BP神经网络的MATLAB实现
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/WuchangI/article/details/79236016#train函数
目录
一. BP神经网络实现(不使用MATLAB神经网络工具箱)
1. 问题
2. 分析
3. MATLAB实现代码
4. 运行结果
二. 使用MATLAB的神经网络工具箱简易实现BP网络
1. 问题
2. 分析
3. 工具箱中的相关函数(一些参考了MATLAB自带的英文手册)
mapminmax函数
newff函数(新版本)
关于net.trainParam的常用属性
train函数
sim函数
4. MATLAB实现代码
一. BP神经网络实现(不使用MATLAB神经网络工具箱)
1. 问题
公路运量主要包括公路客运量和公路货运量两方面。某个地区的公路运量主要与该地区的人数、机动车数量和公路面积有关,已知该地区20年(1990-2009)的公路运量相关数据如下:
人数/万人
20.55 22.44 25.37 27.13 29.45 30.10 30.96 34.06 36.42 38.09 39.13 39.99 41.93 44.59 47.30 52.89 55.73 56.76 59.17 60.63
机动车数量/万辆
0.6 0.75 0.85 0.9 1.05 1.35 1.45 1.6 1.7 1.85 2.15 2.2 2.25 2.35 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.85 2.95 3.1
公路面积/单位:万平方公里
0.09 0.11 0.11 0.14 0.20 0.23 0.23 0.32 0.32 0.34 0.36 0.36 0.38 0.49 0.56 0.59 0.59 0.67 0.69 0.79
公路客运量/万人
5126 6217 7730 9145 10460 11387 12353 15750 18304 19836 21024 19490 20433 22598 25107 33442 36836 40548 42927 43462
公路货运量/万吨
1237 1379 1385 1399 1663 1714 1834 4322 8132 8936 11099 11203 10524 11115 13320 16762 18673 20724 20803 21804
2. 分析
样本数据较多,且已知影响数据的因素(三大因素:该地区的人数、机动车数量和公路面积),可考虑将其作为BP神经网络的训练集,对该神经网络进行训练,然后对训练好的神经网络进行测试,最后使用测试合格的神经网络进行预测工作。
3. MATLAB实现代码
BP_road.m
numberOfSample = 20; %输入样本数量
%取测试样本数量等于输入(训练集)样本数量,因为输入样本(训练集)容量较少,否则一般必须用新鲜数据进行测试
numberOfTestSample = 20;
numberOfForcastSample = 2;
numberOfHiddenNeure = 8;
inputDimension = 3;
outputDimension = 2;
%准备好训练集
%人数(单位:万人)
numberOfPeople=[20.55 22.44 25.37 27.13 29.45 30.10 30.96 34.06 36.42 38.09 39.13 39.99 41.93 44.59 47.30 52.89 55.73 56.76 59.17 60.63];
%机动车数(单位:万辆)
numberOfAutomobile=[0.6 0.75 0.85 0.9 1.05 1.35 1.45 1.6 1.7 1.85 2.15 2.2 2.25 2.35 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.85 2.95 3.1];
%公路面积(单位:万平方公里)
roadArea=[0.09 0.11 0.11 0.14 0.20 0.23 0.23 0.32 0.32 0.34 0.36 0.36 0.38 0.49 0.56 0.59 0.59 0.67 0.69 0.79];
%公路客运量(单位:万人)
passengerVolume = [5126 6217 7730 9145 10460 11387 12353 15750 18304 19836 21024 19490 20433 22598 25107 33442 36836 40548 42927 43462];
%公路货运量(单位:万吨)
