cartographer探秘第四章之代码解析(五) --- 后端优化 --- 闭环约束1 --- PrecomputationGrid2D
本次阅读的源码为 release-1.0 版本的代码
https://github.com/googlecartographer/cartographer_ros/tree/release-1.0
https://github.com/googlecartographer/cartographer/tree/release-1.0
也可以下载我上传的 全套工作空间的代码,包括 protobuf, cartographer, cartographer_ros, ceres,
https://download.csdn.net/download/tiancailx/11224156
PrecomputationGrid2D类
这个类是多分辨率地图具体的实现,首先从他如何初始化开始。
1 初始化
这个类是在FastCorrelativeScanMatcher2D类的构造函数里进行初始化的。
1.1 FastCorrelativeScanMatcher2D类的构造函数
FastCorrelativeScanMatcher2D::FastCorrelativeScanMatcher2D(
const Grid2D& grid,
const proto::FastCorrelativeScanMatcherOptions2D& options)
: options_(options),
limits_(grid.limits()),
// 智能指针的初始化,调用PrecomputationGridStack2D类进行初始化
precomputation_grid_stack_(
common::make_unique(grid, options)) {}
// precomputation_grid_stack_的定义
std::unique_ptr precomputation_grid_stack_; 1.2 PrecomputationGridStack2D类的构造函数
PrecomputationGridStack2D 使用 vector 保存了7个不同分辨率的栅格。
PrecomputationGridStack2D::PrecomputationGridStack2D(
const Grid2D& grid,
const proto::FastCorrelativeScanMatcherOptions2D& options) {
CHECK_GE(options.branch_and_bound_depth(), 1);
// 根据配置文件中 branch_and_bound_depth 的值,默认为7,确定 最大的分辨率,也就是64个栅格合成一个格子。
const int max_width = 1 << (options.branch_and_bound_depth() - 1); // 64
// 7个不同分辨率的地图
precomputation_grids_.reserve(options.branch_and_bound_depth());
std::vector reusable_intermediate_grid;
const CellLimits limits = grid.limits().cell_limits();
// 经过滑窗后产生的栅格地图会变宽,比原地图多了width-1个格子
reusable_intermediate_grid.reserve((limits.num_x_cells + max_width - 1) *
limits.num_y_cells);
// emplace_back会生成一个临时的变量,会调用PrecomputationGrid2D的构造函数
// 分辨率逐渐变大,i=0时就是默认分辨率(0.05),i=6时,width=64,也就是64个格子合成一个值
for (int i = 0; i != options.branch_and_bound_depth(); ++i) {
const int width = 1 << i;
precomputation_grids_.emplace_back(grid, limits, width,
&reusable_intermediate_grid);
}
} 2 SlidingWindowMaximum类
在讲PrecomputationGrid2D类之前首先要说一下这个滑窗的实现。
成员变量只有一个队列,成员函数只有3个方法。
// A collection of values which can be added and later removed, and the maximum
// of the current values in the collection can be retrieved.
// All of it in (amortized) O(1).
class SlidingWindowMaximum {
public:
// 添加值,会将小于填入值的其他值删掉,并将这个值放到最后。
void AddValue(const float value) {
while (!non_ascending_maxima_.empty() &&
value > non_ascending_maxima_.back()) {
non_ascending_maxima_.pop_back();
}
non_ascending_maxima_.push_back(value);
}
// 删除值,如果第一个值等于要删除的这个值,则将这个值删掉。
void RemoveValue(const float value) {
// DCHECK for performance, since this is done for every value in the
// precomputation grid.
DCHECK(!non_ascending_maxima_.empty());
DCHECK_LE(value, non_ascending_maxima_.front());
if (value == non_ascending_maxima_.front()) {
non_ascending_maxima_.pop_front();
}
}
// 获取最大值,因为是按照顺序存储的,第一个值是最大的。
float GetMaximum() const {
// DCHECK for performance, since this is done for every value in the
// precomputation grid.
DCHECK_GT(non_ascending_maxima_.size(), 0);
return non_ascending_maxima_.front();
}
void CheckIsEmpty() const { CHECK_EQ(non_ascending_maxima_.size(), 0); }
private:
// Maximum of the current sliding window at the front. Then the maximum of the
// remaining window that came after this values first occurrence, and so on.
std::deque non_ascending_maxima_;
}; 3 PrecomputationGrid2D类
// A precomputed grid that contains in each cell (x0, y0) the maximum
// probability in the width x width area defined by x0 <= x < x0 + width and
// y0 <= y < y0.
class PrecomputationGrid2D {
public:
PrecomputationGrid2D(const Grid2D& grid, const CellLimits& limits, int width,
std::vector* reusable_intermediate_grid);
// Returns a value between 0 and 255 to represent probabilities between
// min_score and max_score.
