- 2024.8.22 Python,链表两数之和,链表快速反转,二叉树的深度,二叉树前中后序遍历,N叉树递归遍历,翻转二叉树
RaidenQ
python链表开发语言
1.链表两数之和输入:l1=[2,4,3],l2=[5,6,4]输出:[7,0,8]解释:342+465=807.示例2:输入:l1=[0],l2=[0]输出:[0]示例3:输入:l1=[9,9,9,9,9,9,9],l2=[9,9,9,9]输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]昨天的这个题,用自己的办法写的麻烦的要死,然后刚才一看chat归类的办法,感觉自己像个智障。classListNode
- 【树一线性代数】005入门
Owlet_woodBird
算法
Index本文稍后补全,推荐阅读:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_60702024/article/details/141874376分析实现总结本文稍后补全,推荐阅读:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_60702024/article/details/141874376已知非空二叉树T的结点值均为正整数,采用顺序存储方式保存,数据结构定义如下:t
- leetcode-617. 合并二叉树
manba_
leetcodehot100leetcode算法
题目描述给你两棵二叉树:root1和root2。想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新二叉树。合并的规则是:如果两个节点重叠,那么将这两个节点的值相加作为合并后节点的新值;否则,不为null的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。返回合并后的二叉树。注意:合并过程必须从两个树的根节点开始。示例1:输入:root1=[1,3,2,
- leetcode刷题day19|二叉树Part07(235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先、701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作、450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点)
小冉在学习
leetcode算法数据结构
235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先思路:二叉搜索树首先考虑中序遍历。根据二叉搜索树的特性,如果p,q分别在中间节点的左右两边,该中间节点一定是最近公共祖先,如果在同一侧,则递归这一侧即可。递归三部曲:1、传入参数:根节点,p,q,返回节点。2、终止条件:因为p,q一定存在,所以不会遍历到树的最底层,因此可以不写终止条件3、递归逻辑:如果p,q均小于root的值,递归调用左子树;如果p,q均大于roo
- leetcode刷题day13|二叉树Part01(递归遍历、迭代遍历、统一迭代、层序遍历)
小冉在学习
leetcode算法职场和发展
递归遍历思路:使用递归的方式比较简单。1、递归函数的传参:因为最后输出一个数组,所以需要传入根节点和一个容器,本来想写数组,但发现长度不能确定,所以选择list。2、终止条件:当访问的节点为空时,return3、递归函数的逻辑:先访问一个节点,递归访问其他节点144.二叉树的前序遍历代码如下:classSolution{publicListpreorderTraversal(TreeNoderoo
- 【数据结构和算法实践-树-LeetCode113-路径总和Ⅱ】
NeVeRMoRE_2024
数据结构与算法实践数据结构算法leetcodeb树
数据结构和算法实践-树-LeetCode113-路径总和Ⅱ题目MyThought代码示例JAVA-8题目给你二叉树的根节点root和一个整数目标和targetSum,找出所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点输入:root=[5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1],targetSum=22输出:[[5,4,11,2],[
- 【Python】数据结构,链表,算法详解
AIAdvocate
python数据结构链表排序算法广度优先深度优先
今日内容大纲介绍自定义代码-模拟链表删除节点查找节点算法入门-排序类的冒泡排序选择排序插入排序快速排序算法入门-查找类的二分查找-递归版二分查找-非递归版分线性结构-树介绍基本概述特点和分类自定义代码-模拟二叉树1.自定义代码-模拟链表完整版"""案例:自定义代码,模拟链表.背景: 顺序表在存储数据的时候,需要使用到连续的空间,如果空间不够,就会导致扩容失败,针对于这种情况,我们可以通过链表实现
- Ihandy Unity开发 面试题 2024
z2014z
面试职场和发展
1.当i>10时,调用test是否会出现死锁?原因是什么?voidtest(inti){lock(this){if(i>10){i--;test(i);}}}2.有一个表有n条记录,每条记录有两个字段,weight和id,写出程序保证id出现的概率与权重相同3.从1到n,一共有多少个14.二叉树的层次遍历5.给定两个链表,将对应数值相加6.检查两棵树是否相同
- 二叉树--python
电子海鸥
Python数据结构与算法python开发语言数据结构
二叉树一、概述1、介绍是一种非线性数据结构,将数据一分为二,代表根与叶的派生关系,和链表的结构类似,二叉树的基本单元是结点,每个节点包括值和左右子节点引用。每个节点都有两个引用(类似于双向链表),分别指向左子节点和右子节点,该节点被称为这两个子节点的父节点。当给定一个二叉树的结点时,我们将在该节点的左子节点以及其以下结点所形成的树称为左子树,同理,右子节点的部分被称为右子树。在二叉树中,除了叶节点
- 【数据结构和算法实践-树-LeetCode110-平衡二叉树】
NeVeRMoRE_2024
数据结构与算法实践算法数据结构leetcodeb树
数据结构和算法实践-树-LeetCode110-平衡二叉树题目MyThought代码示例JAVA-8题目给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是平衡二叉树输入:root=[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]输出:trueMyThought判断平衡二叉树的条件是树的左右高度相差为1一、利用递归去遍历1、边界为节点为null,树高为0;2、树高的递增规则为,根的左节点和右节点比较值+1二、为了方便信息传
- 【代码随想录Day17】二叉树Part05|练习递归
夜雨翦春韭
代码随想录数据结构算法leetcodejava
654.最大二叉树题目链接/文章讲解:代码随想录视频讲解:又是构造二叉树,又有很多坑!|LeetCode:654.最大二叉树_哔哩哔哩_bilibili思路和昨天的从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树很像,那一题是根节点对数组分割,这一题是最大元素对数组分割。代码解释:基本检查:如果输入数组nums为空,直接返回null。找到最大值的索引:使用getMaxIndex方法找到数组中的最大值的索引。创建根节
- 《剑指offer第二版》面试题7:重建二叉树(java)
castlet
题目描述输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果都不包含重复数字。例如,输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建的二叉树为:1/\23//\456\/78解题思路:以前序遍历序列A:{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列B:{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6}为例。前序遍历的
- 六、二叉树(1)
小霖同学onism
算法基础python
六、二叉树(1)理论基础种类存储方式遍历方式定义144.二叉树的前序遍历递归法,后面见迭代145.二叉树的后序遍历,递归94.二叉树的中序遍历,递归定义特点和区别适用场景迭代遍历前序迭代中序迭代后序迭代中序遍历(InorderTraversal)后序遍历(PostorderTraversal)思路上的主要区别统一迭代(标记法)层序遍历理论基础种类满二叉树:节点都是满的,节点个数2^k-1完全二叉树
- 数据结构初阶(C语言)-二叉树-顺序表建堆
眠りたいです
数据结构算法c语言学习笔记visualstudiocode开发语言
一,堆的概念与结构如果有⼀个关键码的集合,把它的所有元素按完全⼆叉树的顺序存储方式存储,在⼀个⼀维数组中,并满足:,i=0,1,2...则称为小堆(或⼤堆)。将根结点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根结点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。堆具有以下性质:1.堆中某个结点的值总是不大于或不小于其父结点的值2.堆总是⼀棵完全二叉树。这里我们说一下完全二叉树的性质:对于具有n个结点的完全二叉树,如果按照从上至下从
- 《数据结构与算法》知识点(四)
游戏原画设计
第七章查找顺序查找、折半查找、索引查找、分块查找是静态查找,动态查找有二叉排序树查找,最优二叉树查找,键树查找,哈希表查找静态查找表顺序表的顺序查找:应用范围:顺序表或线性链表表示的表,表内元素之间无序。查找过程:从表的一端开始逐个进行记录的关键字和给定值的比较。顺序有序表的二分查找。平均查找时间(n+1)/nlog2(n+1)分块查找:将表分成几块,块内无序,块间有序,即前一块中的最大值小于后一
- 数据结构:链式二叉树及其相关算法
Seaside.
数据结构数据结构c语言
在上一篇树和堆的博客中,有关树的定义已经详细地介绍过了。今天我们要详细介绍的是链式二叉树。链式二叉树,就是它不再是满二叉树或者是完全二叉树,因此不再适合使用数组存储,因此它以链表为基础结构,一个节点中保存着两个地址,指向它的左右孩子。我们要这样看二叉树:总是将它分成左子树和右子树。如上图这个二叉树可以分为以2为根的左子树、以3为根的右子树。而每个子树又可以分为小子树,小子树又可以分为小小子树。直到
- 【华为OD】2024D卷——生成哈夫曼树
简单.is.good
Python解应用题华为odpython霍夫曼树
题目描述:给定长度为n的无序的数字数组,每个数字代表二叉树的叶子节点的权值,数字数组的值均大于等于1。请完成一个函数,根据输入的数字数组,生成哈夫曼树,并将哈夫曼树按照中序遍历输出。为了保证输出的二叉树中序遍历结果统一,增加以下限制:二叉树节点中,左节点权值小于等于右节点权值,根节点权值为左右节点权值之和。当左右节点权值相同时,左子树高度高度小于等于右子树。注意:所有用例保证有效,并能生成哈夫曼树
- 二叉树篇--代码随想录算法训练营第十八天| 530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 , 501.二叉搜索树中的众数 , 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先,235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
热爱编程的OP
leetcode算法leetcode数据结构学习c++
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差题目链接:.-力扣(LeetCode)讲解视频:二叉搜索树中,需要掌握如何双指针遍历!|LeetCode:530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差题目描述:给你一个二叉搜索树的根节点root,返回树中任意两不同节点值之间的最小差值。差值是一个正数,其数值等于两值之差的绝对值。示例1:输入:root=[4,2,6,1,3]输出:1解题思路:该题用到了二叉搜索树的性质:中序遍历元素
- 代码随想录算法训练营第十天 | Javascript | 力扣Leetcode | 144、145、94. 二叉树前序,后续,中序
栗子皮皮布丁
算法leetcode职场和发展
前言踏平坎坷成大道,斗罢艰险又出发!自律的尽头是自控,自控的尽头是硬控。愿道友们披荆斩棘,终能得偿所愿。简介本人是小几年经验的前端开发,算法基础只有力扣几十道题,非常薄弱。今天是个人的代码随想录算法硬控自己第10天,搞搞二叉树,冲!题目链接:144.二叉树前序,145.二叉树后序,94.二叉树中序比较简单,代码差别不大,直接贴上。
- 五一的成果
王跃坤txdy
emm。。五一过了有意义的四天。原来简单的图论我也是可以搞出来的原来DFS放进图论真的会使难度变大原来BFS在没有出口的时候会以超指数的爆炸增长原来二叉树并不是很难原来哈希的速度远超数组原来动态规划滚动起来速度真的快原来栈是那么的有用,可惜来不及学了(遇到一个求化学方程式的算法题,我自己写了133行的字符串处理,原来用栈可以缩减3倍的代码)原来很多复杂的问题都可以拆解成很简单的问题比如我好像发现数
- 【每日一题】LeetCode 104.二叉树的最大深度(树、深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索、二叉树)
Chase-Hart
算法leetcode深度优先宽度优先数据结构java
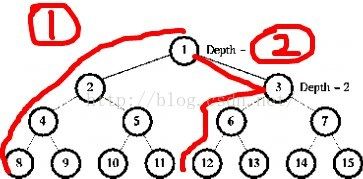
【每日一题】LeetCode104.二叉树的最大深度(树、深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索、二叉树)题目描述给定一个二叉树root,我们需要计算并返回该二叉树的最大深度。二叉树的最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。思路分析为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用递归的方法。递归的基本思想是从根节点开始,逐层向下遍历树的每个节点,同时记录当前的深度。在递归的过程中,我们会遇到两种情况:当前节点为
- 【数据结构和算法实践-树-LeetCode107-二叉树的层序遍历Ⅱ】
NeVeRMoRE_2024
数据结构与算法实践数据结构算法leetcode
数据结构和算法实践-树-LeetCode107-二叉树的层序遍历Ⅱ题目MyThought代码示例JAVA-8题目给你二叉树的根节点root,返回其节点值自底向上的层序遍历。(即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)。输入:root=[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]输出:[[15,7],[9,20],[3]]MyThought题目给定的是通过二叉树的层序去遍历,结合示例
