Gazebo Ros Control 及 Controller运用
- 写在前面
- Gazebo ROS Control
- Default Robot HW SIM
- Gazebo ROS Control Plugin
- ROS Controller运用
- 1 position_controllersJointPositionController
- 2 position_controllersJointGroupPositionController
- 3 joint_state_controller
- 31 方式一
- 32 方式二
- 33 效果验证
- 附录
1. 写在前面
第一篇 – 机器人描述: http://blog.csdn.net/sunbibei/article/details/52297524
第二篇 – TRANSMISSION: http://blog.csdn.net/sunbibei/article/details/53287975
在我上一篇博客上, 我们引入了UR5BH机器人, 另外, 对其描述文件中的transmission进行了解析, 其中摘录了如下文件:
<gazebo>
<plugin filename="libgazebo_ros_control.so" name="ros_control">
plugin>
gazebo>
... ...
<transmission name="shoulder_pan_trans">
<type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmissiontype>
<joint name="shoulder_pan_joint">
<hardwareInterface>PositionJointInterfacehardwareInterface>
joint>
<actuator name="shoulder_pan_motor">
<mechanicalReduction>1mechanicalReduction>
actuator>
transmission>
... ...
<transmission name="bh_j32_transmission">
<type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmissiontype>
<joint name="bh_j32_joint"/>
<actuator name="bh_j32">
<hardwareInterface>PositionJointInterfacehardwareInterface>
<mechanicalReduction>1mechanicalReduction>
<motorTorqueConstant>1motorTorqueConstant>
actuator>
transmission>在这段描述中, 除了transmission之外, 另一个引入的, 就是gazebo_ros_control. 本篇作为第三篇, 主要和大家分享一些关于gazebo_ros_control相关的内容。
2. Gazebo ROS Control
在前一篇的基础上, 实际上我们已经能够开始配置MoveIt!来进行机器人控制了。 但是, 为了更进一步的让事情更加清晰, 我们还是耐下心再探讨一下gazebo_ros_control。 包布局如下图所示:
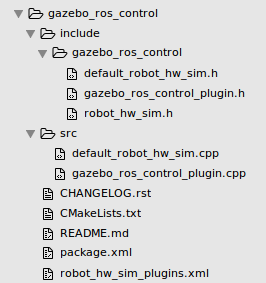
打开package.xml文件, 除了一些依赖包的定义外, 一个比较关键的地方是在export块中, 摘录如下:
... ...
<export>
<gazebo_ros_control plugin="${prefix}/robot_hw_sim_plugins.xml"/>
export>
... ...了解pluginlib的同学肯定知道, 这是将plugin的定义文件导入的步骤。 不熟悉的同学, 可以参考1, 或者 参考2 进行了解。
导入的文件在文件系统中可以看到, 摘录如下:
<library path="lib/libdefault_robot_hw_sim">
<class
name="gazebo_ros_control/DefaultRobotHWSim"
type="gazebo_ros_control::DefaultRobotHWSim"
base_class_type="gazebo_ros_control::RobotHWSim">
<description>
A default robot simulation interface which constructs joint handles from an SDF/URDF.
