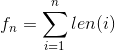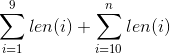Codeforces Round #587 (Div. 3)
A - Prefixes
#include
#define ll long long
#define sc scanf
#define pr printf
using namespace std;
char s[200005];
int main()
{
int n;
sc("%d", &n);
sc("%s", s);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i+=2)
{
if (s[i] == s[i + 1])
{
ans++;
if (s[i] == 'a')
s[i]++;
else
s[i]--;
}
}
pr("%d\n", ans);
pr("%s\n", s);
} B - Shooting
#include
#define ll long long
#define sc scanf
#define pr printf
using namespace std;
char s[200005];
struct node
{
int a;
int b;
}in[200005];
int main()
{
int n;
sc("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
sc("%d", &in[i].a);
in[i].b = i;
}
int ans = 0;
sort(in + 1, in + 1 + n, [](node q, node w) {
return q.a > w.a;
});
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
ans = ans + (i-1) *in[i].a;
pr("%d\n", ans + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
pr("%d%c", in[i].b, i == n ? '\n' : ' ');
} C - White Sheet
由于非整数点部分也算面积,那就离散化一下,然后随机取点,判一下,如果存在这样的点,就是yes
(其实直接读入12个数字,然后判更简单。)
#include
#define ll long long
#define sc scanf
#define pr printf
using namespace std;
struct point
{
int x;
int y;
};
struct node
{
point a;
point b;
}q, w, e;
int t[20];
int cnt = 0;
int s[10][10];
int main()
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
int a, b, c, d;
sc("%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d);
t[cnt++] = a, t[cnt++] = b, t[cnt++] = c, t[cnt++] = d;
q.a = point{ a,b }; q.b = point{ c,d };
sc("%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d);
t[cnt++] = a, t[cnt++] = b, t[cnt++] = c, t[cnt++] = d;
w.a = point{ a,b }; w.b = point{ c,d };
sc("%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d);
t[cnt++] = a, t[cnt++] = b, t[cnt++] = c, t[cnt++] = d;
e.a = point{ a,b }; e.b = point{ c,d };
sort(t, t + cnt);
int qq = unique(t, t + cnt) - t;
q.a.x = lower_bound(t, t + qq, q.a.x) - t + 1;
q.a.y = lower_bound(t, t + qq, q.a.y) - t + 1;
q.b.x = lower_bound(t, t + qq, q.b.x) - t + 1;
q.b.y = lower_bound(t, t + qq, q.b.y) - t + 1;
w.a.x = lower_bound(t, t + qq, w.a.x) - t + 1;
w.a.y = lower_bound(t, t + qq, w.a.y) - t + 1;
w.b.x = lower_bound(t, t + qq, w.b.x) - t + 1;
w.b.y = lower_bound(t, t + qq, w.b.y) - t + 1;
e.a.x = lower_bound(t, t + qq, e.a.x) - t + 1;
e.a.y = lower_bound(t, t + qq, e.a.y) - t + 1;
e.b.x = lower_bound(t, t + qq, e.b.x) - t + 1;
e.b.y = lower_bound(t, t + qq, e.b.y) - t + 1;
int T = 10000;
while (T--)
{
int x = rand() % qq;
double xx = x + 0.5;
int y = rand() % qq;
double yy = y + 0.5;
if (xx > q.a.x && xxq.a.y && yy < q.b.y)
{
if ((xx > w.a.x && xxw.a.y && yy < w.b.y) || (xx > e.a.x && xxe.a.y && yy < e.b.y))
;
else
{
printf("YES\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
printf("NO\n");
} D - Swords
求个gcd,然后往上加
#include
#define ll long long
#define sc scanf
#define pr printf
using namespace std;
ll in[200005], t[200005];
ll gcd(ll in, ll t)
{
return t == 0 ? in : gcd(t, in % t);
}
int main()
{
int n;
sc("%d", &n);
ll maxn = -1e18;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
sc("%lld", &in[i]);
maxn = max(maxn, in[i]);
}
sort(in + 1, in + 1 + n);
int pos = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
if (in[i + 1] != in[i])
t[pos++] = in[i + 1] - in[i];
for (int i = 1; i < pos - 1; ++i)
t[i + 1] = gcd(t[i], t[i + 1]);
ll ans1 = 0, ans2 = t[pos - 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ans1 += (maxn - in[i]) / ans2;
pr("%lld %lld\n", ans1, ans2);
} E1 - Numerical Sequence (easy version)
暴力求在哪一堆,然后再求在哪个数字
E2 - Numerical Sequence (hard version)
由于位数不同,所以考虑分块,将长度1、2、3、4的分成不同的块,那么我们用 ![]() 来表示
来表示 ![]() 排列的长度,那么有
排列的长度,那么有
![]() 显然容易求得,
显然容易求得,
1、若
,对于排列
,他的长度显然是
加上两位数字的个数
3、其中第一项是
,将第二项其中的长度为1的,长度为2的区分开,就变成了 长度为1的块的长度*个数 + 长度为2的块的个数
4、令
,即有
个排列含有长度位于 2 的数字,所以第二项中长度为 2 的数字的个数就是
,然后加上长度为 1 的数字个数
,同理向下扩展。
第一次二分,求出大于等于所求位置的排列和在该排列中的位置。
第二次二分,求出在这个排列里面,所求位置出现在哪个数字里面。
然后暴力输出,就可以了。
(又是赛后一分钟过题,发现少了一个等号,现在还不能提交,不知道对不对)
update:赛后一分钟过题
#include
#define ll unsigned long long
#define sc scanf
#define pr printf
using namespace std;
ll len[20];
ll f[20];
int a[20];
void jzk(ll l, ll n)
{
int cnt = 0;
while (l)
{
a[++cnt] = l % 10;
l /= 10;
}
reverse(a + 1, a + cnt + 1);
printf("%d\n", a[n]);
}
ll power(ll a, int b)
{
ll res = 1;
while (b--)
res *= a;
return res;
}
ll calc(ll k, ll pos)
{
k -= power(10, pos - 1) - 1;
ll ans = f[pos - 1] + pos * ((k * (k + 1)) / 2) + len[pos - 1] * k;
return ans;
}
bool check(ll k, ll n, ll pos)
{
ll ans = calc(k, pos);
if (ans >= n)
return true;
return false;
}
ll calc1(ll k, ll wei)
{
k -= power(10, wei - 1) - 1;
ll ans = len[wei - 1] + k * wei;
return ans;
}
bool check1(ll k, ll wei, ll n)
{
ll ans = calc1(k, wei);
if (ans >= n)
return true;
return false;
}
//[1,end] print n _st
void print(ll n,ll end)
{
int pos = 1;
for (int i = 9; i >= 1; i--)
if (n > len[i])
{
pos = i + 1;
break;
}
ll l = 1;
ll r = end;
while (l + 1 < r)
{
ll k = (l + r) / 2;
if (check1(k, pos, n))
r = k;
else
l = k;
}
if (check1(l, pos, n) == false)
l = r;
ll ans = calc1(l - 1, pos);
n -= ans;
//num l n_st
jzk(l, n);
}
int main()
{
len[1] = 9;
for (int i = 2; i < 10; i++)
len[i] = len[i - 1] + 9 * power(10, i - 1) * i;
f[1] = 45;
for (int i = 2; i < 10; i++)
{
ll t = 9 * power(10, i - 1);
f[i] = f[i - 1] + i * ((t * (t + 1)) / 2) + len[i - 1] * t;
}
int T;
sc("%d", &T);
while (T--)
{
ll n;
sc("%llu", &n);
ll pos = 1;
for (int i = 9; i >= 1; i--)
{
if (n > f[i])
{
pos = i + 1;
break;
}
}
ll l = power(10, pos - 1);
ll r = power(10, pos) - 1;
while (l + 1 < r)
{
ll k = (l + r) / 2;
if (check(k, n, pos))
r = k;
else
l = k;
}
if (check(l, n, pos) == false)
l = r;
ll ans = calc(l - 1, pos);
n -= ans;
print(n, l);
}
} F - Wi-Fi
线段树区间覆盖,本质上应该算线段树加速dp
1、考虑暴力的方法,将区间按右端点排序,若原来的区间有值能到达这个区间(即连续),那么找出在这个区间中的最少花费,加上这个区间的代价,就可以转移到这个右端点;
2、所以如果我们可以在log的时间找到这个区间中的最小值,并且log的时间单点更新右端点的最小值就可以过,线段树加速一下就可以(单点更新还不需要懒惰标记,太爽了)
3、注意当区间在整个区间的左端点时,左端点 1 是可以直接到达的,所以特判左端点为 1 直接跟新就可以。
#include
#include
#include
#define ll long long
#define sc scanf
#define pr printf
#define lson left,mid,k<<1
#define rson mid+1,right,k<<1|1
#define imid int mid=(left+right)>>1;
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 5;
const ll inf = 1e12 + 7;//不能太大,会爆 ll
struct node
{
int l;
int r;
ll minn;
}que[MAXN * 4];
int n, m, q, ql, qr;
ll val, a[MAXN];
void up(int k)
{
que[k].minn = min(que[k << 1].minn, que[k << 1 | 1].minn);
}
void build(int left = 1, int right = n, int k = 1)
{
que[k].l = left;
que[k].r = right;
que[k].minn = inf;
if (left == right)
return;
imid;
build(lson);
build(rson);
}
void update(int left = 1, int right = n, int k = 1)
{
if (qr < left || right < ql)
return;
if (ql <= left && right <= qr)
{
//one point
que[k].minn = min(que[k].minn, val);
return;
}
imid;
update(lson);
update(rson);
up(k);
}
ll query(int left = 1, int right = n, int k = 1)
{
if (qr < left || right < ql)
return inf;
if (ql <= left && right <= qr)
return que[k].minn;
imid;
return min(query(lson), query(rson));
}
struct qwe
{
int l;
int r;
int cost;
}in[MAXN];
char s[MAXN];
int main()
{
sc("%d%d", &n, &m);
sc("%s", s);
build();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (s[i] == '1')
{
in[i].l = max(1, i + 1 - m);
in[i].r = min(n, i + 1 + m);
}
else
in[i].l = in[i].r = i + 1;
in[i].cost = i + 1;
}
sort(in, in + n, [](qwe q, qwe w) {
return q.r < w.r;
});
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (in[i].l == 1)
{
ql = qr = in[i].r;
val = in[i].cost;
update();
}
else
{
ql = in[i].l - 1, qr = in[i].r;//不相邻连接
val = query() + in[i].cost;
ql = qr = in[i].r;
update();
}
}
ql = qr = n;
ll ans = query();
if (ans >= inf)
ans = -1;
pr("%lld\n", ans);
}