freightVolume = [1237 1379 1385 1399 1663 1714 1834 4322 8132 8936 11099 11203 10524 11115 13320 16762 18673 20724 20803 21804];
%由系统时钟种子产生随机数
rand('state', sum(100*clock));
%输入数据矩阵
input = [numberOfPeople; numberOfAutomobile; roadArea];
%目标(输出)数据矩阵
output = [passengerVolume; freightVolume];
%对训练集中的输入数据矩阵和目标数据矩阵进行归一化处理
[sampleInput, minp, maxp, tmp, mint, maxt] = premnmx(input, output);
%噪声强度
noiseIntensity = 0.01;
%利用正态分布产生噪声
noise = noiseIntensity * randn(outputDimension, numberOfSample);
%给样本输出矩阵tmp添加噪声,防止网络过度拟合
sampleOutput = tmp + noise;
%取测试样本输入(输出)与输入样本相同,因为输入样本(训练集)容量较少,否则一般必须用新鲜数据进行测试
testSampleInput = sampleInput;
testSampleOutput = sampleOutput;
%最大训练次数
maxEpochs = 50000;
%网络的学习速率
learningRate = 0.035;
%训练网络所要达到的目标误差
error0 = 0.65*10^(-3);
%初始化输入层与隐含层之间的权值
W1 = 0.5 * rand(numberOfHiddenNeure, inputDimension) - 0.1;
%初始化输入层与隐含层之间的阈值
B1 = 0.5 * rand(numberOfHiddenNeure, 1) - 0.1;
%初始化输出层与隐含层之间的权值
W2 = 0.5 * rand(outputDimension, numberOfHiddenNeure) - 0.1;
%初始化输出层与隐含层之间的阈值
B2 = 0.5 * rand(outputDimension, 1) - 0.1;
%保存能量函数(误差平方和)的历史记录
errorHistory = [];
for i = 1:maxEpochs
%隐含层输出
hiddenOutput = logsig(W1 * sampleInput + repmat(B1, 1, numberOfSample));
%输出层输出
networkOutput = W2 * hiddenOutput + repmat(B2, 1, numberOfSample);
%实际输出与网络输出之差
error = sampleOutput - networkOutput;
%计算能量函数(误差平方和)
E = sumsqr(error);
errorHistory = [errorHistory E];
if E < error0
break;
end
%以下依据能量函数的负梯度下降原理对权值和阈值进行调整
delta2 = error;
delta1 = W2' * delta2.*hiddenOutput.*(1 - hiddenOutput);
dW2 = delta2 * hiddenOutput';
dB2 = delta2 * ones(numberOfSample, 1);
dW1 = delta1 * sampleInput';
dB1 = delta1 * ones(numberOfSample, 1);
W2 = W2 + learningRate * dW2;
B2 = B2 + learningRate * dB2;
W1 = W1 + learningRate * dW1;
B1 = B1 + learningRate * dB1;
end
%下面对已经训练好的网络进行(仿真)测试
%对测试样本进行处理
testHiddenOutput = logsig(W1 * testSampleInput + repmat(B1, 1, numberOfTestSample));
testNetworkOutput = W2 * testHiddenOutput + repmat(B2, 1, numberOfTestSample);
%还原网络输出层的结果(反归一化)
a = postmnmx(testNetworkOutput, mint, maxt);
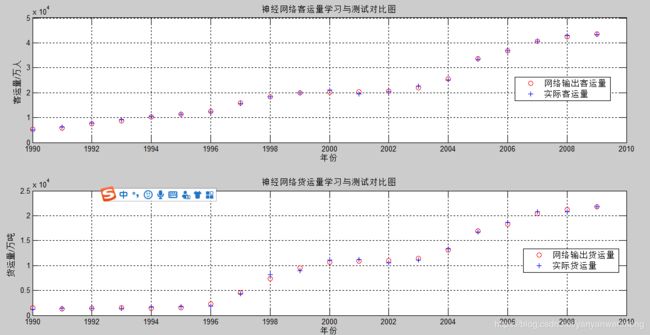
%绘制测试样本神经网络输出和实际样本输出的对比图(figure(1))--------------------------------------
