【文献阅读】结合对抗网络和知识蒸馏,对多模态源的遥感图像分类(S. Pande等人,ICCV,2019)
一、背景
文章题目:《An Adversarial Approach to Discriminative Modality Distillation for Remote Sensing Image Classification》
遥感图像分类一直都是一个热门话题,这篇文章结合对抗网络和知识蒸馏来做遥感图像分类。亮点在于结合不同模态的数据。
文章下载地址:https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCVW_2019/papers/CROMOL/Pande_An_Adversarial_Approach_to_Discriminative_Modality_Distillation_for_Remote_Sensing_ICCVW_2019_paper.pdf
文章引用格式:Shivam Pande, Avinandan Banerjee, Saurabh Kumar, Biplab Banerjee, Subhasis Chaudhuri. "An Adversarial Approach to Discriminative Modality Distillation for Remote Sensing Image Classification." International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2019
项目地址:
二、文章摘要
We deal with the problem of modality distillation for the purpose of remote sensing (RS) image classification by exploring the deep generative models. From the remote sensing perspective, this problem can also be considered in line with the missing bands problem frequently encountered due to sensor abnormality. It is expected that different modalities provide useful complementary information regarding a given task, thus leading to the training of a robust prediction model. Although training data may be collected from different sensor modalities, it is many a time possible that not all the information are readily available during the model inference phase. This paper tackles the problem by proposing a novel adversarial training driven hallucination architecture which is capable of learning discriminative feature representations corresponding to the missing modalities