ROS中用Twist消息控制机器人
ROS中用Twist消息控制机器人
INSTALLING THE ROS-BY-EXAMPLE CODE是书中第五章的内容,如果我们按照上一篇教程执行过了,就可以直接进入第五章,安装一个叫rbx1的包。这个包里面包括了本书中用到的所有例子的源码,包括路径规划,视觉,语音识别等功能。这本书基本就围绕这个包来学习ROS的使用方法。
- 基本包的功能介绍
- 从终端发布Twist消息控制机器人
- 从节点发布Twist消息控制机器人
- 下一步
1.基本包的功能介绍
ROS Base Controller是ROS中的基本控制节点,其中包含基本PID算法来控制电机运动。它主要任务是监听终端中或其他节点发出的以/cmd_vel为topic的控制指令(Topic是ROS中的一个基本概念,不同的节点之间通过发布和订阅相同Topic的消息来通信),然后发布/odom topic的odometry 消息(里程,指直接获得的机器人走过的距离,通常由编码器数据计算得到或结合惯导经EKF得到),同时发布/odom坐标系和机体坐标系之间的转换(如果odom数据由EKF得到的话,这个工作由 robot_pose_ekf 节点完成).
move_base pacakge 可以让机器人移动至我们指定的目标地点,其中包含避障,路径规划等功能。
gmapping package :SLAM,用激光雷达或Kinect构建实时地图
amcl package : 机器人利用SLAM或odometry数据实时定位
下面是整个流程图:
2.从终端发布Twist消息控制机器人
其实这个Twist消息我们上一次已经用过了,它的Topic是/cmd_vel,base controler订阅Twist消息来控制电机。
在终端中执行以下指令查看Twist消息的具体内容:
rosmsg show geometry_msgs/Twist其中有linear和angular两个子消息,可以唯一确定机器人的运动状态。
首先roscore,然后启动机器人和仿真器:
roslaunch rbx1_bringup fake_turtlebot.launchrosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find rbx1_nav`/sim.rviz打开新的终端,执行以下语句:
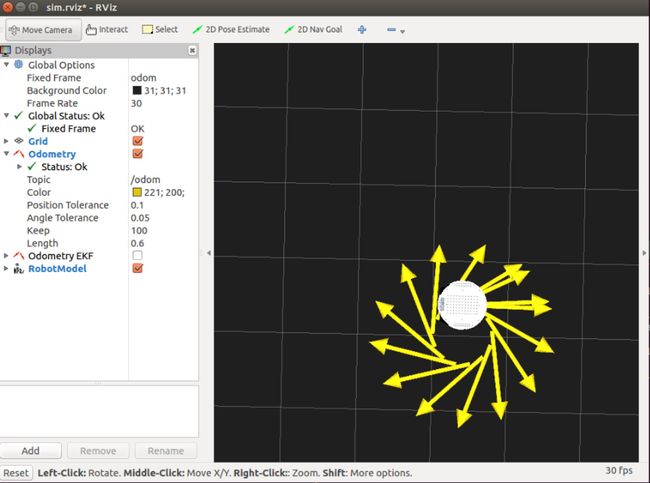
rostopic pub -r 10 /cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 0.1, y: 0, z: 0}, angular: {x: 0, y: 0, z: -0.5}}'现在详细解读一下这条指令,
“-r 10” 表示以10HZ的频率发布这条消息,
“/cmd_vel”为消息的Topic,”geometry_msgs/Twist” 为消息类型,
‘{linear: {x: 0.1, y: 0, z: 0}, angular: {x: 0, y: 0, z: -0.5}}’表示指定的线速度和角速度。
运行效果如下:
然后我们让让机器人停下来,先Ctrl+C终止进程,再输入以下指令:
rostopic pub -1 /cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist '{}'点击Rviz左下角的Reset,清除方向箭头。再执行以下指令:
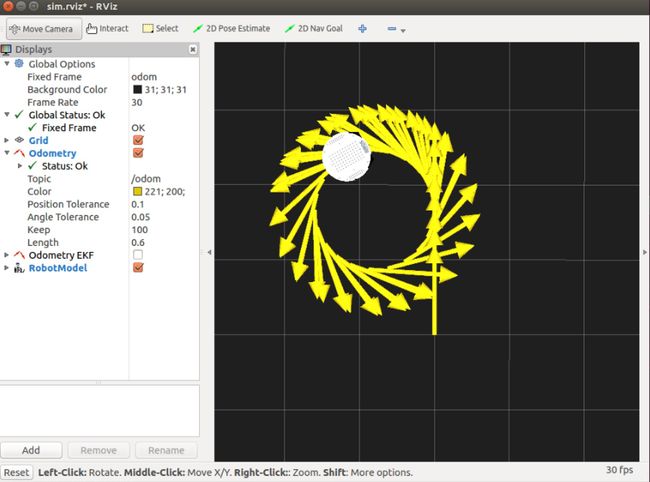
rostopic pub -1 /cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 0.2, y: 0, z: 0}, angular: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}}'; rostopic pub -r 10 /cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 0.2, y: 0, z: 0}, angular: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0.5}}'运行效果如下:
pub -1表示仅发布一次消息,机器人现已0.2m/s直线运行,大概3s之后,开始做圆周运动。
3.从节点发布Twist消息控制机器人
以上演示了如何从终端发布指令控制机器人,但是大多数情况下是在程序中控制的。现在我们来看一下怎么通过节点发布Twist消息控制机器人,这里的demo都是用Python写的,简洁易懂。
还是先启动机器人和仿真器:
roslaunch rbx1_bringup fake_turtlebot.launchrosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find rbx1_nav`/sim.rviz然后启动控制节点:
rosrun rbx1_nav timed_out_and_back.py这个 timed_out_and_back.py 程序在 rbx1/rbx1_nav/nodes 目录下,功能是先让机器人沿直线前进特定的距离,再旋转180度,再前进相同的距离返回出发点。
运行效果如下:
现在我们看一下源代码分析一下具体怎么实现:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
#导入最主要的Python for ROS库
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
from math import pi
#导入geometry_msgs包中的Twist消息类型
class OutAndBack():
def __init__(self):
# 节点名称
rospy.init_node('out_and_back', anonymous=False)
# 当终端按下Ctrl+C之后可以终止节点
rospy.on_shutdown(self.shutdown)
# 定义在/cmd_vel Topic中发布Twist消息,控制机器人速度
self.cmd_vel = rospy.Publisher('/cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size=1)
rate = 50
# 设置更新频率为50HZ
r = rospy.Rate(rate)
# 线速度
linear_speed = 0.2
# 目标距离
goal_distance = 1.0
# 到达目标的时间
linear_duration = goal_distance / linear_speed
# 角速度 1.0rad/s
angular_speed = 1.0
# 转角为Pi(180 degrees)
goal_angle = pi
# How long should it take to rotate?
angular_duration = goal_angle / angular_speed
# Loop through the two legs of the trip
for i in range(2):
# Initialize the movement command
move_cmd = Twist()
# Set the forward speed
move_cmd.linear.x = linear_speed
# 机器人向前运动,延时一定时间
ticks = int(linear_duration * rate)
for t in range(ticks):
self.cmd_vel.publish(move_cmd)
r.sleep()
# 发送一个空的Twist消息是机器人停止
move_cmd = Twist()
self.cmd_vel.publish(move_cmd)
rospy.sleep(1)
move_cmd.angular.z = angular_speed
# 机器人开始旋转,延时一定时间使机器人转180度
ticks = int(goal_angle * rate)
for t in range(ticks):
self.cmd_vel.publish(move_cmd)
r.sleep()
# 停下来
move_cmd = Twist()
self.cmd_vel.publish(move_cmd)
rospy.sleep(1)
# 循环两次之后停止
self.cmd_vel.publish(Twist())
# 定义 shutdown(self)可以手动停止机器人
def shutdown(self):
# Always stop the robot when shutting down the node.
rospy.loginfo("Stopping the robot...")
self.cmd_vel.publish(Twist())
rospy.sleep(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
OutAndBack()
except:
rospy.loginfo("Out-and-Back node terminated.")