t = 1990:2009;
%测试样本网络输出客运量
a1 = a(1,:);
%测试样本网络输出货运量
a2 = a(2,:);
figure(1);
subplot(2, 1, 1); plot(t, a1, 'ro', t, passengerVolume, 'b+');
legend('网络输出客运量', '实际客运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('客运量/万人');
title('神经网络客运量学习与测试对比图');
grid on;
subplot(2, 1, 2); plot(t, a2, 'ro', t, freightVolume, 'b+');
legend('网络输出货运量', '实际货运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('货运量/万吨');
title('神经网络货运量学习与测试对比图');
grid on;
%使用训练好的神经网络对新输入数据进行预测
%新输入数据(2010年和2011年的相关数据)
newInput = [73.39 75.55; 3.9635 4.0975; 0.9880 1.0268];
%利用原始输入数据(训练集的输入数据)的归一化参数对新输入数据进行归一化
newInput = tramnmx(newInput, minp, maxp);
newHiddenOutput = logsig(W1 * newInput + repmat(B1, 1, numberOfForcastSample));
newOutput = W2 * newHiddenOutput + repmat(B2, 1, numberOfForcastSample);
newOutput = postmnmx(newOutput, mint, maxt);
disp('预测2010和2011年的公路客运量分别为(单位:万人):');
newOutput(1,:)
disp('预测2010和2011年的公路货运量分别为(单位:万吨):');
newOutput(2,:)
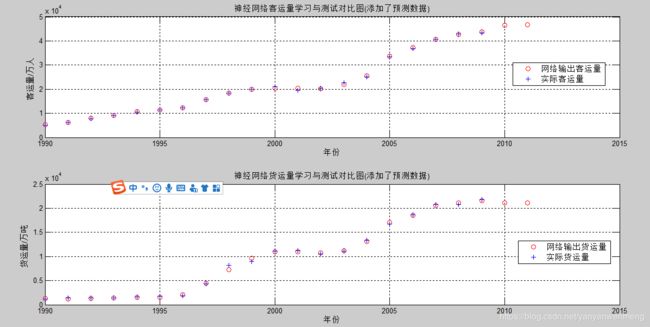
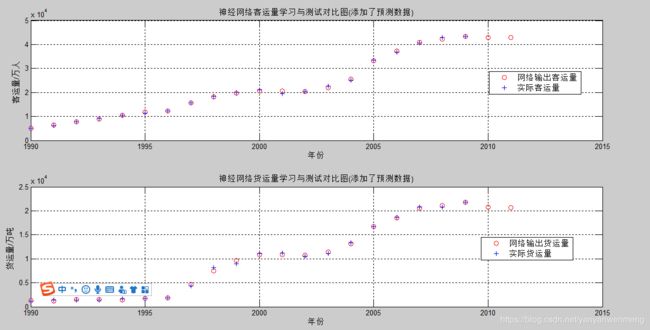
%在figure(1)的基础上绘制2010和2011年的预测情况-------------------------------------------------
figure(2);
t1 = 1990:2011;
subplot(2, 1, 1); plot(t1, [a1 newOutput(1,:)], 'ro', t, passengerVolume, 'b+');
legend('网络输出客运量', '实际客运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('客运量/万人');
title('神经网络客运量学习与测试对比图(添加了预测数据)');
grid on;
subplot(2, 1, 2); plot(t1, [a2 newOutput(2,:)], 'ro', t, freightVolume, 'b+');
legend('网络输出货运量', '实际货运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('货运量/万吨');
title('神经网络货运量学习与测试对比图(添加了预测数据)');
grid on;
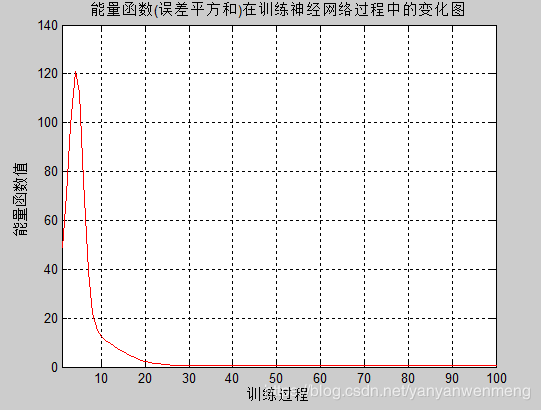
%观察能量函数(误差平方和)在训练神经网络过程中的变化情况------------------------------------------
figure(3);
n = length(errorHistory);
t3 = 1:n;
plot(t3, errorHistory, 'r-');
%为了更加清楚地观察出能量函数值的变化情况,这里我只绘制前100次的训练情况
xlim([1 100]);
xlabel('训练过程');
ylabel('能量函数值');
title('能量函数(误差平方和)在训练神经网络过程中的变化图');
grid on;
4. 运行结果
预测2010和2011年的公路客运量分别为(单位:万人):ans =
1.0e+04 *
4.6188 4.6601
预测2010和2011年的公路货运量分别为(单位:万吨):
ans =
1.0e+04 *
2.1521 2.1519
5. 绘制的图像
可以看出,使用BP网络中的负梯度下降原理之后,效果显著。
二. 使用MATLAB的神经网络工具箱简易实现BP网络
1. 问题
同<一>
2. 分析
同<一>
3. 工具箱中的相关函数(一些参考了MATLAB自带的英文手册)
mapminmax函数
- 功能:通过将原矩阵每行的最小值和最大值映射到[YMIN,YMAX]来得到规范化的矩阵。
- 算法:y = ( ymax - ymin ) * ( x - xmin ) / ( xmax - xmin ) + ymin
(注:当xmax与xmin相等时,则对原矩阵使用mapminmax函数仍得到原矩阵)
- 默认算法:
(默认情况下,mapminmax函数的YMIN和YMAX分别是-1和1)
y = 2 * ( x - xmin ) / ( xmax - xmin ) - 1
- [Y,PS] = mapminmax(X)
- X:原矩阵
- Y:对矩阵X进行规范化得到的矩阵
- PS:存放关于原矩阵规范化过程中的相关映射数据的结构体
- [Y,PS] = mapminmax(X,FP)
- X:原矩阵
- FP:含有字段FP.ymin和FP.ymax的结构体
- Y:对矩阵X进行规范化得到的矩阵(使用在FP的ymin和ymax规定下的算法)
- PS:存放关于原矩阵规范化过程中的相关映射数据的结构体
- Y = mapminmax(‘apply’,X,PS)
- ’apply’:必写
- X:原矩阵
- PS:存放关于某个矩阵规范化过程中的相关映射数据的结构体
- Y:对矩阵X进行规范化得到的矩阵(使用PS中的规范化方式)
- X = mapminmax(‘reverse’,Y,PS)
- ’reverse’:必写
- Y:某个矩阵
- PS:存放关于某个矩阵规范化过程中的相关映射数据的结构体
- X:将矩阵Y反规范化得到的矩阵(使用PS中的规范化方式,这里指将矩阵X转换为矩阵Y的规范化方式)
newff函数(新版本)
- a. 功能:建立一个前馈反向传播(BP)网络。
- b. net=newff(P,T,S)
- P: 输入数据矩阵。(RxQ1),其中Q1代表R元的输入向量。其数据意义是矩阵P有Q1列,每一列都是一个样本,而每个样本有R个属性(特征)。一般矩阵P需要事先归一化好,即P的每一行都归一化到[0 1]或者[-1 1]。
- T:目标数据矩阵。(SNxQ2),其中Q2代表SN元的目标向量。数据意义参考上面,矩阵T也是事先归一化好的。
- S:第i层的神经元个数。(新版本中可以省略输出层的神经元个数不写,因为输出层的神经元个数已经取决于T)
- c. net = newff(P,T,S,TF,BTF,BLF,PF,IPF,OPF,DDF)(提供了可选择的参数)
- TF:相关层的传递函数,默认隐含层使用tansig函数,输出层使用purelin函数。
- BTF:BP神经网络学习训练函数,默认值为trainlm函数。
- BLF:权重学习函数,默认值为learngdm。
- PF:性能函数,默认值为mse。
- PF,OPF,DDF均为默认值即可。
- d. 常用的传递函数:
- purelin:线性传递函数
- tansig:正切 S 型传递函数
- logsig: 对数 S 型传递函数
(注意:隐含层和输出层函数的选择对BP神经网络预测精度有较大影响,一般隐含层节点传递函数选用tansig函数或logsig函数,输出层节点转移函数选用tansig函数或purelin函数。)
关于net.trainParam的常用属性
(假定已经定义了一个BP网络net)
* net.trainParam.show: 两次显示之间的训练次数
* net.trainParam.epochs: 最大训练次数
* net.trainParam.lr: 网络的学习速率
* net.trainParam.goal: 训练网络所要达到的目标误差
* net.trainParam.time: 最长训练时间(秒)
train函数
- 功能:训练一个神经网络
- [NET2,TR] = train(NET1,X,T)(也可[NET2] = train(NET1,X,T) )
- NET1:待训练的网络
- X: 输入数据矩阵(已归一化)
- T:目标数据矩阵(已归一化)
- NET2:训练得到的网络TR:存放有关训练过程的数据的结构体
sim函数
- 功能:模拟Simulink模型
- SimOut = sim(‘MODEL’, PARAMETERS)
- (见名知意,不必再解释)
4. MATLAB实现代码
BP_toolbox_road.m
%准备好训练集
%人数(单位:万人)
numberOfPeople=[20.55 22.44 25.37 27.13 29.45 30.10 30.96 34.06 36.42 38.09 39.13 39.99 41.93 44.59 47.30 52.89 55.73 56.76 59.17 60.63];
%机动车数(单位:万辆)
numberOfAutomobile=[0.6 0.75 0.85 0.9 1.05 1.35 1.45 1.6 1.7 1.85 2.15 2.2 2.25 2.35 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.85 2.95 3.1];
%公路面积(单位:万平方公里)
roadArea=[0.09 0.11 0.11 0.14 0.20 0.23 0.23 0.32 0.32 0.34 0.36 0.36 0.38 0.49 0.56 0.59 0.59 0.67 0.69 0.79];
%公路客运量(单位:万人)
passengerVolume = [5126 6217 7730 9145 10460 11387 12353 15750 18304 19836 21024 19490 20433 22598 25107 33442 36836 40548 42927 43462];
%公路货运量(单位:万吨)
freightVolume = [1237 1379 1385 1399 1663 1714 1834 4322 8132 8936 11099 11203 10524 11115 13320 16762 18673 20724 20803 21804];
%输入数据矩阵
p = [numberOfPeople; numberOfAutomobile; roadArea];
%目标(输出)数据矩阵
t = [passengerVolume; freightVolume];
%对训练集中的输入数据矩阵和目标数据矩阵进行归一化处理
[pn, inputStr] = mapminmax(p);
[tn, outputStr] = mapminmax(t);
%建立BP神经网络
net = newff(pn, tn, [3 7 2], {'purelin', 'logsig', 'purelin'});
%每10轮回显示一次结果
net.trainParam.show = 10;
%最大训练次数
net.trainParam.epochs = 5000;
%网络的学习速率
net.trainParam.lr = 0.05;
%训练网络所要达到的目标误差
net.trainParam.goal = 0.65 * 10^(-3);
%网络误差如果连续6次迭代都没变化,则matlab会默认终止训练。为了让程序继续运行,用以下命令取消这条设置
net.divideFcn = '';
%开始训练网络
net = train(net, pn, tn);
%使用训练好的网络,基于训练集的数据对BP网络进行仿真得到网络输出结果
%(因为输入样本(训练集)容量较少,否则一般必须用新鲜数据进行仿真测试)
answer = sim(net, pn);
%反归一化
answer1 = mapminmax('reverse', answer, outputStr);
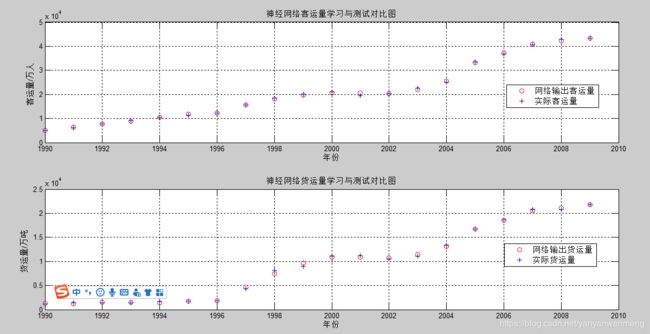
%绘制测试样本神经网络输出和实际样本输出的对比图(figure(1))-------------------------------------------
t = 1990:2009;
%测试样本网络输出客运量
a1 = answer1(1,:);
%测试样本网络输出货运量
a2 = answer1(2,:);
figure(1);
subplot(2, 1, 1); plot(t, a1, 'ro', t, passengerVolume, 'b+');
legend('网络输出客运量', '实际客运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('客运量/万人');
title('神经网络客运量学习与测试对比图');
grid on;
subplot(2, 1, 2); plot(t, a2, 'ro', t, freightVolume, 'b+');
legend('网络输出货运量', '实际货运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('货运量/万吨');
title('神经网络货运量学习与测试对比图');
grid on;
%使用训练好的神经网络对新输入数据进行预测
%新输入数据(2010年和2011年的相关数据)
newInput = [73.39 75.55; 3.9635 4.0975; 0.9880 1.0268];
%利用原始输入数据(训练集的输入数据)的归一化参数对新输入数据进行归一化
newInput = mapminmax('apply', newInput, inputStr);
%进行仿真