from the available ones during the test time. To this end, we follow a teacher-student model where the teacher is trained on the multimodal data (learning with privileged information) and the student model learns to subsequently distill the feature descriptors corresponding to the missing modality. Experimental results obtained on the benchmark hyperspectral (HSI) datasets and another dataset of multispectral (MS)-panchromatic (PAN) image pairs confirm the efficacy of the proposed approach. In particular, we find that the student model is consistently able to surpass the performance of the teacher model for HSI datasets.
作者通过深度生成模型来处理以遥感图像分类为目的的模态蒸馏问题。从遥感的角度来看,这一问题也可与由于传感器异常而经常遇到的缺失波段问题结合起来考虑。通过不同模态提供的与任务有关的有用互补信息,因此可以训练更鲁棒的预测模型。尽管训练数据也许是从不同的传感器模态获得的,但也很有可能在相关时相并没有可用的数据。本文通过提出一种新的对抗训练驱动的结构来解决该问题,该结构可在测试期间从可用模态中学习与缺少的模态相对应的判别性特征表示。基于此,作者采用了teacher-student模型,teacher模型用于训练多模态数据,student模型用于提取与缺失模态相对应的特征描述子。实验基于高光谱数据集HSI和多光谱全色MS-PAN数据集,证明了方法的有效性,而且student模型能够在HSI数据集上比teacher模型的表象更好。
三、文章详细介绍
遥感数据从非常精细的高分辨率数据VHR到高光谱信息,因此对于不同模态数据的结合是非常必要的。然而,受限于时间,天气等因素,不可能所有时间都有不同的模态信息,这对一些实时性的应用是非常关键的,比如灾害管理的快速响应。
对于传统多模态而言,如果测试集中出现的模态数据但是训练集中没有出现过,那就有可能使得模型失效,而这在遥感中是非常常见的。解决方法有两个,一个是在训练集和测试集中同时加上这类数据,另一个是利用隐藏信息,来近似测试集中的缺失数据,这种思路被称为模态蒸馏modality distillation through hallucination。因此本文就提出一种蒸馏结构,用于两种不同的遥感图像分类场景:MS-PAN和VHR。
据作者所知,目前只有一篇RS文章做了知识蒸馏,然而这篇工作的重构损失reconstruction loss却不能在不同模态的数据上很好的学习到数据分布。
本文主要解决的问题是teacher-student模型中的判别模态蒸馏问题。teacher网络用了多层分类器,设计为一个multi-stream网络,其中每一个stream都关注于某一确定模态下的判别特征的学习。然后后面连接一个基于CGAN的hallucination模型,来根据已有模态生成缺失模态下的数据。最后作者又设计了一个student网络,将可用的模态和生成的虚假(hallucination)的模态同时输入到网络中,进行分类。训练过程中,除了知识蒸馏KD(knowledge distillation),还有一个模式倒塌的问题。