- 浅谈一下B树
AIGC Ball
b树
B树(平衡二叉树)是一种自平衡的二叉查找树,它允许搜索、顺序访问、插入和删除操作在对数时间内完成。B树的关键特性是它可以保持所有叶子节点在同一层,这使得它非常适合用于数据库和文件系统中的索引结构。B树的基本概念节点:B树的每个节点可以包含一个键值对和两个子节点的指针,除了根节点和叶子节点。根节点至少含有一个键,叶子节点包含n个键和n+1个子节点指针(n>1)。键:B树中的键是用于排序和查找的值,每
- LeetCode刷题2
Reus_try
leetcode链表算法
0612LeetCode刷题2力扣刷题1力扣刷题2力扣83题:删除排序链表中的重复元素力扣82题:删除排序链表中的重复元素II力扣第8题:字符串转换整数(atoi)力扣22题:括号生成力扣31题:下一个排列怎么用sort()对一个数组的局部进行排序?1143.最长公共子序列力扣93题:复原IP地址力扣151题:颠倒字符串中的单词力扣105题:从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树力扣110题:平衡二叉树力
- 代码随想录算法训练营day18|二叉树06
咕咕鹄鹄
算法数据结构
一、530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差-力扣(LeetCode)给你一棵所有节点为非负值的二叉搜索树,请你计算树中任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。示例:提示:树中至少有2个节点思路:classSolution:def__init__(self):self.vec=[]deftraversal(self,root):ifrootisNone:returnself.trave
- 【数据结构】python实现二叉树
汨攸
笔记python数据结构算法
文章目录@[TOC](文章目录)一、二叉树的概念二、python代码1.定义抽象类2.定义结点类3.实现二叉树基本操作4.删除操作中用到的两个外部函数5.测试一、二叉树的概念二叉树是n个有限元素的集合,该集合或者为空、或者由一个称为根(root)的元素及两个不相交的、被分别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成,是有序树。当集合为空时,称该二叉树为空二叉树。在二叉树中,一个元素也称作一个节点二、pytho
- 九、考研数据结构笔记——二叉树遍历和线索二叉树构造,常见易错点
红袜子i
考研数据结构数据结构算法树结构
一、二叉树的遍历按照某条搜索路径访问树中每个结点,使得每个结点均被访问。主要分为先序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历,层序遍历二、先序遍历2.1手算考试一般给一个树的形状,写出他的先序遍历2.2代码递归先序遍历代码voidPreOrder(BiTreeT){if(T!=NULL)visit(T);//访问根结点PreOrder(T->lchild);//递归遍历左子树PreOrder(T->rchild)
- [排序算法]-拿捏堆排序法
芫荽_
DataStructure&Algorithms二叉树算法数据结构排序算法堆排序
彻底搞懂堆排序法基本介绍核心思想实例讲解主要思路图示演示代码实现基本介绍建堆-交换,往复进行至有序。——爱因斯坦核心思想堆排序是利用堆这种数据结构而设计的一种排序算法,堆排序是一种选择排序,它的最坏,最好,平均时间复杂度均为O(nlogn),它也是不稳定排序。堆是具有以下性质的完全二叉树:每个结点的值都大于或等于其左右孩子结点的值,称为大顶堆,注意:没有要求结点的左孩子的值和右孩子的值的大小关系。
- java将json字符串转换成对象,看这篇足矣了!
imtokenmax合约众筹
程序员面试经验分享java
20个二叉树面试高频0.几个概念1.求二叉树中的节点个数2.求二叉树的最大层数(最大深度)3.先序遍历/前序遍历4.中序遍历5.后序遍历6.分层遍历7.求二叉树第K层的节点个数8.求二叉树第K层的叶子节点个数9.判断两棵二叉树是否结构相同10.判断二叉树是不是平衡二叉树11.求二叉树的镜像12.求二叉树中两个节点的最低公共祖先节点13.求二叉树的直径14.由前序遍历序列和中序遍历序列重建二叉树15
- 面试题28:对称的二叉树
繁星追逐
请实现一个函数,用来判断一颗二叉树是不是对称的。注意,如果一个二叉树同此二叉树的镜像是同样的,定义其为对称的。思路一:递归解决,写一个递归函数,参数是左右子树,从根节点开始调用,递归终结点为左右子树都为空,即对应线路上对称,或者只有一个为空,以及不相等都提出跳出,最后返回调用自身分别比较后两个节点的左右子节点。(左对右,右对左)publicclassTreeNode{intval=0;TreeNo
- [星球大战]阿纳金的背叛
comsci
本来杰迪圣殿的长老是不同意让阿纳金接受训练的.........
但是由于政治原因,长老会妥协了...这给邪恶的力量带来了机会
所以......现代的地球联邦接受了这个教训...绝对不让某些年轻人进入学院
- 看懂它,你就可以任性的玩耍了!
aijuans
JavaScript
javascript作为前端开发的标配技能,如果不掌握好它的三大特点:1.原型 2.作用域 3. 闭包 ,又怎么可以说你学好了这门语言呢?如果标配的技能都没有撑握好,怎么可以任性的玩耍呢?怎么验证自己学好了以上三个基本点呢,我找到一段不错的代码,稍加改动,如果能够读懂它,那么你就可以任性了。
function jClass(b
- Java常用工具包 Jodd
Kai_Ge
javajodd
Jodd 是一个开源的 Java 工具集, 包含一些实用的工具类和小型框架。简单,却很强大! 写道 Jodd = Tools + IoC + MVC + DB + AOP + TX + JSON + HTML < 1.5 Mb
Jodd 被分成众多模块,按需选择,其中
工具类模块有:
jodd-core &nb
- SpringMvc下载
120153216
springMVC
@RequestMapping(value = WebUrlConstant.DOWNLOAD)
public void download(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,String fileName) {
OutputStream os = null;
InputStream is = null;
- Python 标准异常总结
2002wmj
python
Python标准异常总结
AssertionError 断言语句(assert)失败 AttributeError 尝试访问未知的对象属性 EOFError 用户输入文件末尾标志EOF(Ctrl+d) FloatingPointError 浮点计算错误 GeneratorExit generator.close()方法被调用的时候 ImportError 导入模块失
- SQL函数返回临时表结构的数据用于查询
357029540
SQL Server
这两天在做一个查询的SQL,这个SQL的一个条件是通过游标实现另外两张表查询出一个多条数据,这些数据都是INT类型,然后用IN条件进行查询,并且查询这两张表需要通过外部传入参数才能查询出所需数据,于是想到了用SQL函数返回值,并且也这样做了,由于是返回多条数据,所以把查询出来的INT类型值都拼接为了字符串,这时就遇到问题了,在查询SQL中因为条件是INT值,SQL函数的CAST和CONVERST都
- java 时间格式化 | 比较大小| 时区 个人笔记
7454103
javaeclipsetomcatcMyEclipse
个人总结! 不当之处多多包含!
引用 1.0 如何设置 tomcat 的时区:
位置:(catalina.bat---JAVA_OPTS 下面加上)
set JAVA_OPT
- 时间获取Clander的用法
adminjun
Clander时间
/**
* 得到几天前的时间
* @param d
* @param day
* @return
*/
public static Date getDateBefore(Date d,int day){
Calend
- JVM初探与设置
aijuans
java
JVM是Java Virtual Machine(Java虚拟机)的缩写,JVM是一种用于计算设备的规范,它是一个虚构出来的计算机,是通过在实际的计算机上仿真模拟各种计算机功能来实现的。Java虚拟机包括一套字节码指令集、一组寄存器、一个栈、一个垃圾回收堆和一个存储方法域。 JVM屏蔽了与具体操作系统平台相关的信息,使Java程序只需生成在Java虚拟机上运行的目标代码(字节码),就可以在多种平台
- SQL中ON和WHERE的区别
avords
SQL中ON和WHERE的区别
数据库在通过连接两张或多张表来返回记录时,都会生成一张中间的临时表,然后再将这张临时表返回给用户。 www.2cto.com 在使用left jion时,on和where条件的区别如下: 1、 on条件是在生成临时表时使用的条件,它不管on中的条件是否为真,都会返回左边表中的记录。
- 说说自信
houxinyou
工作生活
自信的来源分为两种,一种是源于实力,一种源于头脑.实力是一个综合的评定,有自身的能力,能利用的资源等.比如我想去月亮上,要身体素质过硬,还要有飞船等等一系列的东西.这些都属于实力的一部分.而头脑不同,只要你头脑够简单就可以了!同样要上月亮上,你想,我一跳,1米,我多跳几下,跳个几年,应该就到了!什么?你说我会往下掉?你笨呀你!找个东西踩一下不就行了吗?
无论工作还
- WEBLOGIC事务超时设置
bijian1013
weblogicjta事务超时
系统中统计数据,由于调用统计过程,执行时间超过了weblogic设置的时间,提示如下错误:
统计数据出错!
原因:The transaction is no longer active - status: 'Rolling Back. [Reason=weblogic.transaction.internal
- 两年已过去,再看该如何快速融入新团队
bingyingao
java互联网融入架构新团队
偶得的空闲,翻到了两年前的帖子
该如何快速融入一个新团队,有所感触,就记下来,为下一个两年后的今天做参考。
时隔两年半之后的今天,再来看当初的这个博客,别有一番滋味。而我已经于今年三月份离开了当初所在的团队,加入另外的一个项目组,2011年的这篇博客之后的时光,我很好的融入了那个团队,而直到现在和同事们关系都特别好。大家在短短一年半的时间离一起经历了一
- 【Spark七十七】Spark分析Nginx和Apache的access.log
bit1129
apache
Spark分析Nginx和Apache的access.log,第一个问题是要对Nginx和Apache的access.log文件进行按行解析,按行解析就的方法是正则表达式:
Nginx的access.log解析正则表达式
val PATTERN = """([^ ]*) ([^ ]*) ([^ ]*) (\\[.*\\]) (\&q
- Erlang patch
bookjovi
erlang
Totally five patchs committed to erlang otp, just small patchs.
IMO, erlang really is a interesting programming language, I really like its concurrency feature.
but the functional programming style
- log4j日志路径中加入日期
bro_feng
javalog4j
要用log4j使用记录日志,日志路径有每日的日期,文件大小5M新增文件。
实现方式
log4j:
<appender name="serviceLog"
class="org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender">
<param name="Encoding" v
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-桥接模式
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
/**
* 个人觉得关于桥接模式的例子,蜡笔和毛笔这个例子是最贴切的:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhenyulu/articles/67016.html
* 笔和颜色是可分离的,蜡笔把两者耦合在一起了:一支蜡笔只有一种
- windows7下SVN和Eclipse插件安装
chenyu19891124
eclipse插件
今天花了一天时间弄SVN和Eclipse插件的安装,今天弄好了。svn插件和Eclipse整合有两种方式,一种是直接下载插件包,二种是通过Eclipse在线更新。由于之前Eclipse版本和svn插件版本有差别,始终是没装上。最后在网上找到了适合的版本。所用的环境系统:windows7JDK:1.7svn插件包版本:1.8.16Eclipse:3.7.2工具下载地址:Eclipse下在地址:htt
- [转帖]工作流引擎设计思路
comsci
设计模式工作应用服务器workflow企业应用
作为国内的同行,我非常希望在流程设计方面和大家交流,刚发现篇好文(那么好的文章,现在才发现,可惜),关于流程设计的一些原理,个人觉得本文站得高,看得远,比俺的文章有深度,转载如下
=================================================================================
自开博以来不断有朋友来探讨工作流引擎该如何
- Linux 查看内存,CPU及硬盘大小的方法
daizj
linuxcpu内存硬盘大小
一、查看CPU信息的命令
[root@R4 ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep "model name" && cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep "physical id"
model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU X5450 @ 3.00GHz
model name :
- linux 踢出在线用户
dongwei_6688
linux
两个步骤:
1.用w命令找到要踢出的用户,比如下面:
[root@localhost ~]# w
18:16:55 up 39 days, 8:27, 3 users, load average: 0.03, 0.03, 0.00
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
- 放手吧,就像不曾拥有过一样
dcj3sjt126com
内容提要:
静悠悠编著的《放手吧就像不曾拥有过一样》集结“全球华语世界最舒缓心灵”的精华故事,触碰生命最深层次的感动,献给全世界亿万读者。《放手吧就像不曾拥有过一样》的作者衷心地祝愿每一位读者都给自己一个重新出发的理由,将那些令你痛苦的、扛起的、背负的,一并都放下吧!把憔悴的面容换做一种清淡的微笑,把沉重的步伐调节成春天五线谱上的音符,让自己踏着轻快的节奏,在人生的海面上悠然漂荡,享受宁静与
- php二进制安全的含义
dcj3sjt126com
PHP
PHP里,有string的概念。
string里,每个字符的大小为byte(与PHP相比,Java的每个字符为Character,是UTF8字符,C语言的每个字符可以在编译时选择)。
byte里,有ASCII代码的字符,例如ABC,123,abc,也有一些特殊字符,例如回车,退格之类的。
特殊字符很多是不能显示的。或者说,他们的显示方式没有标准,例如编码65到哪儿都是字母A,编码97到哪儿都是字符
- Linux下禁用T440s,X240的一体化触摸板(touchpad)
gashero
linuxThinkPad触摸板
自打1月买了Thinkpad T440s就一直很火大,其中最让人恼火的莫过于触摸板。
Thinkpad的经典就包括用了小红点(TrackPoint)。但是小红点只能定位,还是需要鼠标的左右键的。但是自打T440s等开始启用了一体化触摸板,不再有实体的按键了。问题是要是好用也行。
实际使用中,触摸板一堆问题,比如定位有抖动,以及按键时会有飘逸。这就导致了单击经常就
- graph_dfs
hcx2013
Graph
package edu.xidian.graph;
class MyStack {
private final int SIZE = 20;
private int[] st;
private int top;
public MyStack() {
st = new int[SIZE];
top = -1;
}
public void push(i
- Spring4.1新特性——Spring核心部分及其他
jinnianshilongnian
spring 4.1
目录
Spring4.1新特性——综述
Spring4.1新特性——Spring核心部分及其他
Spring4.1新特性——Spring缓存框架增强
Spring4.1新特性——异步调用和事件机制的异常处理
Spring4.1新特性——数据库集成测试脚本初始化
Spring4.1新特性——Spring MVC增强
Spring4.1新特性——页面自动化测试框架Spring MVC T
- 配置HiveServer2的安全策略之自定义用户名密码验证
liyonghui160com
具体从网上看
http://doc.mapr.com/display/MapR/Using+HiveServer2#UsingHiveServer2-ConfiguringCustomAuthentication
LDAP Authentication using OpenLDAP
Setting
- 一位30多的程序员生涯经验总结
pda158
编程工作生活咨询
1.客户在接触到产品之后,才会真正明白自己的需求。
这是我在我的第一份工作上面学来的。只有当我们给客户展示产品的时候,他们才会意识到哪些是必须的。给出一个功能性原型设计远远比一张长长的文字表格要好。 2.只要有充足的时间,所有安全防御系统都将失败。
安全防御现如今是全世界都在关注的大课题、大挑战。我们必须时时刻刻积极完善它,因为黑客只要有一次成功,就可以彻底打败你。 3.
- 分布式web服务架构的演变
自由的奴隶
linuxWeb应用服务器互联网
最开始,由于某些想法,于是在互联网上搭建了一个网站,这个时候甚至有可能主机都是租借的,但由于这篇文章我们只关注架构的演变历程,因此就假设这个时候已经是托管了一台主机,并且有一定的带宽了,这个时候由于网站具备了一定的特色,吸引了部分人访问,逐渐你发现系统的压力越来越高,响应速度越来越慢,而这个时候比较明显的是数据库和应用互相影响,应用出问题了,数据库也很容易出现问题,而数据库出问题的时候,应用也容易
- 初探Druid连接池之二——慢SQL日志记录
xingsan_zhang
日志连接池druid慢SQL
由于工作原因,这里先不说连接数据库部分的配置,后面会补上,直接进入慢SQL日志记录。
1.applicationContext.xml中增加如下配置:
<bean abstract="true" id="mysql_database" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourc