timus_1007_bfs
图像编码
题目描述:
有这样一副图,它有黑白像素,黑像素的坐标在1~10之间。有很多种方法来编码这个图。例如下面的图:
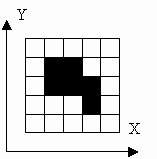
一种表示方法是只描述黑像素,并按x坐标的增序描述,如果x相同,则按y的增序描述,每个像素占一行。按这种编码方式的到的上面图像的编码为:
6
2 3
2 4
3 3
3 4
4 2
4 3
另一种表示方法是第一行包含最左边的黑像素的坐标,然后下一行是第一个黑像素的相邻黑像素,再下一行是第一个黑像素的第一个相邻黑像素的相邻黑像素(有点绕口,其实就是按bfs的方向描述),再下一行是第一个黑像素的第二个相邻黑像素的相邻黑像素,依次类推,直到描述完所有的黑像素。相邻像素的描述从右边开始,按逆时针方向,分别用R,T,L,B来表示,如果碰到某个相邻的黑像素已经被描诉了,就忽略描述该相邻黑像素。每一行都表示某个像素的相邻黑像素,并以“,”结尾。所有黑像素描述完后以“.”结尾。按这种编码方式的到的上面图像的编码为:
2 3
RT,
RT,
,
B,
,
.
要求在给定的一种图像编码的情况下,给出另一种图像编码。
思路:
如果是第一种转第二种,定义一个二维数组来表示这个图像,从最左边的那个点开始,使用bfs搜索四个方向的像素,根据是否有黑像素输出RTLB。
1 void change_two(int lx, int by) 2 { 3 struct queue queue; 4 struct coordinate coord, temp; 5 int flag = 0; //控制输出 6 7 coord.x = lx; 8 coord.y = by; 9 init_queue(&queue); 10 push(&queue, coord); 11 printf("%d %d\n", lx, by); 12 map[lx][by] = 0; 13 while (!is_empty(queue)) 14 { 15 if (!flag) 16 flag = 1; 17 else 18 printf(",\n"); 19 coord = pop(&queue); 20 if (coord.x + 1 <= 10 && map[coord.x + 1][coord.y]) 21 { 22 //R 23 temp.x = coord.x + 1; 24 temp.y = coord.y; 25 push(&queue, temp); 26 printf("R"); 27 map[temp.x][temp.y] = 0; 28 } 29 if (coord.y + 1 <= 10 && map[coord.x][coord.y + 1]) 30 { 31 //T 32 temp.x = coord.x; 33 temp.y = coord.y + 1; 34 push(&queue, temp); 35 printf("T"); 36 map[temp.x][temp.y] = 0; 37 } 38 if (coord.x - 1 >= 1 && map[coord.x - 1][coord.y]) 39 { 40 //L 41 temp.x = coord.x - 1; 42 temp.y = coord.y; 43 push(&queue, temp); 44 printf("L"); 45 map[temp.x][temp.y] = 0; 46 } 47 if (coord.y - 1 >= 1 && map[coord.x][coord.y - 1]) 48 { 49 //B 50 temp.x = coord.x; 51 temp.y = coord.y - 1; 52 push(&queue, temp); 53 printf("B"); 54 map[temp.x][temp.y] = 0; 55 } 56 } 57 printf("."); 58 }
代码20-50行分别以RTLB顺序搜索当前黑像素相邻的像素,如果有黑像素,就将其坐标压入队列,等待下次处理该像素的相邻像素,同时标记map,表示已经访问了该像素。
如果是第二种转第一种,就是找到这个图像对应的二维数组。从给定的点开始,使用bfs来找到每个点相邻四周的黑像素,那后将这些黑像素标记到二维数组中。
1 void change_one(int lx, int by) 2 { 3 struct queue queue; 4 struct coordinate coord; 5 struct coordinate temp; 6 struct coordinate ans[100]; 7 char line[6]; 8 int i, j, maxx, maxy, n; 9 10 maxx = coord.x = lx; 11 maxy = coord.y = by; 12 init_queue(&queue); 13 push(&queue, coord); 14 map[coord.x][coord.y] = 1; 15 while (!is_empty(queue)) 16 { 17 coord = pop(&queue); 18 gets(line); 19 i = 0; 20 while (line[i] != ',' && line[i] != '.') 21 { 22 if (line[i] == 'R') 23 { 24 temp.x = coord.x + 1; 25 if (temp.x > maxx) 26 maxx = temp.x; 27 temp.y = coord.y; 28 } 29 else if (line[i] == 'T') 30 { 31 temp.x = coord.x; 32 temp.y = coord.y + 1; 33 if (temp.y > maxy) 34 maxy = temp.y; 35 } 36 else if (line[i] == 'L') 37 { 38 temp.x = coord.x - 1; 39 temp.y = coord.y; 40 } 41 else 42 { 43 temp.x = coord.x; 44 temp.y = coord.y - 1; 45 } 46 map[temp.x][temp.y] = 1; 47 push(&queue, temp); 48 i++; 49 } 50 } 51 n = 0; 52 for (i = 1; i <= maxx; i++) 53 for (j = 1; j <= maxy; j++) 54 if (map[i][j]) 55 { 56 ans[n].x = i; 57 ans[n ++].y = j; 58 } 59 printf("%d\n", n); 60 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) 61 printf("%d %d\n", ans[i].x, ans[i].y); 62 }
第二种转第一种其实是bfs的逆过程,代码第15-50行目的就是根据当前的黑色像素坐标以及输入数据来获得相邻黑色像素的坐标。
本质上这个题目考察的就是bfs,不过这道题目的输入有点麻烦,因为事先我们无法判断输入的数据是哪种编码,所以必须靠我们自己写个判断函数。我的方法是根据第一行的输入,如果第一行输入的只有一个数,说明输入是第一种编码;如果是两个数,说明是第二种编码。还有就是代码完全是用c写的,不能像使用c++那用直接使用自带的queue。所以只有靠自己实现了个循环队列,根据题目,队列中的最大个数是不会超过12的,所以自己写队列还是可以接受的,不过就是编码花的时间比较久(汗!!以后直接用c++的queue了,这样省事多了,而且代码还很健壮!!)。