int GetValue(const Eigen::Array2i& xy_index) const {
const Eigen::Array2i local_xy_index = xy_index - offset_;
// The static_cast is for performance to check with 2 comparisons
// xy_index.x() < offset_.x() || xy_index.y() < offset_.y() ||
// local_xy_index.x() >= wide_limits_.num_x_cells ||
// local_xy_index.y() >= wide_limits_.num_y_cells
// instead of using 4 comparisons.
if (static_cast(local_xy_index.x()) >=
static_cast(wide_limits_.num_x_cells) ||
static_cast(local_xy_index.y()) >=
static_cast(wide_limits_.num_y_cells)) {
return 0;
}
const int stride = wide_limits_.num_x_cells;
return cells_[local_xy_index.x() + local_xy_index.y() * stride];
}
// Maps values from [0, 255] to [min_score, max_score].
float ToScore(float value) const {
return min_score_ + value * ((max_score_ - min_score_) / 255.f);
}
private:
uint8 ComputeCellValue(float probability) const;
// Offset of the precomputation grid in relation to the 'grid'
// including the additional 'width' - 1 cells.
const Eigen::Array2i offset_;
// Size of the precomputation grid.
const CellLimits wide_limits_;
const float min_score_;
const float max_score_;
// Probabilites mapped to 0 to 255.
std::vector cells_;
};
4 多分辨率地图的实现
PrecomputationGrid2D::PrecomputationGrid2D(
const Grid2D& grid, const CellLimits& limits, const int width,
std::vector* reusable_intermediate_grid)
: offset_(-width + 1, -width + 1),
wide_limits_(limits.num_x_cells + width - 1,
limits.num_y_cells + width - 1),
min_score_(1.f - grid.GetMaxCorrespondenceCost()), // 0.1
max_score_(1.f - grid.GetMinCorrespondenceCost()), // 0.9
cells_(wide_limits_.num_x_cells * wide_limits_.num_y_cells) {
CHECK_GE(width, 1);
CHECK_GE(limits.num_x_cells, 1);
CHECK_GE(limits.num_y_cells, 1);
const int stride = wide_limits_.num_x_cells;
// ....
}
uint8 PrecomputationGrid2D::ComputeCellValue(const float probability) const {
const int cell_value = common::RoundToInt(
(probability - min_score_) * (255.f / (max_score_ - min_score_)));
CHECK_GE(cell_value, 0);
CHECK_LE(cell_value, 255);
return cell_value;
} 4.1 滑窗的工作方式 --- x 方向滑动
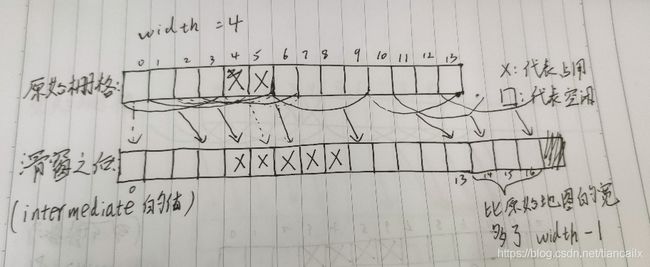
假设原始栅格地图为14个格子,0-13,地图的分辨率width=4,滑窗之后的效果如下图所示:
(图中滑窗之后的占用网格好像画错了。。。只理解概念吧。我是按照将占用的网格的值是0.9存入intermediate的,其实是用1-0.9=0.1。。。)
滑窗首先讲x=0处的栅格的值存入滑窗类,并赋值给 intermediate ,之后会分3个步骤,每个步骤对应一个for循环,合起来是遍历了一整行。
步骤一: 滑窗滑入网格,首先将滑窗中最大的值放入 intermediate的对应位置处,之后向滑窗的最右侧填入一个值,值的大小为 用1减去原网格的值 后放入滑窗,这部分只添加值。也就是网格中,空闲的值为0.1,存入intermediate的值为0.9? carto的grid的占用值是多少?有待确认。
步骤二:滑窗已经完全滑入网格中,滑窗的宽度即为width。此时,首先将滑窗中最大的值放入 intermediate 的对应位置处,之后先删除滑窗的最左侧处的值,之后再向滑窗的最右侧填入一个值。
步骤三:滑窗滑出网格,此时,首先将滑窗中最大的值放入 intermediate的对应位置处,之后逐步删除滑窗的最左侧处的值。此时会导致 intermediate 的宽度比 grid 宽 width-1 个栅格。
之后再将y++,实现了整个原始网格的遍历。
经过这一系列操作,实现了滑窗从网格最左侧开始滑入,每次运动一个栅格,并最后从右侧滑出。实现了将width个栅格合一的操作。
// First we compute the maximum probability for each (x0, y) achieved in the
// span defined by x0 <= x < x0 + width.