这篇文章的主要贡献包括:
• We introduce a novel teacher-student based modality distillation framework for RS image classification where a novel C-GAN based cross-modality mapping module is proposed. We also consider the KD technique to ensure that the student’s classifier does not diverge too much from the teacher’s classifier. 提出了一个teacher-student的模态蒸馏网络,用于遥感图像分类。并且student模型并没有与teacher模型差距很多。
• We perform data augmentation through noise perturbation on the teacher’s training samples in order to train the hallucination and student models. 为了训练模型,使用了数据增强(用了噪声干扰的方式)
• We perform extensive experiments on HSI classification and RS scene classification using MS-PAN image pairs where improved results can be observed. 对HSI分类和MS-PAN场景分类,表明该算法的有效性。
1. 相关工作
遥感图像分类(RS image classification):太多了,有用多光谱MS数据做的,还有用SAR,LiDAR,HSI,PAN数据做的都有。目前已经有相关研究是用CNN做的,当然这些工作都是基于单模态来做的。多模态方法也有,比如Pan-Sharpening GAN(PSGAN),CNN+CGAN,OrthoSeg(三个模态,RGB,DSM,NIR),modified Squeeze and Excitation Networks。
隐藏信息学习(Learning under privileged information (LUPI)):LUPI可以用在很多领域,比如非监督学习(unsupervised learning),度量学习(metric learning),目标定位object localization,人脸检测face detection,表达识别expression recognition。
使用模态蒸馏的隐藏信息学习(LUPI with modality distillation):有人将LUPI+CNN用于分类,姿势识别等,这些都是使用的多模态数据。
有何不同(How are we different):最接近的两篇文章如下:
- S. Roheda, B. S. Riggan, H. Krim, and L. Dai. Crossmodality distillation: A case for conditional generative adversarial networks. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pages 2926–2930. IEEE, 2018.
