机软件抽象类
abstract class HandSoft {
public abstract void Run();
}游戏、通讯录具体类
class HandsetGame : HandsetSoft {}
class HandsetAddrList : HandsetSoft {}手机品牌类
abstract class HandsetBrand {
protected HandsetSoft soft;
//设置手机软件
public void SetHandsetSoft(HandsetSoft soft) {this.soft = soft;}
}手机品牌具体类
22.4 松耦合的程序
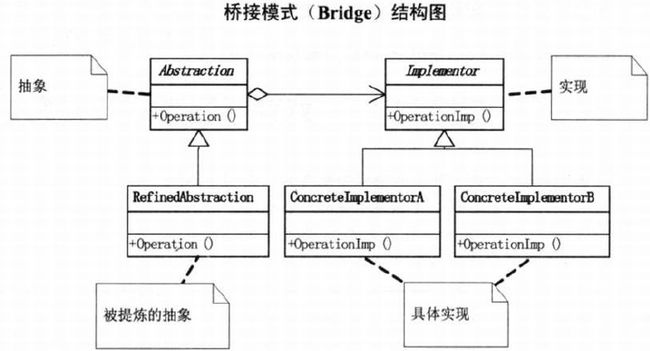
22.5 桥接模式
- 按照品牌分类实现结构图
22.6 桥接模式基本代码
Implementor类
abstract class Implementor {
public abstract void Operation();`
}派生类
class ConcreteImplementorA : Implementor { ... }Abstraction类
class Abstraction {
protected Implementor imp;
}RefinedAbstract类
客户端
- 对比组合模式(第19章)
22.7 我要开发”好”游戏
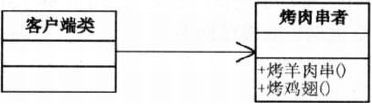
第23章 烤羊肉串引来的思考–命令模式
23.1 吃烤羊肉串!
23.2 烧烤摊vs.烧烤店
- 行为请求者与行为实现者 -> 紧耦合
23.3 紧耦合设计
关联
23.4 松耦合设计
抽象命令类
public abstract class Command{
protected Barbecuer receiver;
public Command(Barbecuer recv){
receiver = recv;
}
//执行命令
abstract public void ExecuteCom();
}具体命令类
//烤羊肉串
public class BakeMuttonCom : Command{
public BakeMuttonCom(Barbecuer recv) : base(recv)
{
receiver = recv;
}
public override void ExecuteCom()
{
receiver.BakeMutton(); //具体执行行为
}
}
//烤鸡翅命令
public class BakeChickenCom : Command{
public BakeChickenCom(Barbecuer recv) : base(recv)
{
receiver = recv;
}
public override void ExecuteCom()
{
receiver.BakeChicken(); //具体执行行为
}
}
服务员类
public class Waiter{
private Command com;
//设置订单
public void SetOrder(Command com) {this.com = com;}
//通知执行
public void Notify(){
com.ExecuteCom();
}
}客户端
23.5 松耦合后
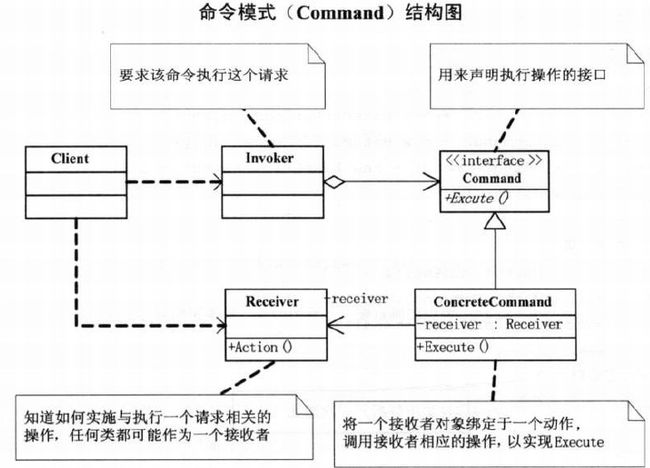
23.6 命令模式
Command: 执行操作的接口
abstract class Command{
protected Receiver receiver;
public Command(Receiver recv) {receiver = recv;}
abstract public void Execute();
}ConcreteCommand:
class ConcreteCommand : Command{
public ConcreteCommand(Receiver recv) : base(recv){}
public void Execute() {receiver.Action();}
}Invoker:
class Invoker{
private Command command;
public void SetCommand(Command com) {command = com;}
public void ExecuteCommand(){
command.Execute();
}
}Receiver:
class Receiver{
public void Action() {}
}客户端
static void Main(string[] args){
Receiver r = new Receiver();
Command c = new Command(r); //r为关联类
Invoker i = new Invoker();
i.SetCommand();
i.ExecuteCommand();
}23.7 命令模式作用
第24章 加薪非要老总批?–职责链模式
24.1 老板,我要加薪!
24.2 加薪代码初步
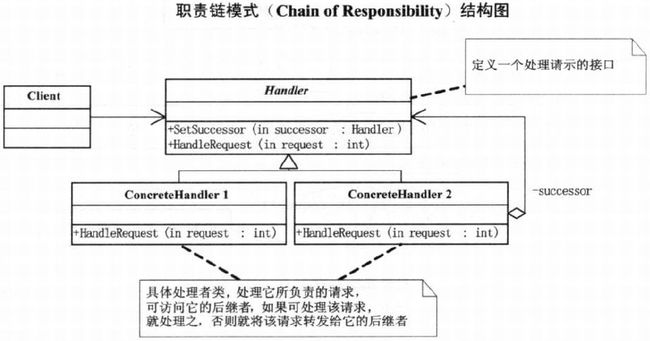
24.3 职责链模式
- Chain of Responsibility
Handler类:定义一个处理请求的接口
abstract class Handler {
protected Handler successor;
//设定继任者
public void SetSuccessor(Handler suc) {this.successor = suc;}
}ConcreteHandler1: 当请求数在0-10之间有权处理,否则转到下一层级处理
class ConcreteHandler1 : Handler{
public override void HandleRequest(int req) {
if(req >= 0 && req < 10) {
...
}else if(successor != NULL) {
successor.HandleRequest(req);
}
}
}ConcreteHandler2: 当请求数在10-20之间有权处理,否则转到下一层级处理
class ConcreteHandler2 : Handler{
public override void HandleRequest(int req) {
if(req >= 10 && req < 20) {
...
}else if(successor != NULL) {
successor.HandleRequest(req);
}
}
}ConcreteHandler3: 当请求数在20-30之间有权处理,否则转到下一层级处理
class ConcreteHandler3 : Handler{
public override void HandleRequest(int req) {
if(req >= 20 && req < 30) {
...
}else if(successor != NULL) {
successor.HandleRequest(req);
}
}
}客户端
static void Main(string[] args){
Handler h1 = new ConcreteHandler1();
Handler h2 = new ConcreteHandler2();
Handler h3 = new ConcreteHandler3();
//设置责任链上/下家
h1.SetSuccessor(h2);
h2.SetSuccessor(h3);
int[] reqs = [2,5,14,22];
foreach(int req in reqs) {h1.HandleRequest(req);}
}24.4 职责链的好处
- 对比数据流
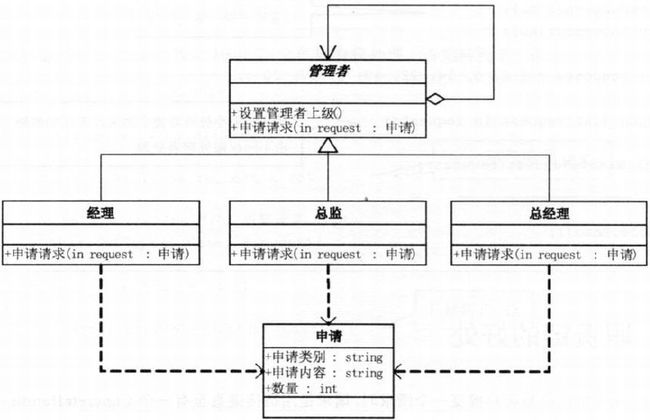
24.5 加薪代码重构
- 注意: 管理者自包含关系
24.6 加薪成功
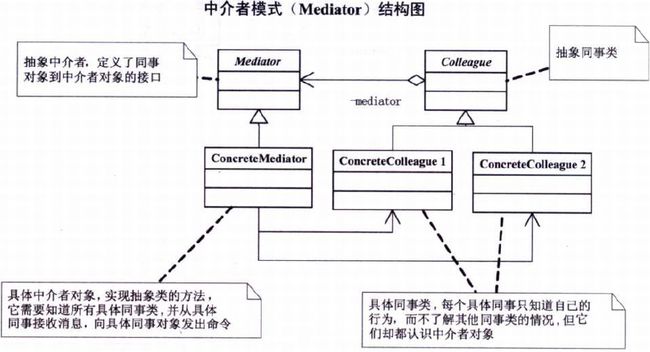
第25章 世界需要和平–中介者模式
25.1 世界需要和平!
25.2 中介者模式
Mediator:
abstract class Mediator {
public abstract void Send(string msg, Colleague colleague);
}Colleague:
abstract class Colleague {
protected Mediator mediator;
//获取中介者对象
public Colleague(Mediator mediator) {this.mediator = mediator;}
}ConcreteMediator:
class ConcreteMediator : Mediator {
private ConcreteColleague1 c1;
private ConcreteColleague2 c2;
}?
25.3 安理会做中介
25.4 中介者模式优缺点
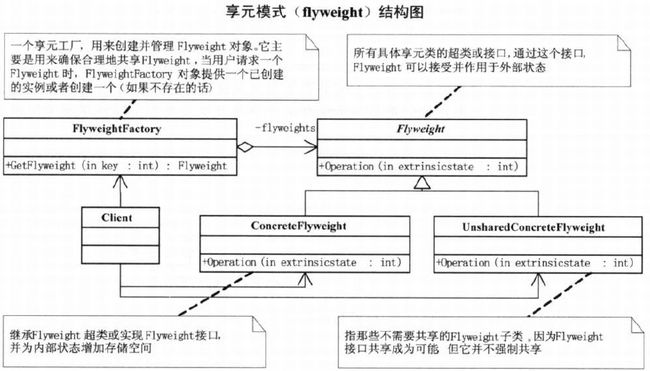
第26章 项目多也别傻做–享元模式
26.1 项目多也别傻做!
26.2 享元模式
- 享元模式 vs 工厂模式?
Flyweight: 享元类的接口和抽象类
abstract class Flyweight{
public abstract void Operate(int extraState);
}ConcreteFlyweight:
abstract class ConcreteFlyweight : Flyweight{
public override void Operate(int extraState) {}
}UnsharedConcreteFlyweight:
abstract class UnsharedConcreteFlyweight : Flyweight{
public override void Operate(int extraState) {}
}FlyweightFactory: 享元工厂
class FlyweightFactory{
private Hashtable flyweights = new Hashtable();
public FlyweightFactory(){
flyweights.Add("X", new ConcreteFlyweight());
flyweights.Add("Y", new ConcreteFlyweight());
flyweights.Add("Z", new ConcreteFlyweight());
}
public Flyweight GetFlyweight(string key){
//根据客户要求,返回已生成的实例
return ((Flyweight) flyweights[key]);
}
}客户端
static void Main(string[] args){
int etraState = 22;
FlyweightFactory f = new FlyweightFactory();
Flyweight fx = f.GetFlyweight("X");
...
}26.3 网站共享代码
个人觉得: 作者没有指出享元模式的核心设计思想?
享元模式核心: 池化机制 = 资源调度 + 分配 + 回收
- 对象池,如线程池、数据库连接池等
服务器资源池化技术思想: 将设备资源都被放到一个池内,再进行统一分配。
- 例如CPU 池、内存池、存储池
- 资源的池化使得用户不再关心计算资源的物理位置和存在形式,IT部门也得以更加灵活地对资源进行配置。
26.4 内部状态与外部状态
26.5 享元模式应用
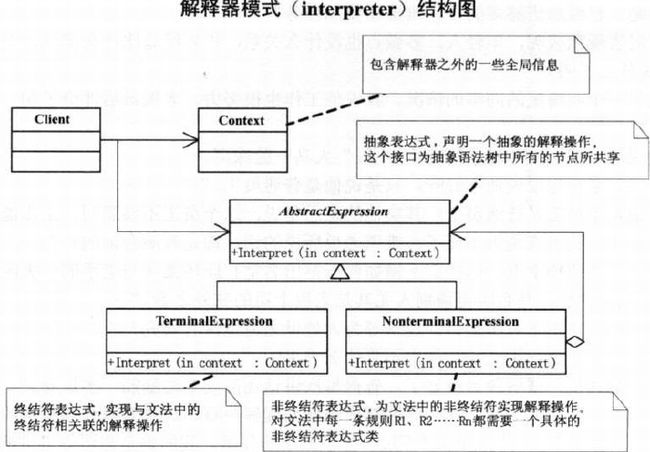
第27章 其实你不懂老板的心–解释器模式
27.1 其实你不懂老板的心
27.2 解释器模式
- 正则表达式
AbstractExpression: 抽象表达式,该接口为抽象语法树中所有节点共享
abstract class AbstractExpression {
public abstract void Interpret(Context context);
}TerminalExpression: 终结符表达式
class TerminalExpression : AbstractExpression {
public override void Interpret(Context context) {...}
}NoterminalExpression: 非终结符表达式
class NonterminalExpression : AbstractExpression {
public override void Interpret(Context context) {...}
}Context: 上下文
class Context{
private string input;
public string Input {
get {return input;}
set {input = value;}
}
...
}客户端:
static void Main(string[] args){
Context context = new Context();
IList list = new List();
list.Add(new TerminalExpression());
...
foreach(AbstractExpression exp in list) {exp.Interpret(context);}
} 27.3 解释器模式好处
- 解释器模式 -> 抽象语法树
- DSL (domain Specific Language)
- 解释器模式缺点
- 编译器生成器
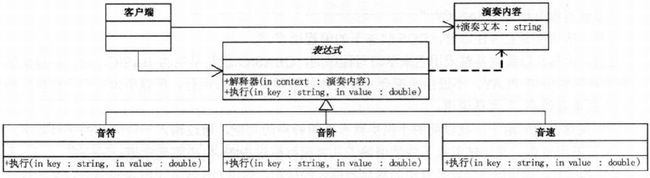
27.4 音乐解释器
27.5 音乐解释器实现
演奏内容类 context:
class PlayContent{
//演奏文本
private string text;
public string PlayText {
get {return text;}
set {text=value;}
}
}表达式类 AbstractExpression:
abstract class Expression{
//解释器
public void Interpret(PlayContent content) {
...
}
//执行
public abstract void Excute(string key, double value);
}音符类 TerminalExpression:
class Note : Expression {
public override void Excute(string key, double value) {...}
}音阶类 TerminalExpression:
class Scale : Expression {
public override void Excute(string key, double value) {...}
}客户端
switch-> 简单工厂 + 反射?
27.6 料事如神
- Programming for Musicians and Digital Artists: Creating music with ChucK:
- 王戈
第28章 男人和女人–访问者模式
28.1 男人和女人!
28.2 最简单的编程实现
28.3 简单的面向对象实现
28.4 用了模式的实现
抽象类
abstract class Action{
//得到男人结论或反应
public abstract void GetManConclusion(Man concreteElementA);
//得到女人结论或反应
public abstract void GetWomanConclusion(Man concreteElementB);
}
//人
abstract class Person
{
}具体类
//男人
class Man : Person
{
public override void Accept(Action visitor)
{
visitor.GetManConclusion(this);
}
}
//女人
class Woman : Person
{
public override void Accept(Action visitor)
{
visitor.GetWomanConclusion(this);
}
}- 双分派
//对象结构
class ObjectStructure
{
private IList elements = new List();
//增加
public void Attach(Person element)
{
elements.Add(element);
}
//移除
public void Detach(Person element)
{
elements.Remove(element);
}
//遍历查看显示
public void Display(Action visitor)
{
foreach (Person e in elements){
e.Accept(visitor);
}
}
} 客户端
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ObjectStructure o = new ObjectStructure();
o.Attach(new Man());
o.Attach(new Woman());
Success v1 = new Success();
o.Display(v1); //遍历Man和Woman的不同反应
Failing v2 = new Failing();
o.Display(v2);
Amativeness v3 = new Amativeness();
o.Display(v3);
Marriage v4 = new Marriage();
o.Display(v4);
Console.Read();
}28.5 访问者模式
28.6 访问者模式基本代码
visitor类
abstract class Visitor
{
public abstract void VisitConcreteElementA(ConcreteElementA concreteElementA);
public abstract void VisitConcreteElementB(ConcreteElementB concreteElementB);
}具体访问类
class ConcreteVisitor1 : Visitor
{
public override void VisitConcreteElementA(ConcreteElementA concreteElementA)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}被{1}访问", concreteElementA.GetType().Name, this.GetType().Name);
}
public override void VisitConcreteElementB(ConcreteElementB concreteElementB)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}被{1}访问", concreteElementB.GetType().Name, this.GetType().Name);
}
}Element类: 定义一个accept操作,以访问者为参数
abstract class Element
{
public abstract void Accept(Visitor visitor);
}ConcreteElementA
class ConcreteElementA : Element
{
public override void Accept(Visitor visitor)
{
visitor.VisitConcreteElementA(this);
}
public void OperationA()
{ }
}objectStructure类: 遍历
class ObjectStructure
{
private IList elements = new List();
public void Attach(Element element)
{
elements.Add(element);
}
public void Detach(Element element)
{
elements.Remove(element);
}
public void Accept(Visitor visitor)
{
foreach (Element e in elements)
{
e.Accept(visitor);
}
}
} 28.7 比上不足,比下有余
- Application: 编译器中AST生成?
第29章 OOTV杯超级模式大赛–模式总结
29.1 演讲任务
29.2 报名参赛
29.3 超模大赛开幕式
29.4 创建型模式比赛
29.5 结构型模式比赛
29.6 行为型模式一组比赛
29.7 行为型模式二组比赛
29.8 决赛
29.9 梦醒时分
29.10 没有结束的结尾
附 录 A 培训实习生–面向对象基础
A.1 培训实习生
A.2 类与实例
- object = attributes + operations
A.3 构造方法
- initialize
A.4 方法重载
A.5 属性与修饰符
- attribute
getset
A.6 封装
A.7 继承
- is-a
- 关键字
base
A.8 多态
- override
- virtual
A.9 重构
A.10 抽象类
- abstract
A.11 接口
A.12 集合
A.13 泛型
A.14 委托与事件
?
- delegate
- event
A.15 客套
附 录 B 参考文献