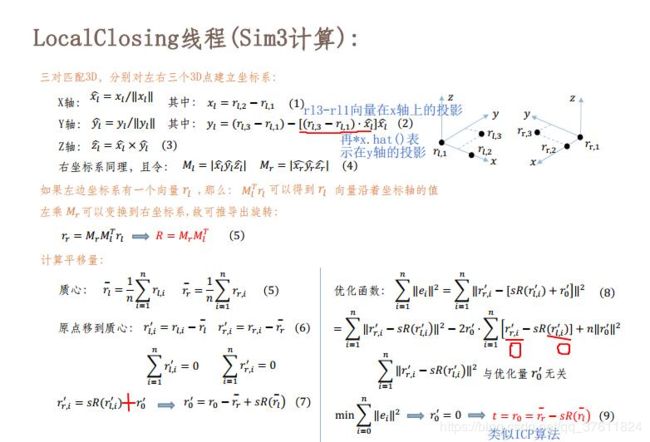
ORB-SLAM中LoopClosing线程的sim3计算
参考论文:http://people.csail.mit.edu/bkph/papers/Absolute_Orientation.pdf
参考ORB-SLAM源码详解
sim3计算:R t s
ORB-SLAM 源码中的文件Sim3Slover.cc
void Sim3Solver::ComputeCentroid(cv::Mat &P, cv::Mat &Pr, cv::Mat &C)
{
cv::reduce(P,C,1,CV_REDUCE_SUM); //计算质心
C = C/P.cols;
for(int i=0; i(0,0)+M.at(1,1)+M.at(2,2);
N12 = M.at(1,2)-M.at(2,1);
N13 = M.at(2,0)-M.at(0,2);
N14 = M.at(0,1)-M.at(1,0);
N22 = M.at(0,0)-M.at(1,1)-M.at(2,2);
N23 = M.at(0,1)+M.at(1,0);
N24 = M.at(2,0)+M.at(0,2);
N33 = -M.at(0,0)+M.at(1,1)-M.at(2,2);
N34 = M.at(1,2)+M.at(2,1);
N44 = -M.at(0,0)-M.at(1,1)+M.at(2,2);
N = (cv::Mat_(4,4) << N11, N12, N13, N14,
N12, N22, N23, N24,
N13, N23, N33, N34,
N14, N24, N34, N44);
// Step 4: Eigenvector of the highest eigenvalue
// N矩阵特征分解
cv::Mat eval, evec;
cv::eigen(N,eval,evec); //evec[0] is the quaternion of the desired rotation
// N矩阵最大特征值(第一个特征值)对应特征向量就是要求的四元数(q0 q1 q2 q3)
// 将(q1 q2 q3)放入vec行向量,vec就是四元数旋转轴乘以sin(ang/2)
cv::Mat vec(1,3,evec.type());
(evec.row(0).colRange(1,4)).copyTo(vec); //extract imaginary part of the quaternion (sin*axis)
// Rotation angle. sin is the norm of the imaginary part, cos is the real part
double ang=atan2(norm(vec),evec.at(0,0));
vec = 2*ang*vec/norm(vec); //Angle-axis representation. quaternion angle is the half
mR12i.create(3,3,P1.type());
cv::Rodrigues(vec,mR12i); // computes the rotation matrix from angle-axis
// Step 5: Rotate set 2
//计算尺度
cv::Mat P3 = mR12i*Pr2;
// Step 6: Scale
if(!mbFixScale)
{
double nom = Pr1.dot(P3);
cv::Mat aux_P3(P3.size(),P3.type());
aux_P3=P3;
cv::pow(P3,2,aux_P3);
double den = 0;
for(int i=0; i(i,j);
}
}
ms12i = nom/den;
}
else
ms12i = 1.0f;
// Step 7: Translation
//计算平移
mt12i.create(1,3,P1.type());
mt12i = O1 - ms12i*mR12i*O2;
// Step 8: Transformation
// Step 8.1 T12
mT12i = cv::Mat::eye(4,4,P1.type());
cv::Mat sR = ms12i*mR12i;
sR.copyTo(mT12i.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3));
mt12i.copyTo(mT12i.rowRange(0,3).col(3));
// Step 8.2 T21
// 构造相似变换矩阵
mT21i = cv::Mat::eye(4,4,P1.type());
cv::Mat sRinv = (1.0/ms12i)*mR12i.t();
sRinv.copyTo(mT21i.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3));
cv::Mat tinv = -sRinv*mt12i;
tinv.copyTo(mT21i.rowRange(0,3).col(3));
} 程序的的设计上是先根据去心的匹配点对构造出了矩阵M,然后构造矩阵N,N矩阵最大特征值(第一个特征值)对应特征向量就是要求的四元数(q0 q1 q2 q3), 将(q1 q2 q3)放入vec行向量,vec就是四元数旋转轴乘以sin(ang/2),计算旋转的角度和旋转向量,再计算出旋转矩阵。再求出尺度(用的非对称模式)和平移量,最后给出位姿变换矩阵。