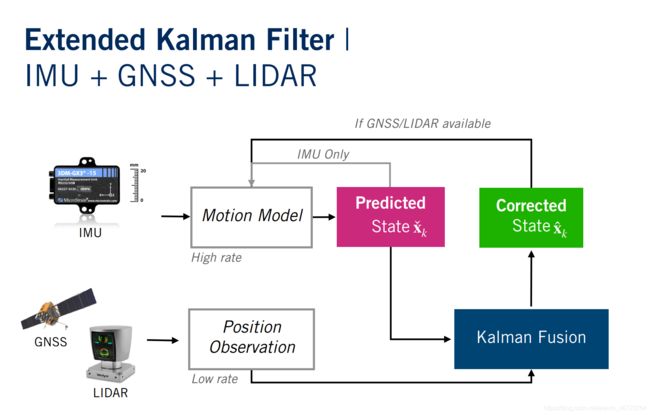
车载多传感器融合定位方案Pipeline:IMU,CNSS,LIDAR
为什么用IMU, CNSS, LIDAR的组合
IMU可以提供连续的位置信息,以补充GNSS可能因为地形等原因缺失的数据信息
GNSS可以提供绝对的位置信息,减轻IMU累积的数据漂移问题
LIDAR可以根据准确的周边信息,确定自己在地图中的位置
三者可相互补充共同确定车辆的状态和所处位置
整体流程图
整个方案的大体思路为:将IMU数据作为输入带入运动学方程计算nominal state,当其他观测数据available时,将其带入计算车辆error state,然后两者相加得出最终的更正状态,用于后续迭代。当没有观测数据时,就将预测数据作为结果进行迭代。
采用这种方式的好处是:将最终的true state的确定分成了两个,nominal state只和状态方程和输入有关,这样一来我们就能很方便的在方程上增加想要的约束。
另一个好处在于能很好地处理传感器数据暂时丢失的问题。有观测数据的时候就拿来修正状态,没有的时候就用预测状态,应用起来比较flexible。当然只用IMU时,数据漂移现象还是没法避免,个人感觉在这种情况下,可能还需要camera辅助。

1. 同步传感器坐标系
通常情况下,IMU和GNSS数据用的是车身坐标系,而LIDAR坐标系与传感器on board位置相关,因此要将LIDAR数据转换到车身坐标系,完成传感器数据坐标系的统一
C_li = np.array([
[ 0.9975 , -0.04742, 0.05235],
[ 0.04992, 0.99763, -0.04742],
[-0.04998, 0.04992, 0.9975 ]
])
t_i_li = np.array([0.5, 0.1, 0.5])
# Transform from the LIDAR frame to the vehicle (IMU) frame.
lidar.data = (C_li @ lidar.data.T).T + t_i_li
2. 设置预估传感器方差和噪音常量
这是滤波器最重要的方面之一,如果出现标定错误或者数据丢失时,通常需要调整传感器方差进行补偿。
var_imu_f = 0.10
var_imu_w = 0.001
var_gnss = 0.01
var_lidar = 100
g = np.array([0, 0, -9.81]) # gravity 1x3
l_jac = np.zeros([9, 6])
l_jac[3:, :] = np.eye(6) # motion model noise jacobian
h_jac = np.zeros([3, 9])
h_jac[:, :3] = np.eye(3) # measurement model jacobian
3. 设置ES-EKF初始变量值
车辆状态包括:位置P_k(3,1), 速度V_k(3,1),姿态q_k(4,1)
IMU数据作为Motion model 的输入:比力f_k(3,1), 角速度(3,1)
同时分别设置Gnss/LIDAR数据索引,因为这些数据并不能100%随时获得,和带有各自的时间戳

p_est = np.zeros([imu_f.data.shape[0], 3]) # position estimates
v_est = np.zeros([imu_f.data.shape[0], 3]) # velocity estimates
q_est = np.zeros([imu_f.data.shape[0], 4]) # orientation estimates as quaternions
p_cov = np.zeros([imu_f.data.shape[0], 9, 9]) # covariance matrices at each timestep
# Set initial values.
p_est[0] = gt.p[0] #p_est.shape (10918, 3)
v_est[0] = gt.v[0]
q_est[0] = Quaternion(euler=gt.r[0]).to_numpy()
p_cov[0] = np.zeros(9) # covariance of estimate
gnss_i = 0 #index of gnss/lidar data
lidar_i = 0
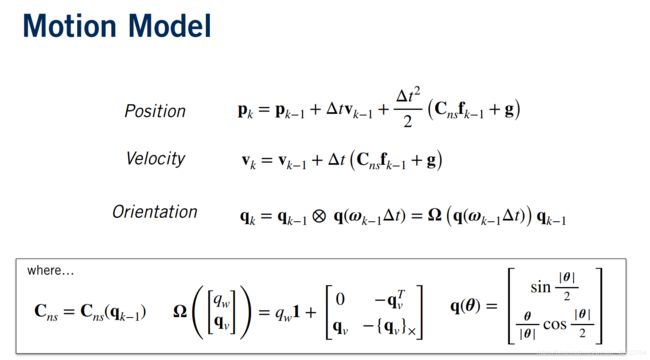
4. 根据IMU数据预估车辆状态-prediction
IMU数据作为输入,根据motion model 预测车辆状态
# 1. Update state with IMU inputs
#orientation of THE sensor why*? Cns
rotation_matrix = Quaternion(*q_est[k - 1]).to_mat() #.shape = 3x3
# 1.1 Linearize the motion model and compute Jacobians 3x1; 3x1, 4x1
p_est[k] = p_est[k-1] + delta_t*v_est[k-1] + (delta_t**2/2)*(rotation_matrix.dot(imu_f.data[k-1])+g)
v_est[k] = v_est[k-1] + delta_t*(rotation_matrix.dot(imu_f.data[k-1])+g)
q_est[k] = Quaternion(axis_angle=imu_w.data[k-1]*delta_t).quat_mult_right(q_est[k-1])
#predicted data used when external data is not available
F = np.identity(9)
#given in C2M5L2
F[:3,3:6] = delta_t*np.identity(3)
F[3:6,6:] = -(rotation_matrix.dot(skew_symmetric(imu_f.data[k-1].reshape((3,1)))))
#measurement noise given in C2M5L2
Q = np.identity(6)
Q[:,:3] *= (delta_t**2)*var_imu_f
Q[:,-3:] *= (delta_t**2)*var_imu_w
# 2. Propagate uncertainty
p_cov[k] = F.dot(p_cov[k-1]).dot(F.T) + l_jac.dot(Q).dot(l_jac.T)
在其他传感器数据non available的情况下,在这里计算出来的predicted state就是下一轮更新用的true state
5. 检测GNSS或LIDAR数据可用性
当与IMU数据时间戳对应的LIDAR/GNSS数据存在时,对车辆状态进行更新。
# 3. Check availability of GNSS and LIDAR measurements : only part value get corrected
#don't forget to check for time consistance
if lidar_i<lidar.t.shape[0] and lidar.t[lidar_i] == imu_f.t[k-1]:
#y_k need to be a 3x1 vector, lidar.data[lidar_i].shape (,3)
y_k = lidar.data[lidar_i].T
p_est[k], v_est[k], q_est[k], p_cov[k] = measurement_update(var_lidar,p_cov[k],y_k,p_est[k],v_est[k],q_est[k])
lidar_i += 1
if gnss_i<gnss.t.shape[0] and gnss.t[gnss_i] == imu_f.t[k-1]:
y_k = gnss.data[gnss_i].T
p_est[k], v_est[k], q_est[k], p_cov[k] = measurement_update(var_gnss, p_cov[k], y_k, p_est[k], v_est[k], q_est[k])
gnss_i += 1
6. 利用GNSS/LIDAR的测量数据对车辆状态更正-correction
计算卡尔曼增益和error state,然后更正预测状态(predicted state),最后更新协方差
# 3.1 Compute Kalman Gain
#R need to be 3x3 : h_jac.dot(p_cov_check).dot(h_jac.T) 3x9 9x9 9x3 shape = 3x3
I = np.identity(3)
R = I*sensor_var
#K.shape = 9x9 9x3 3x3 = 9x3
K = p_cov_check.dot(h_jac.T).dot(np.linalg.inv(h_jac.dot(p_cov_check).dot(h_jac.T)+R))
# 3.2 Compute error state
#error.shape = 9x3 (3x1-3x1) = 9x1
error = K.dot(y_k - p_check) #shape(9,)
p_del = error[:3]
v_del = error[3:6]
phi_del = error[6:]
# 3.3 Correct predicted state
p_hat = p_check + p_del
v_hat = v_check + v_del
q_hat = Quaternion(euler=phi_del).quat_mult_right(q_check) #4x1
# 3.4 Compute corrected covariance
p_cov_hat = (np.identity(9) - K.dot(h_jac)).dot(p_cov_check)
#Output: p_hat 3x1; v_hat 3x1; q_hat 4x1; p_cov_hat 9x9
return p_hat, v_hat, q_hat, p_cov_hat
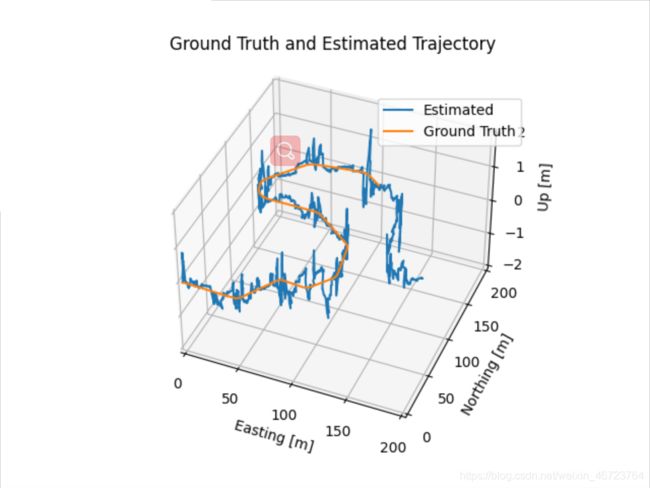
7. 结果
从效果来看位置误差在5之间,姿态误差0.5左右,较好的预测了车辆状态。