- N. C. Garcia, P. Morerio, and V. Murino. Learning with privileged information via adversarial discriminative modality distillation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.08437, 2018.
本文与这两篇工作不同之处在于,(1)数据,本文RS,这两篇RGB-D。(2)在这两篇的基础上,引入CGAN的判别器,解决模式倒塌问题。(3)teacher和student模型都采用了平均softmax。(4)使用了数据增广的概念。
2. 模型方法
模型的训练大致分为三个阶段:训练teacher网络;训练hallucination网络;训练student网络。
(1)训练teacher网络
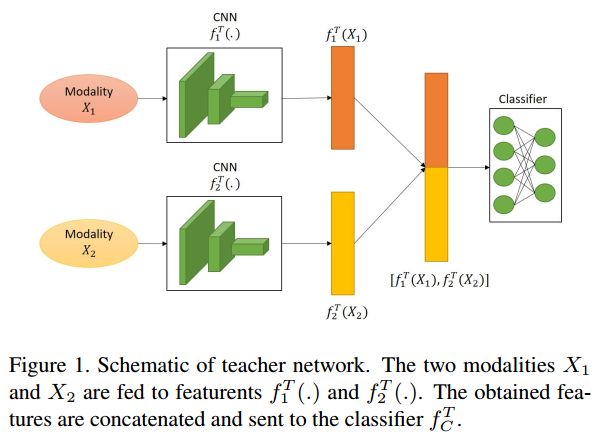
假设有两个模态x1和x2,对应的标签为y,土地利用类型有C类,teacher网络是非常繁杂的,它的训练使用了隐藏信息(privileged information)。它的网络结构如下图所示:
简单来说就是分别提取两个模态的特征,然后把他们连接起来,最后输入分类器中进行分类。
(2)使用CGAN获得虚假的模态(Modality hallucination using C-GAN)
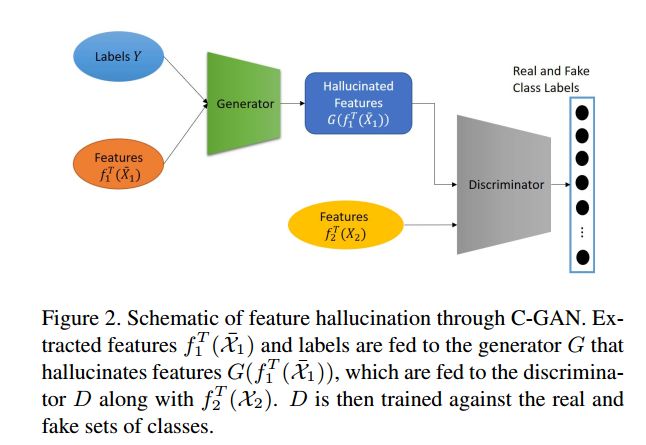
这一步的模型图如下所示:
简单说明一下,假定x2模态是缺失的,现在需要通过已有的x1模态来生成x2模态,那自然就想到了GAN结构,当然了,我们期望生成x2模态的数据,自然需要加入标签进行约束,所以作者就考虑到了CGAN。但是,作者对CGAN进行了两处修改,以避免CGAN出现的问题。修改的部分包括:①利用随机高斯噪声对x1模态的数据进行增广②判别器输出2C个类别得分以避免数据偏见。
(3)训练student网络
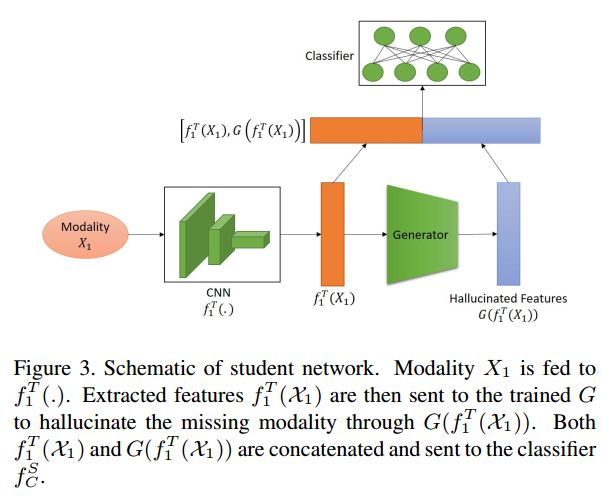
这部分的网络结构如下图所示:
看图也比较好理解,输入模态1的数据,然后CNN提取特征,根据特征输入到生成器中,生成模态2的特征,然后将两个特征连接起来,用于最后的分类。
因为是一个分类问题,损失函数自然考虑交叉熵,同时作者在这里引入了一个温度参数。
3. 实验
(1)数据集
Multispectral-panchromatic dataset:4个MS+一个PAN波段,一共8万张,数据来自GF-1,MS大小为64×64×4,PAN大小为256*256,如下图:
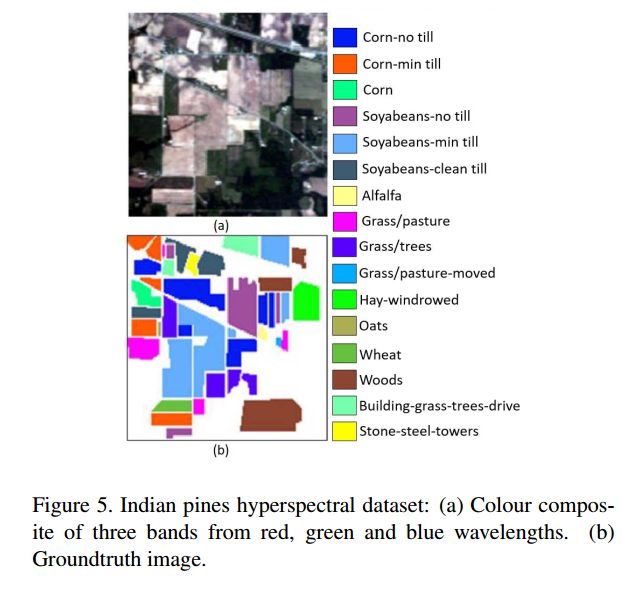
Indian Pines hyperspectral dataset:145×145×200,分辨率20m,如下图:
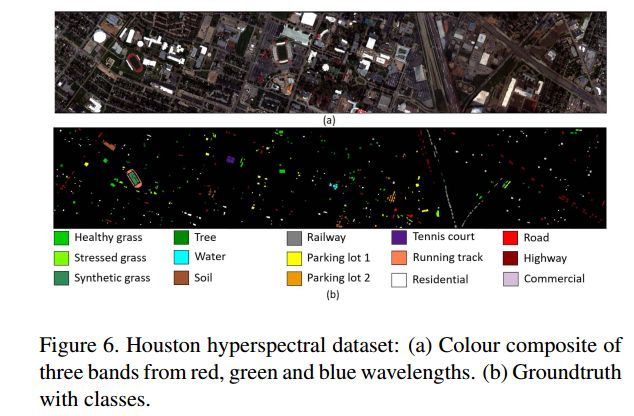
Houston hyperpectral dataset:1905 × 349 × 144(bands),分辨率2.5m,共144类。如下图:
(2)参数设置
这里不多介绍了
(3)结果讨论
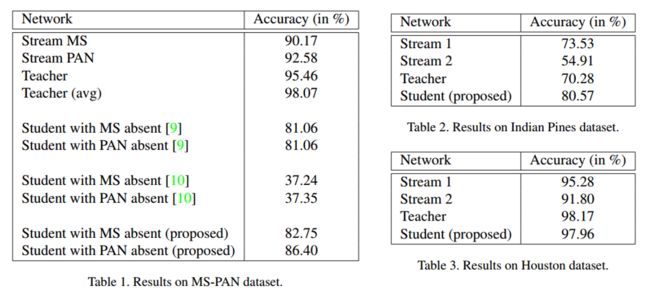
首先是在3个数据集上的结果:
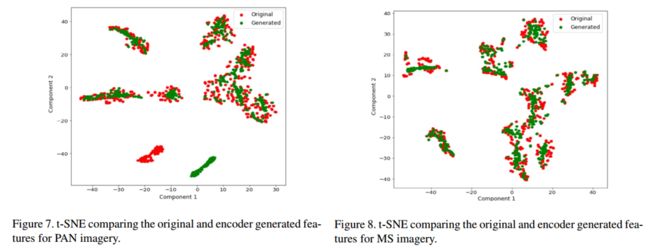
然后是在第一个数据集上的t-SNE:
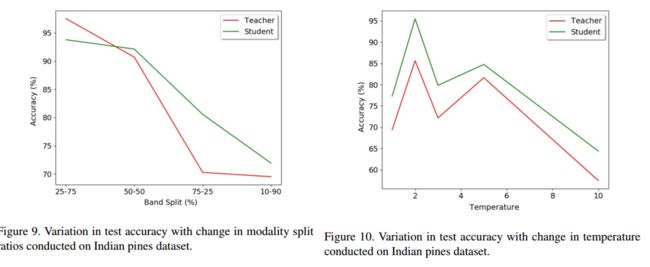
最后在第三个数据集上探究了测试精度与分裂模态比率和测试精度与温度参数之间的关系: