Python计算机视觉编程(七)基础矩阵
多视图几何
- 对极几何
- 本质矩阵
- 基础矩阵
- 8点算法估计基础矩阵F
- SFM:估算空间中的3D点
- 代码及其结果
对极几何
在上一篇相机模型里我们知道x=PX。通过小孔相机模型,可知从相机的中心C向点x投影一条射线Cx,则该射线必定经过对应像点的三维空间点X,但显然仅仅通过一个像点无法确定X的具体位置。那么如果两个相匹配的像点呢?
设x′是三维点X的另一个像点,其对应相机的中心为C′,那么从相机的中心C′向点也投影一条射线C′x′,并且该射线也必定经过X,也就是说从一对相匹配的像点反投影两条射线,必定相交于空间三维点X。那么一对匹配的像点之间存在这某种约束关系,这种约束被称为两视图的对极约束。
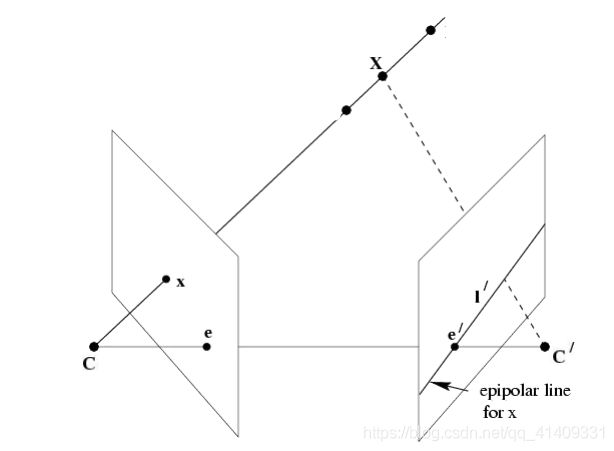
本质矩阵
设X在C, C’坐标系中的相对坐标分别p, p’, 则有
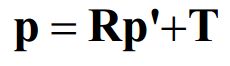
根据三线共面有

又有


将其改写成

变换有

最后得到本质矩阵E
本质矩阵描述了空间中的点在两个坐标系中的坐标对应关系。
基础矩阵
根据前述, K 和 K’ 分别为两个相机的内参矩阵, 有:

带入上式,我们可以得到
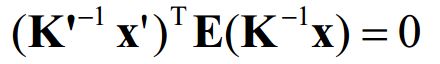
变化有

我们将方框称为基础矩阵F

基础矩阵描述了空间中的点在两个像平面中的坐标对应关系。可以用于
- 简化匹配
- 去除错配特征
8点算法估计基础矩阵F
任给两幅图像中的匹配点 x 与 x’
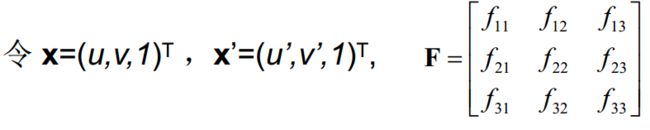
得到
![]()

在实际计算中, 可以直接用ATA的分解来求解参数。也可以用非线性优化, 通过搜索f使得||Af||最小化,同时满足||f||=1的约束。上述求解后的F不一定能满足秩为2的约束, 因此还要在F基础上加以约束。
通过SVD分解可以解决上述问题, 令

则

最终解为
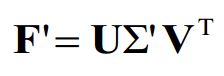
SFM:估算空间中的3D点
首先计算两幅图像之间的基础矩阵 F,再假设第一个相机矩阵:

第二相机矩阵

![]()
代码及其结果
from PIL import Image
from numpy import *
from pylab import *
import numpy as np
import PCV.geometry.camera as camera
import PCV.geometry.homography as homography
import PCV.geometry.sfm as sfm
import PCV.localdescriptors.sift as sift
im1 = array(Image.open('002.jpg'))
sift.process_image('002.jpg', 'im1.sift')
im2 = array(Image.open('001.jpg'))
sift.process_image('001.jpg', 'im2.sift')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('im1.sift')
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('im2.sift')
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
ndx = matches.nonzero()[0]
x1 = homography.make_homog(l1[ndx, :2].T)
ndx2 = [int(matches[i]) for i in ndx]
x2 = homography.make_homog(l2[ndx2, :2].T)
d1n = d1[ndx]
d2n = d2[ndx2]
x1n = x1.copy()
x2n = x2.copy()
figure(figsize=(16,16))
sift.plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, True)
show()
def F_from_ransac(x1, x2, model, maxiter=5000, match_threshold=1e-6):
""" Robust estimation of a fundamental matrix F from point
correspondences using RANSAC (ransac.py from
http://www.scipy.org/Cookbook/RANSAC).
input: x1, x2 (3*n arrays) points in hom. coordinates. """
import PCV.tools.ransac as ransac
data = np.vstack((x1, x2))
d = 10 # 20 is the original
F, ransac_data = ransac.ransac(data.T, model,
8, maxiter, match_threshold, d, return_all=True)
return F, ransac_data['inliers']
model = sfm.RansacModel()
F, inliers = F_from_ransac(x1n, x2n, model, maxiter=5000, match_threshold=1e-5)
print F
P1 = array([[1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0]])
P2 = sfm.compute_P_from_fundamental(F)
X = sfm.triangulate(x1n[:, inliers], x2n[:, inliers], P1, P2)
cam1 = camera.Camera(P1)
cam2 = camera.Camera(P2)
x1p = cam1.project(X)
x2p = cam2.project(X)
figure(figsize=(16, 16))
imj = sift.appendimages(im1, im2)
imj = vstack((imj, imj))
imshow(imj)
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
rows1 = im1.shape[0]
for i in range(len(x1p[0])):
if (0<= x1p[0][i]<cols1) and (0<= x2p[0][i]<cols1) and (0<=x1p[1][i]<rows1) and (0<=x2p[1][i]<rows1):
plot([x1p[0][i], x2p[0][i]+cols1],[x1p[1][i], x2p[1][i]],'c')
axis('off')
show()
d1p = d1n[inliers]
d2p = d2n[inliers]
# Read features
im3 = array(Image.open('003.jpg'))
sift.process_image('003.jpg', 'im3.sift')
l3, d3 = sift.read_features_from_file('im3.sift')
matches13 = sift.match_twosided(d1p, d3)
ndx_13 = matches13.nonzero()[0]
x1_13 = homography.make_homog(x1p[:, ndx_13])
ndx2_13 = [int(matches13[i]) for i in ndx_13]
x3_13 = homography.make_homog(l3[ndx2_13, :2].T)
figure(figsize=(16, 16))
imj = sift.appendimages(im1, im3)
imj = vstack((imj, imj))
imshow(imj)
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
rows1 = im1.shape[0]
for i in range(len(x1_13[0])):
if (0<= x1_13[0][i]<cols1) and (0<= x3_13[0][i]<cols1) and (0<=x1_13[1][i]<rows1) and (0<=x3_13[1][i]<rows1):
plot([x1_13[0][i], x3_13[0][i]+cols1],[x1_13[1][i], x3_13[1][i]],'c')
axis('off')
show()
P3 = sfm.compute_P(x3_13, X[:, ndx_13])
print P1
print P2
print P3