description>
class>
library>可以看到, 该文件中定义了一个plugin, 就是gazebo_ros_control::DefaultRobotHWSim, 该plugin可以动态的被加载进来。再查看该包的CMakeLists.txt, 可以看到下述内容:
## 2.1. Libraries
add_library(${PROJECT_NAME} src/gazebo_ros_control_plugin.cpp)
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} ${catkin_LIBRARIES} ${GAZEBO_LIBRARIES})
add_library(default_robot_hw_sim src/default_robot_hw_sim.cpp)
target_link_libraries(default_robot_hw_sim ${catkin_LIBRARIES} ${GAZEBO_LIBRARIES})该包总共会生成两个库, 第一个库是gazebo_ros_control, 第二个库是default_robot_hw_sim, 分别都只有一个文件。 下面我们分别来分析这两个库的源码以及所对应完成的任务。
3. Default Robot HW SIM
在default_robot_hw_sim.cpp中, 定义了类DefaultRobotHWSim, 该类继承于gazebo_ros_control::RobotHWSim, 父类定义摘录如下:
namespace gazebo_ros_control {
// Struct for passing loaded joint data
struct JointData
{
std::string name_;
std::string hardware_interface_;
JointData(const std::string& name, const std::string& hardware_interface) :
name_(name),
hardware_interface_(hardware_interface)
{}
};
class RobotHWSim : public hardware_interface::RobotHW
{
public:
virtual ~RobotHWSim() { }
virtual bool initSim(
const std::string& robot_namespace,
ros::NodeHandle model_nh,
gazebo::physics::ModelPtr parent_model,
const urdf::Model *const urdf_model, // 留意该指针有两个const
// TransmissionInfo的内容在前一篇博客中有介绍
std::vector该类定义了gazebo plugin版本的RobotHW,RobotHW定义于ros control包中, 定义了与实际机器人通讯的基本接口, 在编写实际机器人的ros control体系时, 该类是用户必须实现的类。 主要重载read(), write(), preparewitch() 以及doSwitch()四个接口。 在RobotHW中, 这四个函数都有默认实现(默认实现是空, 什么都不做), 都不是纯虚函数。 一般而言, 重载读写函数即可正常工作了。 这个地方, 只是将接口换了个名字, 并且, 几个纯虚函数都必须在子类中进行实现。
类DefaultRobotHWSim的定义摘录如下:
namespace gazebo_ros_control
{
class DefaultRobotHWSim : public gazebo_ros_control::RobotHWSim
{
public:
// 四个纯需函数必须在子类中进行实现。
virtual bool initSim(
const std::string& robot_namespace,
ros::NodeHandle model_nh,
gazebo::physics::ModelPtr parent_model,
const urdf::Model *const urdf_model,
std::vector DefaultRobotHWSimPtr;
}
#endif // #ifndef __GAZEBO_ROS_CONTROL_PLUGIN_DEFAULT_ROBOT_HW_SIM_H_ 由于关于Safty Limits 并不是我们关注的内容。 所以在后面的解析过程中, 我们也会忽略该部分内容, 感兴趣的同学, 可以参考上述网站, 内容也不是很多。下面我们主要关注initSim()的实现, 其他几个函数无非是调用Gazebo的API完成关节数据的读写。
iniSim()函数的实现摘录如下:
bool DefaultRobotHWSim::initSim(
const std::string& robot_namespace,
ros::NodeHandle model_nh,
gazebo::physics::ModelPtr parent_model,
const urdf::Model *const urdf_model,
std::vector element of tranmission " <<
transmissions[j].name_ << " should be nested inside the element, not . " <<
"The transmission will be properly loaded, but please update " <<
"your robot model to remain compatible with future versions of the plugin.");
}
if (joint_interfaces.empty()) {
ROS_WARN_STREAM_NAMED("default_robot_hw_sim", "Joint " << transmissions[j].joints_[0].name_ <<
" of transmission " << transmissions[j].name_ << " does not specify any hardware interface. " <<
"Not adding it to the robot hardware simulation.");
continue;
} else if (joint_interfaces.size() > 1) {
ROS_WARN_STREAM_NAMED("default_robot_hw_sim", "Joint " << transmissions[j].joints_[0].name_ <<
" of transmission " << transmissions[j].name_ << " specifies multiple hardware interfaces. " <<
"Currently the default robot hardware simulation interface only supports one. Using the first entry!");
//continue;
} // 至少包含一个transmission, 多个的话, 将会默认使用第一个, 但并不算错误(没有continue)。
// 初始化各变量(name, pos, vel, eff, 以及cmd
joint_names_[j] = transmissions[j].joints_[0].name_;
joint_position_[j] = 1.0;
joint_velocity_[j] = 0.0;
joint_effort_[j] = 1.0; // N/m for continuous joints
joint_effort_command_[j] = 0.0;
joint_position_command_[j] = 0.0;
joint_velocity_command_[j] = 0.0;
// 常引用
const std::string& hardware_interface = joint_interfaces.front();
// Debug
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM_NAMED("default_robot_hw_sim","Loading joint '" << joint_names_[j]
<< "' of type '" << hardware_interface << "'");
// hardware_interface::JointStateInterface初始化
// 将类中pos, vel, eff三个变量的地址绑定对应于三个变量joint_xxx[j]
js_interface_.registerHandle(hardware_interface::JointStateHandle(
joint_names_[j], &joint_position_[j], &joint_velocity_[j], &joint_effort_[j]));
// 根据申明的transmission, 创建对应的JointHandle.