newOutput = sim(net, newInput);
%反归一化
newOutput = mapminmax('reverse',newOutput, outputStr);
disp('预测2010和2011年的公路客运量分别为(单位:万人):');
newOutput(1,:)
disp('预测2010和2011年的公路货运量分别为(单位:万吨):');
newOutput(2,:)
%在figure(1)的基础上绘制2010和2011年的预测情况-------------------------------------------------------
figure(2);
t1 = 1990:2011;
subplot(2, 1, 1); plot(t1, [a1 newOutput(1,:)], 'ro', t, passengerVolume, 'b+');
legend('网络输出客运量', '实际客运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('客运量/万人');
title('神经网络客运量学习与测试对比图(添加了预测数据)');
grid on;
subplot(2, 1, 2); plot(t1, [a2 newOutput(2,:)], 'ro', t, freightVolume, 'b+');
legend('网络输出货运量', '实际货运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('货运量/万吨');
title('神经网络货运量学习与测试对比图(添加了预测数据)');
grid on;
5. 运行结果
预测2010和2011年的公路客运量分别为(单位:万人):ans =
1.0e+04 *
4.4384 4.4656
预测2010和2011年的公路货运量分别为(单位:万吨):
ans =
1.0e+04 *
2.1042 2.1139
6. 绘制的图像
figure(1)
训练集和测试集不同的代码
%% 准备好训练集和测试集
%人数(单位:万人)
numberOfPeople=[20.55 22.44 25.37 27.13 29.45 30.10 30.96 34.06 36.42 38.09 39.13 39.99 41.93 44.59 47.30 52.89 55.73 56.76 59.17 60.63];
%机动车数(单位:万辆)
numberOfAutomobile=[0.6 0.75 0.85 0.9 1.05 1.35 1.45 1.6 1.7 1.85 2.15 2.2 2.25 2.35 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.85 2.95 3.1];
%公路面积(单位:万平方公里)
roadArea=[0.09 0.11 0.11 0.14 0.20 0.23 0.23 0.32 0.32 0.34 0.36 0.36 0.38 0.49 0.56 0.59 0.59 0.67 0.69 0.79];
%公路客运量(单位:万人)
passengerVolume = [5126 6217 7730 9145 10460 11387 12353 15750 18304 19836 21024 19490 20433 22598 25107 33442 36836 40548 42927 43462];
%公路货运量(单位:万吨)
freightVolume = [1237 1379 1385 1399 1663 1714 1834 4322 8132 8936 11099 11203 10524 11115 13320 16762 18673 20724 20803 21804];
%输入数据矩阵
p = [numberOfPeople; numberOfAutomobile; roadArea];
%目标(输出)数据矩阵
t = [passengerVolume; freightVolume];
%% 2. 不随机产生训练集和测试集,前15个训练集,后五个验证集
%temp = [1:25];
% 训练集——15个样本
P_train =p(:,1:20);%取前15行数据
T_train =t(:,1:20);
% 测试集——5个样本
P_test=p(:,6:20);
T_test=t(:,6:20);
%% 对训练集中的输入数据矩阵和目标数据矩阵进行归一化处理
%[pn, inputStr] = mapminmax(P_train);
%[tn, outputStr] = mapminmax(T_train);
%p_test = mapminmax('apply',P_test,ps_input);
