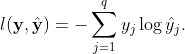1--线性神经网络(softmax回归)
1.1 softmax简述
1.1.1 softmax回归和线性回归的异同
首先线性回归是一种回归算法,根据当前数据去学习直线的两个参数,适⽤于输出为连续值的情景。而softmax回归则是一种分类算法,该算法将输出的是该样本属于每个类别的概率(即输出值个数等于标签⾥的类别数),适用于对离散值的预测问题(引⼊了softmax 运算使得输出更适合离散值的预测和训练)。
1.1.2 softmax函数
softmax函数能够将未规范化的预测变换为非负数并且总和为1,同时让模型保持可导的性质。首先对每个未规范化的预测求幂,这样可以确保输出非负,为了确保最终输出的概率值总和为1,再让每个求幂后的结果除以它们的总和。如下式:
1.1.3 交叉熵损失函数
如果跟线性回归一样使用平方损失函数![]() 这将过于严格,因为想要预测分类正确,只需要真实类别的概率大于其他类别的概率,而不需要预测概率完全等于标签概率。如yi = 3(第i个样本属于第三类),只需要yi = 1,yi=2的概率均小于yi=3就能预测正确。所以需要一个衡量两个概率分布差异的函数来作为损失函数:
这将过于严格,因为想要预测分类正确,只需要真实类别的概率大于其他类别的概率,而不需要预测概率完全等于标签概率。如yi = 3(第i个样本属于第三类),只需要yi = 1,yi=2的概率均小于yi=3就能预测正确。所以需要一个衡量两个概率分布差异的函数来作为损失函数:
1.2 softmax回归实现
!pip install git+https://github.com/d2l-ai/d2l-zh@release # installing d2l
import torch
from IPython import display
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
num_inputs = 784# 展平每个图像,把它们看作长度为28*28=784的向量
num_outputs = 10#一共10个类别
W = torch.normal(0, 0.01, size=(num_inputs, num_outputs), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(num_outputs, requires_grad=True)
print("heh",W.shape[0])
#实现softmax的三个步骤
def softmax(X):
X_exp = torch.exp(X)# 1)对每个项求幂
partition = X_exp.sum(1, keepdim=True)# 2)对每一行求和(即每个样本)得到规范化的分母
return X_exp / partition # 这里应用了广播机制 3)将每一行除以规范化分母 确保结果的和为1
def net(X):
return softmax(torch.matmul(X.reshape((-1, W.shape[0])), W) + b)
def cross_entropy(y_hat, y):#交叉损失熵函数
return - torch.log(y_hat[range(len(y_hat)), y])#得到真实类别预测的概率
def accuracy(y_hat, y):#计算预测正确的数量
if len(y_hat.shape) > 1 and y_hat.shape[1] > 1:
#y_hat是矩阵,那么假定第二个维度存储每个类的预测分数。
#使用argmax获得每行中最大元素的索引来获得预测类别
y_hat = y_hat.argmax(axis=1)
cmp = y_hat.type(y.dtype) == y#如果预测类别相同 cmp=1
return float(cmp.type(y.dtype).sum())#得到正确预测的数量
def evaluate_accuracy(net, data_iter):
#计算在指定数据集上模型的精度
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.eval() # 将模型设置为评估模式
metric = Accumulator(2) #Accumulator用于对多个变量进行累加 这里是在Accumulator实例中创建了2个变量,分别用于存储正确预测的数量和预测的总数量
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in data_iter:
metric.add(accuracy(net(X), y), y.numel())#累加
return metric[0] / metric[1]#预测正确的个数/预测总数
class Accumulator: #在n个变量上累加
def __init__(self, n):
self.data = [0.0] * n
def add(self, *args):
self.data = [a + float(b) for a, b in zip(self.data, args)]
def reset(self):
self.data = [0.0] * len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.data[idx]
def train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, updater):#训练模型一个迭代周期(定义见第3章)"""
# 将模型设置为训练模式
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.train()
# 训练损失总和、训练准确度总和、样本数
metric = Accumulator(3)
for X, y in train_iter:
# 计算梯度并更新参数
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
if isinstance(updater, torch.optim.Optimizer):
# 使用PyTorch内置的优化器和损失函数
updater.zero_grad()
l.mean().backward()
updater.step()
else:
# 使用定制的优化器和损失函数
l.sum().backward()
updater(X.shape[0])
metric.add(float(l.sum()), accuracy(y_hat, y), y.numel())
# 返回训练损失和训练精度
#print('训练损失:",(metric[0] / metric[2]),"训练精度:",(metric[1] / metric[2]))
return metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[2]
class Animator: # 在动画中绘制数据
def __init__(self, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=None, xlim=None,
ylim=None, xscale='linear', yscale='linear',
fmts=('-', 'm--', 'g-.', 'r:'), nrows=1, ncols=1,
figsize=(3.5, 2.5)):
# 增量地绘制多条线
if legend is None:
legend = []
d2l.use_svg_display()
self.fig, self.axes = d2l.plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize=figsize)
if nrows * ncols == 1:
self.axes = [self.axes, ]
# 使用lambda函数捕获参数
self.config_axes = lambda: d2l.set_axes(
self.axes[0], xlabel, ylabel, xlim, ylim, xscale, yscale, legend)
self.X, self.Y, self.fmts = None, None, fmts
def add(self, x, y):
# 向图表中添加多个数据点
if not hasattr(y, "__len__"):
y = [y]
n = len(y)
if not hasattr(x, "__len__"):
x = [x] * n
if not self.X:
self.X = [[] for _ in range(n)]
if not self.Y:
self.Y = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for i, (a, b) in enumerate(zip(x, y)):
if a is not None and b is not None:
self.X[i].append(a)
self.Y[i].append(b)
self.axes[0].cla()
for x, y, fmt in zip(self.X, self.Y, self.fmts):
self.axes[0].plot(x, y, fmt)
self.config_axes()
display.display(self.fig)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
def train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater): #训练模型(定义见第3章)
animator = Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0.3, 0.9],
legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_metrics = train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, updater)
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, train_metrics + (test_acc,))
train_loss, train_acc = train_metrics
assert train_loss < 0.5, train_loss
assert train_acc <= 1 and train_acc > 0.7, train_acc
assert test_acc <= 1 and test_acc > 0.7, test_acc
lr = 0.1
def updater(batch_size):
return d2l.sgd([W, b], lr, batch_size)#随机小批量梯度下降
!pip install matplotlib==3.0.0#要将matplotlib替换为3.0.0的版本 不然画图有问题
num_epochs = 10
train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, cross_entropy, num_epochs, updater)
def predict_ch3(net, test_iter, n=6): #预测标签
for X, y in test_iter:
break
trues = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(y)
preds = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(net(X).argmax(axis=1))
titles = [true +'\n' + pred for true, pred in zip(trues, preds)]
d2l.show_images(
X[0:n].reshape((n, 28, 28)), 1, n, titles=titles[0:n])
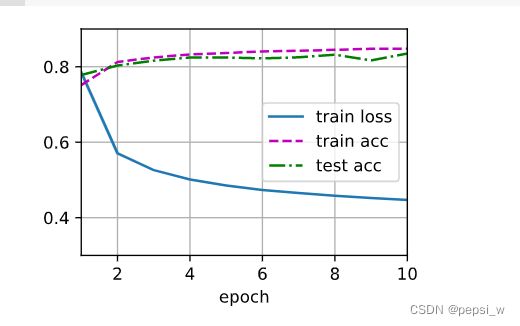
predict_ch3(net, test_iter)
print("测试集上的精度:",evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter))运行结果:
1.3softmax使用模块实现
!pip install git+https://github.com/d2l-ai/d2l-zh@release # installing d2l
!pip install matplotlib==3.0.0
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
# PyTorch不会隐式地调整输入的形状。因此,
# 我们在线性层前定义了展平层(flatten),来调整网络输入的形状
#nn.Sequential有顺序的容器,将特定神经网络模块按照在传入构造器的顺序依次被添加到计算图中执行。
#torch.flatten(x)等于torch.flatten(x,0)默认将张量拉成一维的向量 从第一维开始平坦化
#torch.nn.Flatten()默认从第二维开始平坦化
#nn.Linear 设置网络中的全连接层的
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784,10))
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01)
net.apply(init_weights)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr=0.1)
num_epochs = 10
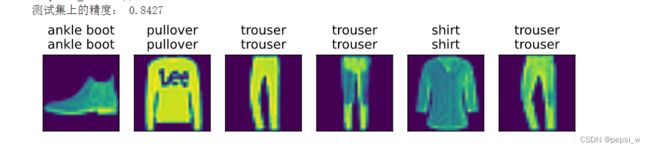
d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)
运行结果