hardware_interface::JointHandle joint_handle;
if(hardware_interface == "EffortJointInterface") {
// Create effort joint interface
joint_control_methods_[j] = EFFORT;
joint_handle = hardware_interface::JointHandle(js_interface_.getHandle(joint_names_[j]),
&joint_effort_command_[j]);
ej_interface_.registerHandle(joint_handle);
} else if(hardware_interface == "PositionJointInterface") {
// Create position joint interface
joint_control_methods_[j] = POSITION;
joint_handle = hardware_interface::JointHandle(js_interface_.getHandle(joint_names_[j]),
&joint_position_command_[j]);
pj_interface_.registerHandle(joint_handle);
} else if(hardware_interface == "VelocityJointInterface") {
// Create velocity joint interface
joint_control_methods_[j] = VELOCITY;
joint_handle = hardware_interface::JointHandle(js_interface_.getHandle(joint_names_[j]),
&joint_velocity_command_[j]);
vj_interface_.registerHandle(joint_handle);
} else {
ROS_FATAL_STREAM_NAMED("default_robot_hw_sim","No matching hardware interface found for '"
<< hardware_interface );
return false;
}
// Get the gazebo joint that corresponds to the robot joint.
gazebo::physics::JointPtr joint = parent_model->GetJoint(joint_names_[j]);
if (!joint) {
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("This robot has a joint named \"" << joint_names_[j]
<< "\" which is not in the gazebo model.");
return false;
}
sim_joints_.push_back(joint);
registerJointLimits(joint_names_[j], joint_handle, joint_control_methods_[j],
joint_limit_nh, urdf_model,
&joint_types_[j], &joint_lower_limits_[j], &joint_upper_limits_[j],
&joint_effort_limits_[j]);
// 初始化控制器
if (joint_control_methods_[j] != EFFORT) {
const ros::NodeHandle nh(model_nh, "/gazebo_ros_control/pid_gains/" +
joint_names_[j]);
if (pid_controllers_[j].init(nh, true)) {
switch (joint_control_methods_[j]) {
case POSITION:
joint_control_methods_[j] = POSITION_PID;
break;
case VELOCITY:
joint_control_methods_[j] = VELOCITY_PID;
break;
}
} else {
#if GAZEBO_MAJOR_VERSION > 2
joint->SetParam("fmax", 0, joint_effort_limits_[j]);
#else
joint->SetMaxForce(0, joint_effort_limits_[j]);
#endif
}
}
}
// 注册接口, 父类RobotHW是继承于InterfaceManager的
// 实则是调用InterfaceManager的方法。
registerInterface(&js_interface_);
registerInterface(&ej_interface_);
registerInterface(&pj_interface_);
registerInterface(&vj_interface_);
// Initialize the emergency stop code.
e_stop_active_ = false;
last_e_stop_active_ = false;
return true;
}从上面的实现可以看到, 通过URDF文件中设定transmission, DefaultRobotHWSim解析所有的transmission块, 保存每个关节的JointHandle, 并提供读写数据的接口。其中JointHandle的管理方式是调用ROS Control中的hardware_interface, 而这一块的内容, 将在后面的博客中专门分析, 这部分的实现非常巧妙, 也很有意思。
4. Gazebo ROS Control Plugin
GazeboRosControlPlugin继承于gazebo::ModelPlugin类, 是一个可以由Gazebo加载的Plugin, 该类中最为关键的两个函数分别是: Load() and Update(). 分别的实现如下:
Load()的实现如下所示:
void GazeboRosControlPlugin::Load(gazebo::physics::ModelPtr parent, sdf::ElementPtr sdf)
{
ROS_INFO_STREAM_NAMED("gazebo_ros_control","Loading gazebo_ros_control plugin");
// Save pointers to the model
parent_model_ = parent;
sdf_ = sdf;
// 一系列的容错判断, 以及获取sdf中所定义的参数
... ...
// 从sdf_中获得RobotHWSim的类型
if(sdf_->HasElement("robotSimType")) {
robot_hw_sim_type_str_ = sdf_->Get<std::string>("robotSimType");
} else {
robot_hw_sim_type_str_ = "gazebo_ros_control/DefaultRobotHWSim";
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM_NAMED("loadThread","Using default plugin for RobotHWSim (none specified in URDF/SDF)\""<"\"");
}
... ...
// Get parameters/settings for controllers from ROS param server
model_nh_ = ros::NodeHandle(robot_namespace_);
... ...
// 从参数服务器中获得URDF
const std::string urdf_string = getURDF(robot_description_);
if (!parseTransmissionsFromURDF(urdf_string)) {
ROS_ERROR_NAMED("gazebo_ros_control",
"Error parsing URDF in gazebo_ros_control plugin, plugin not active.\n");
return;
}
// 通过ClassLoader加载RobotHWSim(默认使用的是DefaultRobotHWSim)
try {
robot_hw_sim_loader_.reset
(new pluginlib::ClassLoader
("gazebo_ros_control",
"gazebo_ros_control::RobotHWSim"));
robot_hw_sim_ = robot_hw_sim_loader_->createInstance(robot_hw_sim_type_str_);
urdf::Model urdf_model;
const urdf::Model *const urdf_model_ptr = urdf_model.initString(urdf_string) ? &urdf_model : NULL;
// 调用前面分析过的那个函数, initSim, 在RobotHWSim中初始化所有关节句柄
if(!robot_hw_sim_->initSim(robot_namespace_, model_nh_, parent_model_, urdf_model_ptr, transmissions_)) {
ROS_FATAL_NAMED("gazebo_ros_control","Could not initialize robot simulation interface");
return;
}
// 创建ControllerManager, 可以看到, ControllerManager是在这个地方被初始化。
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM_NAMED("ros_control_plugin","Loading controller_manager");
controller_manager_.reset
(new controller_manager::ControllerManager(robot_hw_sim_.get(), model_nh_));
// 监听update event, 每个simulation iteration都会广播该event.
update_connection_ =
gazebo::event::Events::ConnectWorldUpdateBegin
(boost::bind(&GazeboRosControlPlugin::Update, this));
} catch(pluginlib::LibraryLoadException &ex) {
ROS_FATAL_STREAM_NAMED("gazebo_ros_control", "Failed to create robot simulation interface loader: "
<< ex.what());
}
ROS_INFO_NAMED("gazebo_ros_control", "Loaded gazebo_ros_control.");
} 上述函数的实现中, ... ...代表有省略部分。 仅抽离出来了比较重要的部分, 将一些容错和参数获取的代码给省略了。 可以看到, 在该函数中, 完成了RobotHW的初始化(在Gazebo中, 是通过RobotHWSim类呈现, 该类实际上也是RobotHW的子类), 完成了ControllerManager的初始化, 并将RosControl循环(update()函数)与update event进行了绑定, 在每次事件到来的时候, 都将会进行循环。
update()函数的实现如下所示:
// Called by the world update start event
void GazeboRosControlPlugin::Update() {
// 得到当前时间以及和上一次更新的时间间隔
gazebo::common::Time gz_time_now = parent_model_->GetWorld()->GetSimTime();
ros::Time sim_time_ros(gz_time_now.sec, gz_time_now.nsec);
ros::Duration sim_period = sim_time_ros - last_update_sim_time_ros_;
robot_hw_sim_->eStopActive(e_stop_active_);
// Check if we should update the controllers
if(sim_period >= control_period_) {
// 交替更新前一次时间变量
last_update_sim_time_ros_ = sim_time_ros;
// 调用RobotHW接口, 读关节数据, 保证当前关节值是最新值
robot_hw_sim_->readSim(sim_time_ros, sim_period);
// Compute the controller commands
bool reset_ctrlrs;
if (e_stop_active_) {
reset_ctrlrs = false;
last_e_stop_active_ = true;
} else {
if (last_e_stop_active_) {
reset_ctrlrs = true;
last_e_stop_active_ = false;
} else {
reset_ctrlrs = false;
}
}
// ControlManager类的update接口调用, 将会顺序调用每一个加载上来的控制器的update()
controller_manager_->update(sim_time_ros, sim_period, reset_ctrlrs);
}
// 每一个正在运行的控制器update调用之后, 对应被控制关节的命令就更新完成
// 现在再调用RobotHW的写操作。 完成对关节命令的写入。
// 不但在仿真中RosControl循环是这个流程, 在实际RosControl循环中, 也是这个流程。
robot_hw_sim_->writeSim(sim_time_ros, sim_time_ros - last_write_sim_time_ros_);
last_write_sim_time_ros_ = sim_time_ros;// 交替更新前一次时间变量
}5. ROS Controller运用
在前一篇中, 我们在Gazebo中已经启动起来了ur2bh机器人。 输入命令:roslaunch ur5bh_gazebo ur5bh_gazebo.launch。 在启动起来Gazebo之后, 命令行中可以看到如下几行输出:

而这几行的输出, 正是在前面Load()函数中的提示输出。 显然, 我们的GazeboRosControlPlugin已经在launch文件中, 被启动加载了。当然, 这个时候ControllerManager也处于就绪状态, 可以重新打开命令行, 输入rosservice call /controller_manager/list_controller_types进行验证, 该服务器将会返回一大堆信息。现在, 我们就可以在配置文件里面指定我们所需要的控制器了。 比如说, 由于我们在transmission块中, 指定的是PositionJointInterface, 所以, 我们可以使用的控制器只能是位置控制器。 下面我们试着加一两个控制器。
5.1. position_controllers/JointPositionController
该控制器实现于ros_controllers包中, 这个包提供了很多默认控制器, 可以直接使用, 感兴趣的同学, 也可以到Github 上进行下载查看他们的源码。要配置这些控制器, 只需要简单的配置文件即可搞定。
打开命令行, 以此输入:
roscd ur5bh_gazebo && mkdir config
vim config/controllers.yaml将下述内容复制到该文件中:
shoulder_pan_position_controller:
type: position_controllers/JointPositionController
joint: shoulder_pan_joint
pid:
p: 100.0
d: 10.0第一行是控制器名称, 第二行是控制器类型, 第三行是欲控制的关节名称, 第四行是指定该控制器的PID参数。运行rosed ur5bh_gazebo ur5bh_gazebo.launch, 加入下述内容在文件中:
<rosparam file="$(find ur5bh_gazebo)/config/controllers.yaml" command="load"/>
<node name="joint_controller_spawner" pkg="controller_manager" type="controller_manager"
args="spawn shoulder_pan_position_controller"
respawn="false" output="screen"/>上述内容, 第一行是将yaml文件中定义的内容, 加载到参数服务器。 第二行类似于在命令行中运行rosrun controller_manager controller_manager spawn shoulder_pan_position_controller. 完成的功能, 是创建一个节点, 请求ControllerManager的加载服务器的服务, 请求加载控制器shoulder_pan_position_controller, 而该控制器的相关参数定义于yaml文件中。
复制保存之后, 打开命令行, 运行roslaunch ur5bh_gazebo ur5bh_gazebo.launch, 同样, 可以看到前篇博客所示的状态, 同时, 在命令行中, 可以看到如下输出。
再打开一个命令行, 输入下述命令可以查看我们加载的控制器的效果, rostopic pub /shoulder_pan_position_controller/command std_msgs/Float64 50
在Gazebo中可以看到, 我们的机器人转动了。 我们在上述yaml中, 只是定义了一个关节的控制器, 当然, 我们可以配置多个控制器, 分别控制多个关节. 方法类似, 就不示例了。
5.2. position_controllers/JointGroupPositionController
另一种方式, 可以加载position_controllers/JointGroupPositionController, 指定一个控制器控制多个关节。示例如下, 首先在config/controllers.yaml中添加下述内容:
finger1_position_controller:
type: position_controllers/JointGroupPositionController
joints:
- bh_j11_joint
- bh_j12_joint
- bh_j13_joint在launch文件中, 将发起的节点那一行更换成:
<node name="joint_controller_spawner" pkg="controller_manager" type="controller_manager"
args="spawn shoulder_pan_position_controller finger1_position_controller"
respawn="false" output="screen"/>同样, 打开命令行, 运行roslaunch ur5bh_gazebo ur5bh_gazebo.launch, 打开Gazebo之后, 应该能够在命令行中看到下述输出内容:

新打开一个命令行, 输入下述命令:
rostopic pub /finger1_position_controller/command std_msgs/Float64MultiArray '{data: [10.0, 10.0, 10.0]}', 在Gazebo中, 可以看到手指动了。
5.3. joint_state_controller
一般情况下, 我们的关节数据都是需要通过/joint_states话题传递出来, 这样, RobotStatePublisher才能够解析发布/tf数据。 而现在我们是没有/joint_states话题的(可以在命令行中通过rostopic list来查看)。这个话题一个最直接的使用, 就是在rviz中。 在rviz中是可以直接查看我们机器人当前状态的。比如, 打开rviz(运行rosrun rviz rviz), 当前我们在rviz中添加RobotModel插件, 看到的应该是下述状态:

当然, 也是不能在该插件中看到我们的ur5bh机器人。 解决这个问题, ros control为我们提供了一个默认控制器, 专门用来发布/joint_states话题数据。有两种方式可以添加该控制器, 完成其中一种即可。
5.3.1. 方式一
首先在config/controllers.yaml中添加下述内容:
joint_state_controller:
type: joint_state_controller/JointStateController
publish_rate: 50在launch文件中, 将发起的节点那一行更换成:
<node name="joint_controller_spawner" pkg="controller_manager" type="controller_manager"
args="spawn shoulder_pan_position_controller finger1_position_controller joint_state_controller"
respawn="false" output="screen"/>5.3.2. 方式二
除了通过上述方式加载joint_state_controller外, 还可以直接将该控制器写到URDF文件中去。由于我们在ur5bh_gazebo.launch文件中, 上传到参数服务器的文件是ur5bh.urdf, 所以修改该模型文件, 在ur5bh.urdf中的gazebo块中(在该文件的头部)。修改后gazebo块的内容如下(删除了其中注释的部分内容):
<gazebo>
<plugin filename="libgazebo_ros_control.so" name="ros_control">
plugin>
<plugin name="joint_state_publisher" filename="libgazebo_ros_joint_state_publisher.so">
<jointName>
bh_j11_joint, bh_j12_joint, bh_j13_joint, bh_j21_joint, bh_j22_joint, bh_j23_joint,
bh_j32_joint, bh_j33_joint, elbow_joint, shoulder_lift_joint, shoulder_pan_joint,
wrist_1_joint, wrist_2_joint, wrist_3_joint
jointName>
<updateRate>50updateRate>
<alwaysOn>truealwaysOn>
plugin>
gazebo>5.3.3. 效果验证
同样, 打开命令行, 运行roslaunch ur5bh_gazebo ur5bh_gazebo.launch, 打开Gazebo之后, 再新打开一个命令行, 输入rostopic echo /joint_states, 可以看到该话题的数据, 发布频率是按照我们指定的50Hz. 这个时候再看rviz, 其中RobotModel还是一堆错误, 这是因为该插件需要的/tf数据还是没有。 解决办法: 新打开一个命令行, 输入rosrun robot_state_publisher robot_state_publisher。 不出意外, 可以看到如下效果:
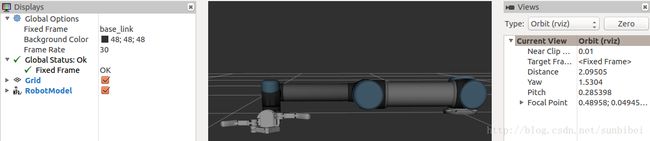
可以看到, rviz中, 模型的状态和Gazebo中是保持一直的。所以robot_state_publisher节点的运行是必要的。 可以将其直接添加到ur5bh_gazebo.launch文件中, 将下述内容添加到launch文件中:
<node pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" name="robot_state_publisher">
<param name="publish_frequency" type="double" value="50.0" />
<param name="tf_prefix" type="string" value="" />
node>附录
从rqt的插件中, 可以查看到整体的结构图, 可以清晰的看到/joint_states起到的作用。

下面把最终的controller.yaml 和 ur5bh_gazebo.launch 两个文件的全部内容附属在下面:
ur5bh_gazebo/config/controllers.launch
shoulder_pan_position_controller:
type: position_controllers/JointPositionController
joint: shoulder_pan_joint
pid:
p: 100.0
d: 10.0
finger1_position_controller:
type: position_controllers/JointGroupPositionController
joints:
- bh_j11_joint
- bh_j12_joint
- bh_j13_joint
joint_state_controller:
type: joint_state_controller/JointStateController
publish_rate: 50ur5bh_gazebo/launch/ur5bh_gazebo.launch
<launch>
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch" />
<param name="robot_description"
command="$(find xacro)/xacro.py '$(find ur5bh_description)/urdf/ur5bh.urdf'" />
<node name="spawn_gazebo_model" pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model"
args="-urdf -param robot_description -model robot -z 0.1"
respawn="false" output="screen" />
<rosparam file="$(find ur5bh_gazebo)/config/controller.yaml" command="load"/>
<node name="joint_controller_spawner" pkg="controller_manager" type="controller_manager"
args="spawn shoulder_pan_position_controller finger1_position_controller joint_state_controller"
respawn="false" output="screen"/>
<node pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" name="robot_state_publisher">
<param name="publish_frequency" type="double" value="50.0" />
<param name="tf_prefix" type="string" value="" />
node>
launch>