Pytorch深度学习(4) -- BN层及ResNet + DenseNet实现
Pytorch深度学习(4) -- BN层及ResNet + DenseNet实现
- 1.批量归一化(BN)
- 2.ResNet
-
- 2.1 残差块
- 2.2 ResNet 模型实现
-
- 结构:
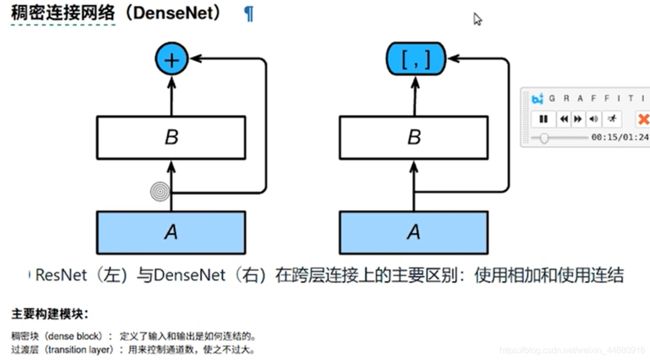
- 3.DenseNet 稠密连接网络
-
- 3.1 稠密块(DenseBlock)
- 3.3 过滤层(transition_block)
- 3.4 DenseNet模型总实现
1.批量归一化(BN)
nn.BatchNorm2d(6) — 卷积层使用,超参数为输出通道数
nn.BatchNorm1d(120) – 全连接层使用,超参数为输出单元个数
2.ResNet
2.1 残差块
输入为X + Y,因而X Y的输出通道要一致
可以用1*1的卷积层来调整通道的大小

class Residual(nn.Module):
#可以设定输出通道数、是否使用额外的1x1卷积层来修改通道数以及卷积层的步幅。
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, use_1x1conv=False, stride=1):
super(Residual, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if use_1x1conv:
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride)
else:
self.conv3 = None
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
def forward(self, X):
Y = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(X)))
Y = self.bn2(self.conv2(Y))
if self.conv3:
X = self.conv3(X)
return F.relu(Y + X)
2.2 ResNet 模型实现
结构:
卷积(64,7x7,3)
批量一体化
最大池化(3x3,2)
残差块x4 (通过步幅为2的残差块在每个模块之间减小高和宽)
全局平均池化
全连接
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
def resnet_block(in_channels, out_channels, num_residuals, first_block=False):
if first_block:
assert in_channels == out_channels # 第一个模块的通道数同输入通道数一致
blk = []
for i in range(num_residuals):
if i == 0 and not first_block:
blk.append(Residual(in_channels, out_channels, use_1x1conv=True, stride=2))
else:
blk.append(Residual(out_channels, out_channels))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
net.add_module("resnet_block1", resnet_block(64, 64, 2, first_block=True))
net.add_module("resnet_block2", resnet_block(64, 128, 2))
net.add_module("resnet_block3", resnet_block(128, 256, 2))
net.add_module("resnet_block4", resnet_block(256, 512, 2))
net.add_module("global_avg_pool", d2l.GlobalAvgPool2d()) # GlobalAvgPool2d的输出: (Batch, 512, 1, 1)
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(d2l.FlattenLayer(), nn.Linear(512, 10)))
输入结构:
X = torch.rand((1, 1, 224, 224))
for name, layer in net.named_children():
X = layer(X)
print(name, ' output shape:\t', X.shape)
0 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
1 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
2 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
3 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56])
resnet_block1 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56])
resnet_block2 output shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 28, 28])
resnet_block3 output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14])
resnet_block4 output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 7, 7])
global_avg_pool output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 1, 1])
fc output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
3.DenseNet 稠密连接网络
主要由稠密层和过滤层组成
稠密层:使X Y不必相加(输出通道一样),直接cat即可
过滤层:防止相加之后的输出通道数过大
3.1 稠密块(DenseBlock)
def conv_block(in_channels, out_channels): # 卷积层一套
blk = nn.Sequential(nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
return blk
class DenseBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_convs, in_channels, out_channels):
super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
net = []
for i in range(num_convs):
in_c = in_channels + i * out_channels
net.append(conv_block(in_c, out_channels))
self.net = nn.ModuleList(net)
self.out_channels = in_channels + num_convs * out_channels # 计算输出通道数
def forward(self, X):
for blk in self.net:
Y = blk(X)
X = torch.cat((X, Y), dim=1) # 在通道维上将输入和输出连结
return X
3.3 过滤层(transition_block)
1*1卷积层:来减小通道数
步幅为2的平均池化层:减半高和宽
# 使得23的输出通道数变为10
def transition_block(in_channels, out_channels):
blk = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
return blk
blk = transition_block(23, 10)
blk(Y).shape # torch.Size([4, 10, 4, 4])
3.4 DenseNet模型总实现
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
num_channels, growth_rate = 64, 32 # num_channels为当前的通道数
num_convs_in_dense_blocks = [4, 4, 4, 4]
for i, num_convs in enumerate(num_convs_in_dense_blocks):
DB = DenseBlock(num_convs, num_channels, growth_rate)
net.add_module("DenseBlosk_%d" % i, DB)
# 上一个稠密块的输出通道数
num_channels = DB.out_channels
# 在稠密块之间加入通道数减半的过渡层
if i != len(num_convs_in_dense_blocks) - 1:
net.add_module("transition_block_%d" % i, transition_block(num_channels, num_channels // 2))
num_channels = num_channels // 2
net.add_module("BN", nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels))
net.add_module("relu", nn.ReLU())
net.add_module("global_avg_pool", d2l.GlobalAvgPool2d()) # GlobalAvgPool2d的输出: (Batch, num_channels, 1, 1)
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(d2l.FlattenLayer(), nn.Linear(num_channels, 10)))
X = torch.rand((1, 1, 96, 96))
for name, layer in net.named_children():
X = layer(X)
print(name, ' output shape:\t', X.shape)
0 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 48, 48])
1 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 48, 48])
2 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 48, 48])
3 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 24, 24])
DenseBlosk_0 output shape: torch.Size([1, 192, 24, 24])
transition_block_0 output shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 12, 12])
DenseBlosk_1 output shape: torch.Size([1, 224, 12, 12])
transition_block_1 output shape: torch.Size([1, 112, 6, 6])
DenseBlosk_2 output shape: torch.Size([1, 240, 6, 6])
transition_block_2 output shape: torch.Size([1, 120, 3, 3])
DenseBlosk_3 output shape: torch.Size([1, 248, 3, 3])
BN output shape: torch.Size([1, 248, 3, 3])
relu output shape: torch.Size([1, 248, 3, 3])
global_avg_pool output shape: torch.Size([1, 248, 1, 1])
fc output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])