OpenRisc-35-基于orpsoc,eCos的sd card controller的测试实验
引言
之前,曾经在orpsoc的平台上,测试验证过其sd card controller的linux的驱动,但是并不是很完美,经过努力,终于在eCos下完成了其全部功能的验证,包括驱动层验证,文件系统的挂载,应用层的创建文件,打开文件,复制文件,源文件与复制文件的比较等,此外,还有创建目录,切换目录等操作。
本小节就分享一下整个验证过程。
关于基于orpsoc+linux下的sd card controller验证,请参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/rill_zhen/article/details/9111213
关于linux下的SD卡驱动,请参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/rill_zhen/article/details/9419651
1,硬件部分
1>基本信息
本次验证,采用的是最初的orpsoc的硬件结构,没有进行任何改动,唯一做的工作就是将硬件配置信息提前烧到了外部的spi-flash,每次上电可自动执行,省去每次调试前的FPGA配置工作。
关于如何烧写外部spi-flash,请参考:http://blog.csdn.net/rill_zhen/article/details/9162275
此外,需要了解sd卡控制器这个ipcore的一些信息,比如wishbone地址等,也在之前的blog中做过介绍,这里不再赘述。
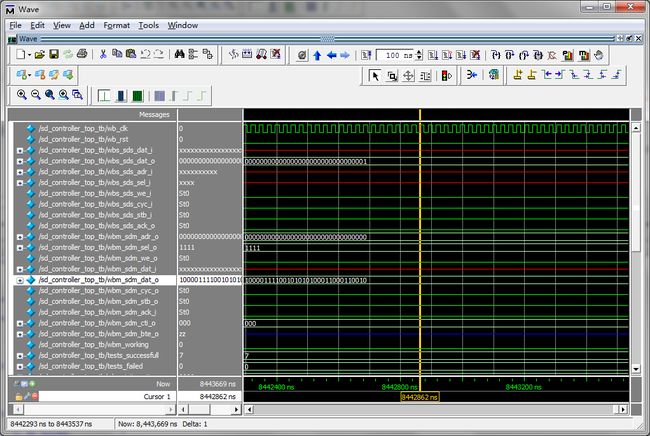
2>sd card controller的仿真
关于ipcore的仿真,之前也做过很多实验,如果有什么问题,可以先参考之前的内容,或者写评论给我,我会尽快回答。这里只给出仿真波形和仿真输出信息。如下:
1》仿真波形
2》仿真信息
可以看出,有一个错误。但我觉得不影响使用。
# T0 Start
#
# access_to_reg TEST
# Time: 925
# TEST 0: 3 32-BIT READ-WRITE REGISTERS ( VARIOUS BUS DELAYS )
#
# ===========================================================================
# T0 test_access_to_reg Completed
# ===========================================================================
# T1 Start
#
# test_send_cmd TEST
# Time: 4435
# TEST 0: 0: Send CMD, No Response
#
# ===========================================================================
# T1 test_send_cmd Completed
# ===========================================================================
# T2 Start
#
# access_to_reg TEST
# Time: 8153
# TEST 3.0: 0: Init Seq, No Response
# V 1.0 Card, Timeout In TEST 3.0 00008004
# CID reg 1: ffffffdd
# RCA Response: 20000700
# RCA Nr for data transfer: 00002000
#
# ===========================================================================
# T2 test_init_sequence Completed
# ===========================================================================
# T3 Start
#
# access_to_reg TEST
# Time: 61583
# TEST 4.0: Send data
# V 1.0 Card, Timeout In TEST 4.0 00008004
# CID reg 1: ffffffdd
# RCA Response: 20000700
# RCA Nr for data transfer: 00002000
# 2**BUS WIDTH 4
# Card status after Bus width set 00000920
#
# ===========================================================================
# T3 test_send_data Completed
# ===========================================================================
# T4 Start
# Time: 208639
# TEST 4.0: Send data
# V 1.0 Card, Timeout In TEST 4.0 00008004
# CID reg 1: ffffffdd
# RCA Response: 20000700
# RCA Nr for data transfer: 00002000
# 2**BUS WIDTH 4
# Card status after Bus width set 00000920
#
# ===========================================================================
# T4 test_send_rec_data Completed
# ===========================================================================
# T5 Start
#
# test_send_cmd_error_rsp
# Time: 416327
# TEST 5 part 0: Send CMD, No Response
# Time: 419969
# TEST 5, part 1: Send CMD, 48-Bit Response, No error check
# Time: 426521
# TEST 5, part 2: Send CMD3, 48-Bit Response, All Error check enable
# Time: 433177
# Bus error succesfully catched, Error status register: 0000000a
# Time: 433177
# Test 5 part 4: Send CMD2, 136-Bit
#
# ===========================================================================
# T5 test_send_cmd_error_rsp Complete
# ===========================================================================
#
# access_to_reg TEST
# Time: 444277
# TEST 4.0: Send data
# V 1.0 Card, Timeout In TEST 4.0 00008004
# CID reg 1: ffffffdd
# RCA Response: 20000700
# RCA Nr for data transfer: 00002000
# 2**BUS WIDTH 4
# Card status after Bus width set 00000920
# T6 test_send_cmd_error_rsp Complete
# All Test finnished. Nr Failed: 0, Nr Succes: 72,软件部分
1>与上次的比较
本次验证和上次验证的最大不同是软件。
首先,OS变了,上次采用的是linux,SD controller的驱动也是参考ipcore附带的testbench,ipcore附带的裸机程序,经过自己整理,变换,最后完成的linux下的驱动。
其次,测试程序也变了,上次只在linux驱动层进行了测试,这次不仅进行了driver的测试,还进行了应用层的测试。
最后,验证形式也变了,上次只是进行了基本的I/O验证,这次验证包括了文件系统,是文件级的测试。
2>验证准备
首先要搭建eCos运行环境,请参考:http://blog.csdn.net/rill_zhen/article/details/9271721
其次是搭建ORPSoC的调试环境,请参考:http://blog.csdn.net/rill_zhen/article/details/8700937
3>软件编码
1》编写基于eCos的sd卡控制器的driver
此驱动已经在eCos工程内,路径是:eCos/packages/devs/disk/opencores/sdcmsc/current/src/if_sdcmsc.c
为了更清楚,更真实的展示验证过程,在里面增加调试信息,修改后,代码请参考附录。
2》修改eCos中关于fatfs部分的代码
eCos本身的fatfs部分有一些问题,如果不修改的话,在测试程序将无法挂载sd卡的文件系统。
在这之前,有必要梳理一下mount()函数的执行过程,如下:
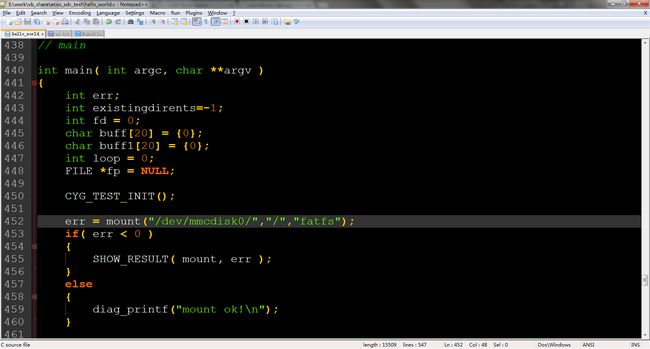
a,应用程序的mount()
如下便是测试程序的部分代码:
这里需要说明的是,mount的第一个参数,必须和驱动中注册的设备名称一致。
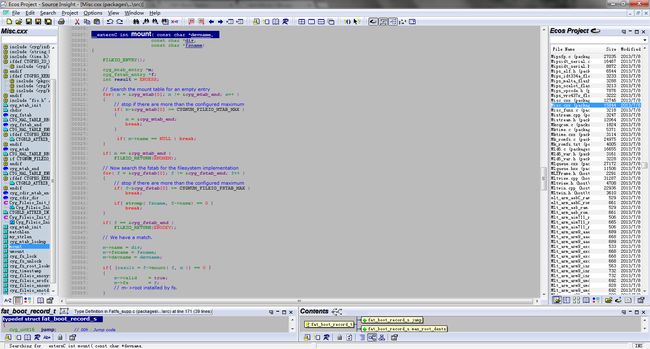
b,eCos中mount()函数的实现入口,misc.cxx:mount()
之前说过,eCos只是一个库,并不是一个platform,所以应用程序和eCos在逻辑上是平等的,既然应用程序mount()返回错误,那么我们需要查找其具体实现。
如下图:
c,mount()对应的具体文件系统的mount实现入口,fatfs.c:fatfs_mount()
这里需要说明的有两点:
第一,fatfs_mount()会首先调用cyg_io_lookup()函数,而这个函数最终会调用驱动(if_sdcmsc.c)中的sdcmsc_disk_loopup()函数,sdcmsc_disk_loopup()函数会调用sdcmsc_disk_init(),实现SD卡的初始化工作,也就是上次基于linux的验证时,给SD卡发送一连串的命令。
第二,fatfs_mount()会调用cyg_io_lookup()函数之后,会调用fatfs_init()函数,fatfs_init()函数会首先调用read_boot_record()函数,这个函数会读取FATFS的格式化信息。
如下图:
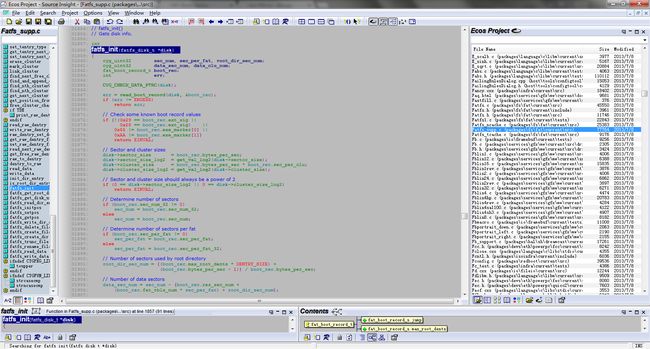
d,读取boot record信息,fatfs_supp.c:fatfs_init()
eCos就是在这里出现了问题!eCos默认是从SD卡的第0个sector读取boot record,但是并不是所有的SD卡的文件系统格式化信息都存在那里,所以,如果你的SD卡的文件系统信息没有存在第0个sector,eCos就无法挂载。很不幸,我用的SD卡的fat fs的boot record 信息就不在第0个sector,所以一直无法挂载,出现“invalid argument”的错误。
如果想让eCos能读到boot record信息,需要修改读取地址。如何知道你的SD卡的boot record信息的起始地址在哪里呢?可以下载安装winhex这个软件来查看,安装完成后,将SD卡通过读卡器插到电脑上,打开winhex的tool->open disk,选择你的SD卡,就可以看到文件系统的格式化信息。
我的SD卡的boot record信息在第135个sector,起始地址是0x10e00,eCos里面的地址是0,所以肯定读不到正确的值,无法挂载也就可以理解了。
winhex我已上传:http://download.csdn.net/detail/rill_zhen/5776013
关于fat fs的格式化信息,请参考:http://averstak.tripod.com/fatdox/bootsec.htm#ef
fatfs_init(),如下图:
read_boot_record(),如下图:这里需要修改!
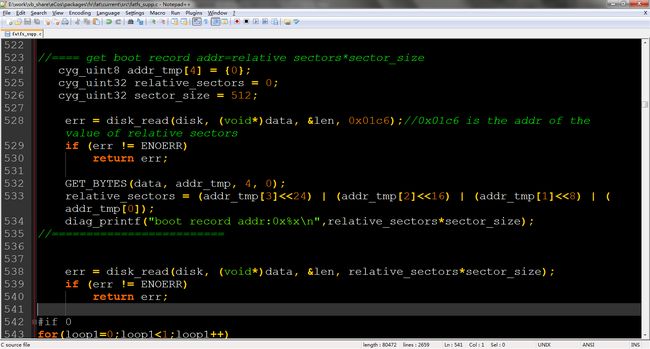
上面是手工指定bootrecord的地址,这样会有问题,可能对于不同的SD卡,其bootrecord的地址是不同的,所以这样修改只能对一个SD卡有效,显然是不行的。如何能兼容所有SD卡呢,其实在第0个sector有一个地方(0x01c6)就存有relative sectors,这个值就是bootrecord的相对sector数量,获得相对地址只需要将这个值乘以sector大小即可。
更多内容请参考:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Master_boot_record 或者: http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-22915173-id-597702.html
改进代码如下:
需要注意的是从0x01c6开始读到的四个字节是大端的,所以我们需要做一下byteorder的转换。
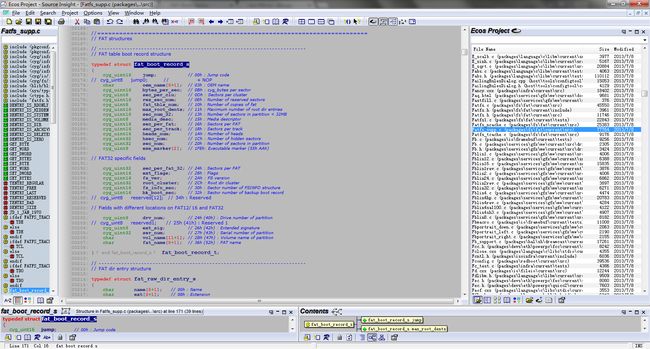
boot record的结构体,如下图:
e,code list
请参考附录部分的内容。
3,验证
验证过程是简单的。
1>配置eCos
要进行本次验证,需要增加5个package。执行如下操作:
如下所示:
1》增加依赖包:
ecosconfig new orpsoc default
ecosconfig add CYGPKG_IO_DISK
ecosconfig add CYGPKG_IO_FILEIO
ecosconfig add CYGPKG_FS_FAT
ecosconfig add CYGPKG_BLOCK_LIB
ecosconfig add CYGPKG_LINUX_COMPAT
2》检查冲突,要没有冲突才行
ecosconfig check
3》编译
ecosconfig tree
make
4》编译测试
make tests
2>编译测试文件
到测试文件所在目录,执行make即可。
如果有问题,请参考:http://blog.csdn.net/rill_zhen/article/details/9271721
3>下载验证
将生成的测试文件,通过or32-elf-gdb烧到板子上。
当然,如果你的板子的硬件配置没有事先烧到spi-flash里面,需要用jtag将orpsoc_top.svf 烧到板子上。
这一步的具体操作过程,之前也有介绍,这里不再赘述。
4,验证结果
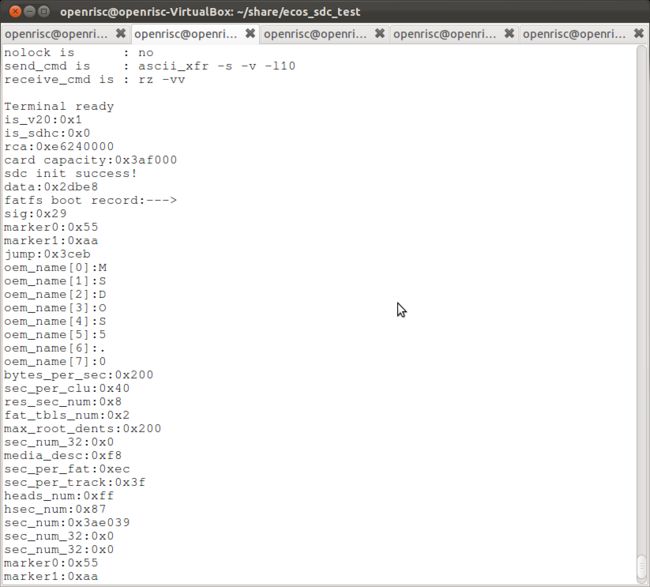
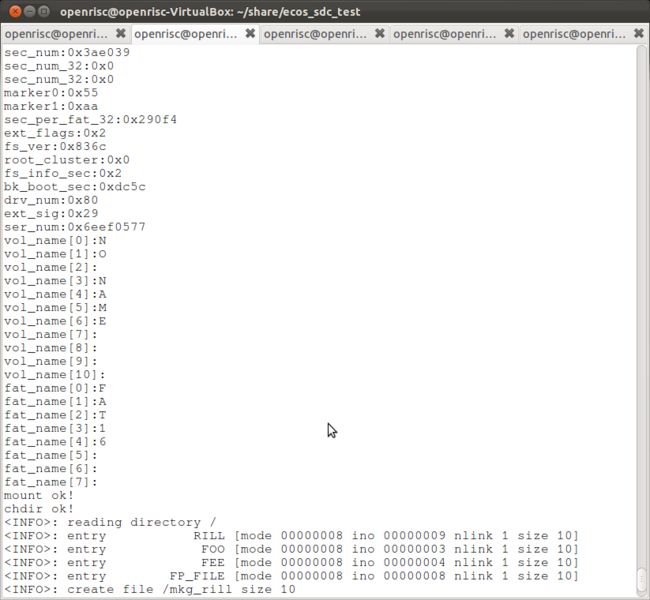
如果一切顺利,你会看到如下打印信息。
从中可以看出,我的SD卡是FAT16格式的,卡的capacity是1.9G左右,mount成功,可以read,write文件。
打印信息如下:
openrisc@openrisc-VirtualBox:~/share/ecos_sdc_test$ picocom --b 115200 --p n --d 8 --f xon /dev/ttyUSB2
picocom v1.4
port is : /dev/ttyUSB2
flowcontrol : xon/xoff
baudrate is : 115200
parity is : none
databits are : 8
escape is : C-a
noinit is : no
noreset is : no
nolock is : no
send_cmd is : ascii_xfr -s -v -l10
receive_cmd is : rz -vv
Terminal ready
is_v20:0x1
is_sdhc:0x0
rca:0xe6240000
card capacity:0x3af000
sdc init success!
data:0x2dbe8
fatfs boot record:--->
sig:0x29
marker0:0x55
marker1:0xaa
jump:0x3ceb
oem_name[0]:M
oem_name[1]:S
oem_name[2]:D
oem_name[3]:O
oem_name[4]:S
oem_name[5]:5
oem_name[6]:.
oem_name[7]:0
bytes_per_sec:0x200
sec_per_clu:0x40
res_sec_num:0x8
fat_tbls_num:0x2
max_root_dents:0x200
sec_num_32:0x0
media_desc:0xf8
sec_per_fat:0xec
sec_per_track:0x3f
heads_num:0xff
hsec_num:0x87
sec_num:0x3ae039
sec_num_32:0x0
sec_num_32:0x0
marker0:0x55
marker1:0xaa
sec_per_fat_32:0x290f4
ext_flags:0x2
fs_ver:0x836c
root_cluster:0x0
fs_info_sec:0x2
bk_boot_sec:0xdc5c
drv_num:0x80
ext_sig:0x29
ser_num:0x6eef0577
vol_name[0]:N
vol_name[1]:O
vol_name[2]:
vol_name[3]:N
vol_name[4]:A
vol_name[5]:M
vol_name[6]:E
vol_name[7]:
vol_name[8]:
vol_name[9]:
vol_name[10]:
fat_name[0]:F
fat_name[1]:A
fat_name[2]:T
fat_name[3]:1
fat_name[4]:6
fat_name[5]:
fat_name[6]:
fat_name[7]:
mount ok!
chdir ok!
: reading directory /
: entry RILL [mode 00000008 ino 00000009 nlink 1 size 10]
: entry FOO [mode 00000008 ino 00000003 nlink 1 size 10]
: entry FEE [mode 00000008 ino 00000004 nlink 1 size 10]
: entry FP_FILE [mode 00000008 ino 00000008 nlink 1 size 10]
: create file /mkg_rill size 10
: check file mkg_rill
: copy file mkg_rill -> mkg_rill_bak
: check file mkg_rill_bak
: compare files mkg_rill_bak == /mkg_rill
buf1[0](00) == buf2[0](00)
buf1[1](01) == buf2[1](01)
buf1[2](02) == buf2[2](02)
buf1[3](03) == buf2[3](03)
buf1[4](04) == buf2[4](04)
buf1[5](05) == buf2[5](05)
buf1[6](06) == buf2[6](06)
buf1[7](07) == buf2[7](07)
buf1[8](08) == buf2[8](08)
buf1[9](09) == buf2[9](09)
PASS:
EXIT: 5,小结
经过努力,基于ORPSoC的SD卡控制器的验证工作终于可以告一段落了。通过目前的工作,有如下收获:
首先,证明了opencores上面的这个sd卡控制器的硬件是没有问题的。
其次,ORPSoC对这个ipcore的集成,也是没问题的。
第三,得到了一个可以work的SD卡控制器的基于eCos的驱动。
6,future work
1,将if_sdcmsc.c移植到linux上,实现SD卡的基本I/O操作。
2,基于linux系统,实现SD卡文件系统的挂载。
7,附录 code list
1>驱动:if_sdcmsc.c
//=========================================================================
//
// if_sdcmsc.c
//
// Provide a disk device driver for SDCard Mass Storage Controller
//
//==========================================================================
// ####ECOSGPLCOPYRIGHTBEGIN####
// -------------------------------------------
// This file is part of eCos, the Embedded Configurable Operating System.
// Copyright (C) 2004, 2006 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
//
// eCos is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
// the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free
// Software Foundation; either version 2 or (at your option) any later
// version.
//
// eCos is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
// ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
// FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
// for more details.
//
// You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
// along with eCos; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
// 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301, USA.
//
// As a special exception, if other files instantiate templates or use
// macros or inline functions from this file, or you compile this file
// and link it with other works to produce a work based on this file,
// this file does not by itself cause the resulting work to be covered by
// the GNU General Public License. However the source code for this file
// must still be made available in accordance with section (3) of the GNU
// General Public License v2.
//
// This exception does not invalidate any other reasons why a work based
// on this file might be covered by the GNU General Public License.
// -------------------------------------------
// ####ECOSGPLCOPYRIGHTEND####
//==========================================================================
//#####DESCRIPTIONBEGIN####
//
// Author: Piotr Skrzypek
// Date: 2012-05-01
//
//####DESCRIPTIONEND####
//==========================================================================
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
// Settings exported from CDL
#include
// SDCMSC address space
#define SDCMSC_BASE 0x9e000000
// Register space
#define SDCMSC_ARGUMENT 0x00
#define SDCMSC_COMMAND 0x04
#define SDCMSC_CARD_STATUS 0x08
#define SDCMSC_RESPONSE 0x0C
#define SDCMSC_CONTROLLER_SETTING 0x1C
#define SDCMSC_BLOCK_SIZE 0x20
#define SDCMSC_POWER_CONTROL 0x24
#define SDCMSC_SOFTWARE_RESET 0x28
#define SDCMSC_TIMEOUT 0x2C
#define SDCMSC_NORMAL_INT_STATUS 0x30
#define SDCMSC_ERROR_INT_STATUS 0x34
#define SDCMSC_NORMAL_INT_ENABLE 0x38
#define SDCMSC_ERROR_INT_ENABLE 0x3C
#define SDCMSC_CAPABILITY 0x48
#define SDCMSC_CLOCK_DIVIDER 0x4C
#define SDCMSC_BD_BUFFER_STATUS 0x50
#define SDCMSC_DAT_INT_STATUS 0x54
#define SDCMSC_DAT_INT_ENABLE 0x58
#define SDCMSC_BD_RX 0x60
#define SDCMSC_BD_TX 0x80
// SDCMSC_COMMAND bits
#define SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(x) (x << 8)
#define SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDW(x) (x << 6)
#define SDCMSC_COMMAND_CICE 0x10
#define SDCMSC_COMMAND_CIRC 0x08
#define SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_48 0x02
#define SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_136 0x01
//SDCMSC_CARD_STATUS bits
#define SDCMSC_CARD_STATUS_CICMD 0x01
// SDCMSC_NORMAL_INT_STATUS bits
#define SDCMSC_NORMAL_INT_STATUS_EI 0x8000
#define SDCMSC_NORMAL_INT_STATUS_CC 0x0001
// SDCMSC_DAT_INT_STATUS
#define SDCMSC_DAT_INT_STATUS_TRS 0x01
typedef struct cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t {
int is_v20;
int is_sdhc;
cyg_uint32 rca;
int connected;
} cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t;
static int sdcmsc_card_cmd(cyg_uint32 cmd,
cyg_uint32 arg,
cyg_uint32 *response) {
// Send command to card
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_COMMAND, cmd);
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_ARGUMENT, arg);
// Wait for response
cyg_uint32 reg;
cyg_uint32 mask = SDCMSC_NORMAL_INT_STATUS_EI |
SDCMSC_NORMAL_INT_STATUS_CC;
do {
HAL_READ_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_NORMAL_INT_STATUS, reg);
} while(!(reg & mask));
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_NORMAL_INT_STATUS, 0);
// Optionally read response register
if(response) {
HAL_READ_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_RESPONSE, *response);
}
// Check for errors
if(reg & SDCMSC_NORMAL_INT_STATUS_EI) {
HAL_READ_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_ERROR_INT_STATUS, reg);
if(reg & (1 << 3)) diag_printf("Command index error\n");
if(reg & (1 << 1)) diag_printf("Command CRC error\n");
if(reg & (1 << 0)) diag_printf("Command timeout\n");
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_ERROR_INT_STATUS, 0);
return 0;
}
else {
return 1;
}
}
// Card initialization and identification implemented according to
// Physical Layer Simplified Specification Version 3.01
static int sdcmsc_card_init(cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t *data,
char *serial,
char *firmware_rev,
char *model_num,
cyg_uint32 *capacity) {
cyg_uint32 reg;
cyg_uint32 cmd;
cyg_uint32 arg;
// Send CMD0 to switch the card to idle state
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(0);
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, 0, NULL)) return 0;
// Send CMD8 offering 2.7V to 3.6V range
// If the card doesn't responde it means either:
// 1. Card supports v2.0 but can't communicate using
// current voltage levels
// 2. Card does not support v2.0
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(8) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CICE |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CIRC |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_48;
data->is_v20 = sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, 0x1AA, NULL);
diag_printf("is_v20:0x%x\n",data->is_v20);//rill add debug
do {
HAL_READ_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_CARD_STATUS, reg);
} while(reg & SDCMSC_CARD_STATUS_CICMD);
// Repeat ACMD41 until card set the busy bit to 1
// Since ACMD is an extended command, it must be preceded
// by CMD55
do {
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(55) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CICE |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CIRC |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_48;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, 0, NULL)) return 0;
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(41) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_48;
arg = data->is_v20 ?
0x40FF8000 :
0x00FF8000;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, arg, ®)) return 0;
} while(!(reg & 0x80000000));
data->is_sdhc = !!(reg & 0x40000000);
diag_printf("is_sdhc:0x%x\n",data->is_sdhc);
// Issue CMD2 to switch from ready state to ident. Unfortunately, it is
// not possible to read whole CID because the command can be issued only
// once, and the peripheral can store only 32bit of the command at once.
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(2) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_136;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, 0, NULL)) return 0;
// Issue CMD3 to get RCA and switch from ident state to stby.
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(3) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CICE |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CIRC |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_48;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, 0, ®)) return 0;
data->rca = reg & 0xFFFF0000;
diag_printf("rca:0x%x\n",data->rca);
// Calculate card capacity. Use information stored in CSD register.
cyg_uint32 card_capacity;
if(data->is_sdhc) {
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(9) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDW(1) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_136;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, data->rca, ®)) return 0;
card_capacity = reg & 0x3F;
card_capacity <<= 16;
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(9) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDW(2) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_136;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, data->rca, ®)) return 0;
reg >>= 16;
card_capacity |= reg;
card_capacity += 1;
card_capacity *= 1000;
}
else {
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(9) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDW(1) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_136;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, data->rca, ®)) return 0;
cyg_uint32 read_bl_len = (reg >> 16) & 0x0F;
cyg_uint32 c_size = reg & 0x3FF;
c_size <<= 2;
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(9) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDW(2) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_136;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, data->rca, ®)) return 0;
c_size |= (reg >> 30) & 0x03;
cyg_uint32 c_size_mult = (reg >> 15) & 0x07;
card_capacity = c_size + 1;
card_capacity *= 1 << (c_size_mult + 2);
card_capacity *= 1 << (read_bl_len);
card_capacity >>= 9;
}
diag_printf("card capacity:0x%x\n",card_capacity);
// Fill disk identification struct using information in CID register
// use OEM/APPlication ID field to fill model_num,
// Product revision field to fill firmware_rev,
// and Product serial number to field to fill serial
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(10) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDW(0) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_136;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, data->rca, ®)) return 0;
model_num[0] = (reg >> 16) & 0xFF;
model_num[1] = (reg >> 8) & 0xFF;
model_num[2] = 0;
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(10) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDW(2) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_136;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, data->rca, ®)) return 0;
firmware_rev[0] = (reg >> 24) & 0xFF;
firmware_rev[1] = 0;
serial[0] = (reg >> 16) & 0xFF;
serial[1] = (reg >> 8) & 0xFF;
serial[2] = reg & 0xFF;
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(10) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDW(3) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_136;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, data->rca, ®)) return 0;
serial[3] = (reg >> 24) & 0xFF;
// Put card in transfer state
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(7) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CICE |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CIRC |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_48;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, data->rca, ®)) return 0;
if(reg != 0x700) return 0;
// Set block size to 512
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(16) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CICE |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CIRC |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_48;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, 512, NULL)) return 0;
// Set 4-bits bus mode
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(55) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CICE |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CIRC |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_48;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, data->rca, NULL)) return 0;
cmd = SDCMSC_COMMAND_CMDI(6) |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CICE |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_CIRC |
SDCMSC_COMMAND_RTS_48;
if(!sdcmsc_card_cmd(cmd, 0x02, NULL)) return 0;
diag_printf("sdc init success!\n");
return 1;
}
static int sdcmsc_card_queue(cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t *data,
int direction_transmit,
int block_addr,
cyg_uint32 buffer_addr) {
// SDSC cards use byte addressing, while SDHC use block addressing.
// It is therefore required to multiply the address by 512 if
// we are dealing with SDSC card, to remain compatible with the API.
if(!data->is_sdhc) {
block_addr <<= 9;
}
if(direction_transmit) {
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_BD_TX, buffer_addr);
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_BD_TX, block_addr);
}
else {
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_BD_RX, buffer_addr);
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_BD_RX, block_addr);
}
// Now wait for the response
cyg_uint32 reg;
do {
HAL_READ_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_DAT_INT_STATUS, reg);
} while(!reg);
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_DAT_INT_STATUS, 0);
// Check for errors
if(reg == SDCMSC_DAT_INT_STATUS_TRS) {
return 1;
}
else {
if(reg & (1 << 5)) diag_printf("Transmission error\n");
if(reg & (1 << 4)) diag_printf("Command error\n");
if(reg & (1 << 2)) diag_printf("FIFO error\n");
if(reg & (1 << 1)) diag_printf("Retry error\n");
return 0;
}
}
// This is an API function. Is is called once, in the beginning
static cyg_bool sdcmsc_disk_init(struct cyg_devtab_entry* tab) {
// Set highest possible timeout
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_TIMEOUT, 0xFFFE);
// Reset the peripheral
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_SOFTWARE_RESET, 1);
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_CLOCK_DIVIDER, 2);
HAL_WRITE_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_SOFTWARE_RESET, 0);
// Call upper level
disk_channel* ch = (disk_channel*) tab->priv;
return (*ch->callbacks->disk_init)(tab);
}
// This function is called when user mounts the disk
static Cyg_ErrNo sdcmsc_disk_lookup(struct cyg_devtab_entry** tab,
struct cyg_devtab_entry *sub_tab,
const char* name) {
disk_channel *ch = (disk_channel*) (*tab)->priv;
cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t *data = (cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t*) ch->dev_priv;
// If the card was not initialized yet, it's time to do it
// and call disk_connected callback
if(!data->connected) {
cyg_disk_identify_t id;
// Pass dummy CHS geometry and hope the upper level
// will use LBA mode. To guess CHS we would need to
// analyze partition table and confront LBA and CHS
// addresses. And it would work only if proper LBA
// field is stored in MBR. Is is definitely something
// that should be done by upper level.
id.cylinders_num = 1;
id.heads_num = 1;
id.sectors_num = 1;
id.phys_block_size = 1;
id.max_transfer = 512;
// Initialize the card
data->connected = sdcmsc_card_init(data,
id.serial,
id.firmware_rev,
id.model_num,
&id.lba_sectors_num);
if(data->connected) {
// Let upper level know there is a new disk
(*ch->callbacks->disk_connected)(*tab, &id);
}
}
// Call upper level
return (*ch->callbacks->disk_lookup)(tab, sub_tab, name);
}
// API function to read block from the disk
static Cyg_ErrNo sdcmsc_disk_read(disk_channel* ch,
void* buf,
cyg_uint32 blocks,
cyg_uint32 first_block) {
cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t *data = (cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t*) ch->dev_priv;
int i;
int result;
cyg_uint32 reg;
for(i = 0; i < blocks; i++) {
// Check for free receive buffers
HAL_READ_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_BD_BUFFER_STATUS, reg);
reg >>= 8;
reg &= 0xFF;
if(reg == 0) {
return -EIO;
}
result = sdcmsc_card_queue(data, 0, first_block, (cyg_uint32) buf);
if(!result) {
return -EIO;
}
}
return ENOERR;
}
// API function to write block to disk
static Cyg_ErrNo sdcmsc_disk_write(disk_channel* ch,
const void* buf,
cyg_uint32 blocks,
cyg_uint32 first_block) {
cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t *data = (cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t*) ch->dev_priv;
int i;
int result;
cyg_uint32 reg;
for(i = 0; i < blocks; i++) {
// Check for free transmit buffers
HAL_READ_UINT32(SDCMSC_BASE + SDCMSC_BD_BUFFER_STATUS, reg);
reg &= 0xFF;
if(reg == 0) {
return -EIO;
}
result = sdcmsc_card_queue(data, 1, first_block, (cyg_uint32) buf);
if(!result) {
return -EIO;
}
}
return ENOERR;
}
// API function to fetch driver configuration and disk info.
static Cyg_ErrNo sdcmsc_disk_get_config(disk_channel* ch,
cyg_uint32 key,
const void* buf,
cyg_uint32* len) {
CYG_UNUSED_PARAM(disk_channel*, ch);
CYG_UNUSED_PARAM(cyg_uint32, key);
CYG_UNUSED_PARAM(const void*, buf);
CYG_UNUSED_PARAM(cyg_uint32*, len);
return -EINVAL;
}
// API function to update driver status information.
static Cyg_ErrNo sdcmsc_disk_set_config(disk_channel* ch,
cyg_uint32 key,
const void* buf,
cyg_uint32* len) {
cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t *data = (cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t*) ch->dev_priv;
if(key == CYG_IO_SET_CONFIG_DISK_UMOUNT) {
if(ch->info->mounts == 0) {
data->connected = false;
return (ch->callbacks->disk_disconnected)(ch);
}
else {
return ENOERR;
}
}
else {
return -EINVAL;
}
}
// Register the driver in the system
static cyg_sdcmsc_disk_info_t cyg_sdcmsc_disk0_hwinfo = {
.connected = 0
};
DISK_FUNS(cyg_sdcmsc_disk_funs,
sdcmsc_disk_read,
sdcmsc_disk_write,
sdcmsc_disk_get_config,
sdcmsc_disk_set_config
);
DISK_CONTROLLER(cyg_sdcmsc_disk_controller_0, cyg_sdcmsc_disk0_hwinfo);
DISK_CHANNEL(cyg_sdcmsc_disk0_channel,
cyg_sdcmsc_disk_funs,
cyg_sdcmsc_disk0_hwinfo,
cyg_sdcmsc_disk_controller_0,
true, //mbr supported
4 //partitions
);
BLOCK_DEVTAB_ENTRY(cyg_sdcmsc_disk0_devtab_entry,
CYGDAT_DEVS_DISK_OPENCORES_SDCMSC_DISK0_NAME,
0,
&cyg_io_disk_devio,
&sdcmsc_disk_init,
&sdcmsc_disk_lookup,
&cyg_sdcmsc_disk0_channel);
// EOF if_sdcmsc.c
2>测试程序:helloworld.c,Makefile
1》helloworld.c
//==========================================================================
//
// fatfs1.c
//
// Test fileio system
//
//==========================================================================
// ####ECOSGPLCOPYRIGHTBEGIN####
// -------------------------------------------
// This file is part of eCos, the Embedded Configurable Operating System.
// Copyright (C) 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2004 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
//
// eCos is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
// the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free
// Software Foundation; either version 2 or (at your option) any later
// version.
//
// eCos is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
// ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
// FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
// for more details.
//
// You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
// along with eCos; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
// 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301, USA.
//
// As a special exception, if other files instantiate templates or use
// macros or inline functions from this file, or you compile this file
// and link it with other works to produce a work based on this file,
// this file does not by itself cause the resulting work to be covered by
// the GNU General Public License. However the source code for this file
// must still be made available in accordance with section (3) of the GNU
// General Public License v2.
//
// This exception does not invalidate any other reasons why a work based
// on this file might be covered by the GNU General Public License.
// -------------------------------------------
// ####ECOSGPLCOPYRIGHTEND####
//==========================================================================
//#####DESCRIPTIONBEGIN####
//
// Author(s): nickg
// Contributors: nickg
// Date: 2000-05-25
// Purpose: Test fileio system
// Description: This test uses the testfs to check out the initialization
// and basic operation of the fileio system
//
//
//
//
//
//
//
//####DESCRIPTIONEND####
//
//==========================================================================
#include
#include
#include
#include // tracing macros
#include // assertion macros
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include // HAL polled output
#include
//==========================================================================
#define SHOW_RESULT( _fn, _res ) \
diag_printf(": " #_fn "() returned %d %s\n", _res, _res<0?strerror(errno):"");
//==========================================================================
#define IOSIZE 100
#define LONGNAME1 "long_file_name_that_should_take_up_more_than_one_directory_entry_1"
#define LONGNAME2 "long_file_name_that_should_take_up_more_than_one_directory_entry_2"
//==========================================================================
#ifndef CYGPKG_LIBC_STRING
char *strcat( char *s1, const char *s2 )
{
char *s = s1;
while( *s1 ) s1++;
while( (*s1++ = *s2++) != 0);
return s;
}
#endif
//==========================================================================
static void listdir( char *name, int statp, int numexpected, int *numgot )
{
int err;
DIR *dirp;
int num=0;
diag_printf(": reading directory %s\n",name);
dirp = opendir( name );
if( dirp == NULL ) SHOW_RESULT( opendir, -1 );
for(;;)
{
struct dirent *entry = readdir( dirp );
if( entry == NULL )
break;
num++;
diag_printf(": entry %14s",entry->d_name);
#ifdef CYGPKG_FS_FAT_RET_DIRENT_DTYPE
diag_printf(" d_type %2x", entry->d_type);
#endif
if( statp )
{
char fullname[PATH_MAX];
struct stat sbuf;
if( name[0] )
{
strcpy(fullname, name );
if( !(name[0] == '/' && name[1] == 0 ) )
strcat(fullname, "/" );
}
else fullname[0] = 0;
strcat(fullname, entry->d_name );
err = stat( fullname, &sbuf );
if( err < 0 )
{
if( errno == ENOSYS )
diag_printf(" ");
else SHOW_RESULT( stat, err );
}
else
{
diag_printf(" [mode %08x ino %08x nlink %d size %ld]",
sbuf.st_mode,sbuf.st_ino,sbuf.st_nlink,(long)sbuf.st_size);
}
#ifdef CYGPKG_FS_FAT_RET_DIRENT_DTYPE
if ((entry->d_type & S_IFMT) != (sbuf.st_mode & S_IFMT))
CYG_TEST_FAIL("File mode's don't match between dirent and stat");
#endif
}
diag_printf("\n");
}
err = closedir( dirp );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( stat, err );
if (numexpected >= 0 && num != numexpected)
CYG_TEST_FAIL("Wrong number of dir entries\n");
if ( numgot != NULL )
*numgot = num;
}
//==========================================================================
static void createfile( char *name, size_t size )
{
char buf[IOSIZE];
int fd;
ssize_t wrote;
int i;
int err;
diag_printf(": create file %s size %zd \n",name,size);
err = access( name, F_OK );
if( err < 0 && errno != EACCES ) SHOW_RESULT( access, err );
for( i = 0; i < IOSIZE; i++ ) buf[i] = i%256;
fd = open( name, O_WRONLY|O_CREAT );
if( fd < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( open, fd );
while( size > 0 )
{
ssize_t len = size;
if ( len > IOSIZE ) len = IOSIZE;
wrote = write( fd, buf, len );
if( wrote != len ) SHOW_RESULT( write, (int)wrote );
size -= wrote;
}
err = close( fd );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( close, err );
}
//==========================================================================
static void maxfile( char *name )
{
char buf[IOSIZE];
int fd;
ssize_t wrote;
int i;
int err;
size_t size = 0;
size_t prevsize = 0;
diag_printf(": create maximal file %s\n",name);
diag_printf(": This may take a few minutes\n");
err = access( name, F_OK );
if( err < 0 && errno != EACCES ) SHOW_RESULT( access, err );
for( i = 0; i < IOSIZE; i++ ) buf[i] = i%256;
fd = open( name, O_WRONLY|O_CREAT );
if( fd < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( open, fd );
do
{
wrote = write( fd, buf, IOSIZE );
//if( wrote < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( write, wrote );
if( wrote >= 0 )
size += wrote;
if( (size-prevsize) > 100000 )
{
diag_printf(": size = %zd \n", size);
prevsize = size;
}
} while( wrote == IOSIZE );
diag_printf(": file size == %zd\n",size);
err = close( fd );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( close, err );
}
//==========================================================================
static void checkfile( char *name )
{
char buf[IOSIZE];
int fd;
ssize_t done;
int i;
int err;
off_t pos = 0;
diag_printf(": check file %s\n",name);
err = access( name, F_OK );
if( err != 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( access, err );
fd = open( name, O_RDONLY );
if( fd < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( open, fd );
for(;;)
{
done = read( fd, buf, IOSIZE );
if( done < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( read, (int)done );
if( done == 0 ) break;
for( i = 0; i < done; i++ )
if( buf[i] != i%256 )
{
diag_printf("buf[%ld+%d](%02x) != %02x\n",pos,i,buf[i],i%256);
CYG_TEST_FAIL("Data read not equal to data written\n");
}
pos += done;
}
err = close( fd );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( close, err );
}
#ifdef CYGCFG_FS_FAT_USE_ATTRIBUTES
//==========================================================================
static void checkattrib(const char *name,
const cyg_fs_attrib_t test_attrib )
{
int err;
cyg_fs_attrib_t file_attrib;
diag_printf(": check attrib %s\n",name);
err = cyg_fs_get_attrib(name, &file_attrib);
if( err != 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( stat, err );
if ( (file_attrib & S_FATFS_ATTRIB) != test_attrib )
diag_printf(": attrib %s incorrect\n\tExpected %x Was %x\n",
name,test_attrib,(file_attrib & S_FATFS_ATTRIB));
}
#endif // CYGCFG_FS_FAT_USE_ATTRIBUTES
//==========================================================================
static void copyfile( char *name2, char *name1 )
{
int err;
char buf[IOSIZE];
int fd1, fd2;
ssize_t done, wrote;
diag_printf(": copy file %s -> %s\n",name2,name1);
err = access( name1, F_OK );
if( err < 0 && errno != EACCES ) SHOW_RESULT( access, err );
err = access( name2, F_OK );
if( err != 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( access, err );
fd1 = open( name1, O_WRONLY|O_CREAT );
if( fd1 < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( open, fd1 );
fd2 = open( name2, O_RDONLY );
if( fd2 < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( open, fd2 );
for(;;)
{
done = read( fd2, buf, IOSIZE );
if( done < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( read, (int)done );
if( done == 0 ) break;
wrote = write( fd1, buf, done );
if( wrote != done ) SHOW_RESULT( write, (int) wrote );
if( wrote != done ) break;
}
err = close( fd1 );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( close, err );
err = close( fd2 );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( close, err );
}
//==========================================================================
static void comparefiles( char *name2, char *name1 )
{
int err;
char buf1[IOSIZE];
char buf2[IOSIZE];
int fd1, fd2;
ssize_t done1, done2;
int i;
diag_printf(": compare files %s == %s\n",name2,name1);
err = access( name1, F_OK );
if( err != 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( access, err );
err = access( name1, F_OK );
if( err != 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( access, err );
fd1 = open( name1, O_RDONLY );
if( fd1 < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( open, fd1 );
fd2 = open( name2, O_RDONLY );
if( fd2 < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( open, fd2 );
for(;;)
{
done1 = read( fd1, buf1, IOSIZE );
if( done1 < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( read, (int)done1 );
done2 = read( fd2, buf2, IOSIZE );
if( done2 < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( read, (int)done2 );
if( done1 != done2 )
diag_printf("Files different sizes\n");
if( done1 == 0 ) break;
for( i = 0; i < done1; i++ )
if( buf1[i] != buf2[i] )
{
diag_printf("buf1[%d](%02x) != buf1[%d](%02x)\n",i,buf1[i],i,buf2[i]);
CYG_TEST_FAIL("Data in files not equal\n");
}
else
{
diag_printf("buf1[%d](%02x) == buf2[%d](%02x)\n",i,buf1[i],i,buf2[i]);
}
}
err = close( fd1 );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( close, err );
err = close( fd2 );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( close, err );
}
//==========================================================================
void checkcwd( const char *cwd )
{
static char cwdbuf[PATH_MAX];
char *ret;
ret = getcwd( cwdbuf, sizeof(cwdbuf));
if( ret == NULL ) SHOW_RESULT( getcwd, (int)ret );
if( strcmp( cwdbuf, cwd ) != 0 )
{
diag_printf( "cwdbuf %s cwd %s\n",cwdbuf, cwd );
CYG_TEST_FAIL( "Current directory mismatch");
}
}
//==========================================================================
// main
int main( int argc, char **argv )
{
int err;
int existingdirents=-1;
int fd = 0;
char buff[20] = {0};
char buff1[20] = {0};
int loop = 0;
FILE *fp = NULL;
CYG_TEST_INIT();
err = mount("/dev/mmcdisk0/","/","fatfs");
if( err < 0 )
{
SHOW_RESULT( mount, err );
}
else
{
diag_printf("mount ok!\n");
}
err = chdir( "/" );
if( err < 0 )
{
SHOW_RESULT( chdir, err );
}
else
{
diag_printf("chdir ok!\n");
}
checkcwd( "/" );
listdir( "/", true, -1, &existingdirents );
createfile( "/mkg_rill", 10 );
checkfile( "mkg_rill" );
copyfile( "mkg_rill", "mkg_rill_bak");
checkfile( "mkg_rill_bak" );
comparefiles( "mkg_rill_bak", "/mkg_rill" );
#if 0
diag_printf(": mkdir bar\n");
err = mkdir( "/bar", 0 );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( mkdir, err );
listdir( "/" , true, existingdirents+3, NULL );
copyfile( "fee", "/bar/fum" );
checkfile( "bar/fum" );
comparefiles( "/fee", "bar/fum" );
diag_printf(": cd bar\n");
err = chdir( "bar" );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( chdir, err );
checkcwd( "/bar" );
diag_printf(": rename /foo bundy\n");
err = rename( "/foo", "bundy" );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( rename, err );
listdir( "/", true, existingdirents+2, NULL );
listdir( "" , true, 4, NULL );
checkfile( "/bar/bundy" );
comparefiles("/fee", "bundy" );
diag_printf(": unlink fee\n");
err = unlink( "/fee" );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( unlink, err );
diag_printf(": unlink fum\n");
err = unlink( "fum" );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( unlink, err );
diag_printf(": unlink /bar/bundy\n");
err = unlink( "/bar/bundy" );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( unlink, err );
diag_printf(": cd /\n");
err = chdir( "/" );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( chdir, err );
checkcwd( "/" );
diag_printf(": rmdir /bar\n");
err = rmdir( "/bar" );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( rmdir, err );
listdir( "/", false, existingdirents, NULL );
#endif
err = umount( "/" );
if( err < 0 ) SHOW_RESULT( umount, err );
CYG_TEST_PASS_FINISH("fatfs1");
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// EOF fatfs1.c
2》Makefile
# This variable should point to the directory where you
# installed your eCos build.
ECOS_INSTALL := /home/openrisc/share/eCos/ecos-work/install
# As part of the build process, eCos automatically creates
# a file with compiler flags. Those flags are computed based
# on the ecc configuration file. It is smart to use them when
# compiling your application.
include $(ECOS_INSTALL)/include/pkgconf/ecos.mak
# Unfortunately, some flags are C++ flags and some are C. We
# need to separate them. The file rules.mak shipped with the eCos
# repository contains the rules to do it. So we need to include
# this file in the end of the makefile and use more generic
# names. We also add the paths to the installation directory.
CFLAGS := $(ECOS_GLOBAL_CFLAGS) -I $(ECOS_INSTALL)/include
LDFLAGS := $(ECOS_GLOBAL_LDFLAGS) -L $(ECOS_INSTALL)/lib -T $(ECOS_INSTALL)/lib/target.ld
# Rules to build the application
all: hello_world
hello_world: hello_world.c
$(ECOS_COMMAND_PREFIX)gcc $(ACTUAL_CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) $< -o $@
# Now include the file with rules. This file must be included
# in the end, otherwise it interferes with the makefile target.
#include $(ECOS_REPOSITORY)/pkgconf/rules.mak
include /home/openrisc/share/eCos/packages/pkgconf/rules.mak
3>read_boot_record()函数修改
static int
read_boot_record(fatfs_disk_t *disk, fat_boot_record_t *fbr)
{
cyg_uint8 data[0x5A];
cyg_uint32 len;
int err;
len = 0x5A;
err = disk_read(disk, (void*)data, &len, 0x10e00);//Rill modify at 130717
if (err != ENOERR)
return err;
GET_WORD(data, fbr->jump, 0x00);
GET_BYTES(data, fbr->oem_name, 8, 0x03);
GET_WORD(data, fbr->bytes_per_sec, 0x0B);
GET_BYTE(data, fbr->sec_per_clu, 0x0D);
GET_WORD(data, fbr->res_sec_num, 0x0E);
GET_BYTE(data, fbr->fat_tbls_num, 0x10);
GET_WORD(data, fbr->max_root_dents, 0x11);
GET_WORD(data, fbr->sec_num_32, 0x13);
GET_BYTE(data, fbr->media_desc, 0x15);
GET_WORD(data, fbr->sec_per_fat, 0x16);
GET_WORD(data, fbr->sec_per_track, 0x18);
GET_WORD(data, fbr->heads_num, 0x1A);
GET_DWORD(data, fbr->hsec_num, 0x1C);
GET_DWORD(data, fbr->sec_num, 0x20);
// This is a quick check for FAT12/16 or FAT32 boot record.
// The sec_per_fat field must be 0 on FAT32, since this
// field plays a crucial role in detection of the FAT type
// (12,16,32) it is quite safe to make this assumption.
if (0 == fbr->sec_per_fat)
{
GET_DWORD(data, fbr->sec_per_fat_32, 0x24);
GET_WORD(data, fbr->ext_flags, 0x28);
GET_WORD(data, fbr->fs_ver, 0x2A);
GET_DWORD(data, fbr->root_cluster, 0x2C);
GET_WORD(data, fbr->fs_info_sec, 0x30);
GET_WORD(data, fbr->bk_boot_sec, 0x32);
GET_BYTE(data, fbr->drv_num, 0x40);
GET_BYTE(data, fbr->ext_sig, 0x42);
GET_DWORD(data, fbr->ser_num, 0x43);
GET_BYTES(data, fbr->vol_name, 11, 0x47);
GET_BYTES(data, fbr->fat_name, 8, 0x52);
}
else
{
GET_BYTE(data, fbr->drv_num, 0x24);
GET_BYTE(data, fbr->ext_sig, 0x26);
GET_DWORD(data, fbr->ser_num, 0x27);
GET_BYTES(data, fbr->vol_name, 11, 0x2B);
GET_BYTES(data, fbr->fat_name, 8, 0x36);
}
// Read the end marker
len = 0x02;
err = disk_read(disk, (void*)data, &len, 0x1FE);
if (err != ENOERR)
return err;
GET_BYTES(data, fbr->exe_marker, 2, 0);
// Zero terminate strings
fbr->oem_name[8] = '\0';
fbr->vol_name[11] = '\0';
fbr->fat_name[8] = '\0';
#if TDE
print_boot_record(fbr);
#endif
return ENOERR;
}