[p_train, ps_input] = mapminmax(P_train,-1,1);
p_test = mapminmax('apply',P_test,ps_input);
[t_train, ps_output] = mapminmax(T_train,-1,1);
%建立BP神经网络
net = newff(p_train, t_train, [3 7 2], {'purelin', 'logsig', 'purelin'});
%每10轮回显示一次结果
net.trainParam.show = 10;
%最大训练次数
net.trainParam.epochs = 5000;
%网络的学习速率
net.trainParam.lr = 0.05;
%训练网络所要达到的目标误差
net.trainParam.goal = 0.65 * 10^(-3);
%网络误差如果连续6次迭代都没变化,则matlab会默认终止训练。为了让程序继续运行,用以下命令取消这条设置
net.divideFcn = '';
%开始训练网络
net = train(net, p_train, t_train);
%使用训练好的网络,基于训练集的数据对BP网络进行仿真得到网络输出结果,对于测试集进行预测
answer = sim(net, p_test);
%反归一化
answer1 = mapminmax('reverse', answer, outputStr);
%绘制测试样本神经网络输出和实际样本输出的对比图(figure(1))-------------------------------------------
t1 = 1995:2009;
%测试样本网络输出客运量
a1 = answer1(1,:);
b1 = T_test(1,:);
%测试样本网络输出货运量
a2 = answer1(2,:);
b2 = T_test(2,:);
figure(1);
subplot(2, 1, 1); plot(t1, a1, 'ro', t1, b1, 'b+');
legend('网络输出客运量', '实际客运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('客运量/万人');
title('神经网络客运量学习与测试对比图');
grid on;
subplot(2, 1, 2); plot(t1, a2, 'ro', t1, b2, 'b+');
legend('网络输出货运量', '实际货运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('货运量/万吨');
title('神经网络货运量学习与测试对比图');
grid on;
%使用训练好的神经网络对新输入数据进行预测
%新输入数据(2010年和2011年的相关数据)
newInput = [73.39 75.55; 3.9635 4.0975; 0.9880 1.0268];
%利用原始输入数据(训练集的输入数据)的归一化参数对新输入数据进行归一化
newInput = mapminmax('apply', newInput, inputStr);
%进行仿真
newOutput = sim(net, newInput);
%反归一化
newOutput = mapminmax('reverse',newOutput, outputStr);
disp('预测2010和2011年的公路客运量分别为(单位:万人):');
newOutput(1,:)
disp('预测2010和2011年的公路货运量分别为(单位:万吨):');
newOutput(2,:)
%在figure(1)的基础上绘制2010和2011年的预测情况-------------------------------------------------------
figure(2);
t2 = 1995:2011;
subplot(2, 1, 1); plot(t2, [a1 newOutput(1,:)], 'ro', t1, b1, 'b+');
legend('网络输出客运量', '实际客运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('客运量/万人');
title('神经网络客运量学习与测试对比图(添加了预测数据)');
grid on;
subplot(2, 1, 2); plot(t2, [a2 newOutput(2,:)], 'ro', t1, b2, 'b+');
legend('网络输出货运量', '实际货运量');
xlabel('年份'); ylabel('货运量/万吨');
title('神经网络货运量学习与测试对比图(添加了预测数据)');
grid on;