std::vector& intermediate = *reusable_intermediate_grid;
intermediate.resize(wide_limits_.num_x_cells * limits.num_y_cells);
for (int y = 0; y != limits.num_y_cells; ++y) {
SlidingWindowMaximum current_values;
// 获取 grid 的x坐标的索引: 首先获取 (0, y)
current_values.AddValue(
1.f - std::abs(grid.GetCorrespondenceCost(Eigen::Array2i(0, y))));
// 步骤一
// x + width - 1 + y * stride 的范围 (从 0 到 width-2) 再加上 y * stride
// 获取 grid 的x坐标的索引: (x + width, y) 的坐标从 (1 ,y) 到 (width-1, y)
// 滑动窗口在x方向开始划入地图,所以只进行 填入值
for (int x = -width + 1; x != 0; ++x) {
intermediate[x + width - 1 + y * stride] = current_values.GetMaximum();
if (x + width < limits.num_x_cells) {
current_values.AddValue(1.f - std::abs(grid.GetCorrespondenceCost(
Eigen::Array2i(x + width, y))));
}
}
// 步骤二
// x + width - 1 + y * stride 的范围 从 (width-1 到 limits.num_x_cells-2) 再加上 y * stride
// 获取 grid 的x坐标的索引: (x + width, y) 的坐标从 (width, y) 到 (limits.num_x_cells-width-1, y)
// 滑动窗口已经完全在地图里了,如果 地图中(x,y)处的值 是当前滑窗内的最大值,则删掉,
// 之后再将(x+width,y)的值放入滑窗里
for (int x = 0; x < limits.num_x_cells - width; ++x) {
intermediate[x + width - 1 + y * stride] = current_values.GetMaximum();
current_values.RemoveValue(
1.f - std::abs(grid.GetCorrespondenceCost(Eigen::Array2i(x, y))));
current_values.AddValue(1.f - std::abs(grid.GetCorrespondenceCost(
Eigen::Array2i(x + width, y))));
}
// 步骤三
// x + width - 1 + y * stride 的范围 从 (limits.num_x_cells-1 到 limits.num_x_cells+width-1) 再加上 y * stride
// 获取 grid 的x坐标的索引: (x, y) 的坐标从 (limits.num_x_cells-width ,y) 到 (limits.num_x_cells-1, y)
// 滑动窗口正在划出,一次减少一个值,所以intermediate的宽度比grid多 width-1
for (int x = std::max(limits.num_x_cells - width, 0);
x != limits.num_x_cells; ++x) {
intermediate[x + width - 1 + y * stride] = current_values.GetMaximum();
current_values.RemoveValue(
1.f - std::abs(grid.GetCorrespondenceCost(Eigen::Array2i(x, y))));
}
// 理论上,滑窗走完地图的一行之后应该是空的,经过 只入,一出一入,只出,3个步骤
current_values.CheckIsEmpty();
} 4.2 生成将width*width个栅格合一的栅格地图
首先,x的遍历范围为 intermediate 的宽,比 grid 的网格数多width-1。
之后,进行Y方向的遍历,y方向的滑窗遍历不再去读取原始grid了,直接去读取 intermediate ,所以他是可重用的。
由于使用滑窗的方式,所以 cells的 高会比 intermediate 的高 多 width - 1。
逐步的将 滑窗的值 放入 cells 变量,也就是多分辨率网格的存储的真实位置。
cells的 宽与 intermediate 的宽大小一致,为 limits.num_x_cells + width - 1,cells的 高为 limits.num_y_cells + width - 1 。
// For each (x, y), we compute the maximum probability in the width x width
// region starting at each (x, y) and precompute the resulting bound on the
// score.
// 滑窗竖着走一遍,只不过这次添加到滑窗里的值是 intermediate
// 所以intermediate 是 可重用的:reusable_intermediate_grid
for (int x = 0; x != wide_limits_.num_x_cells; ++x) {
SlidingWindowMaximum current_values;
current_values.AddValue(intermediate[x]);
for (int y = -width + 1; y != 0; ++y) {
cells_[x + (y + width - 1) * stride] =
ComputeCellValue(current_values.GetMaximum());
if (y + width < limits.num_y_cells) {
current_values.AddValue(intermediate[x + (y + width) * stride]);
}
}
for (int y = 0; y < limits.num_y_cells - width; ++y) {
cells_[x + (y + width - 1) * stride] =
ComputeCellValue(current_values.GetMaximum());
current_values.RemoveValue(intermediate[x + y * stride]);
current_values.AddValue(intermediate[x + (y + width) * stride]);
}
for (int y = std::max(limits.num_y_cells - width, 0);
y != limits.num_y_cells; ++y) {
cells_[x + (y + width - 1) * stride] =
ComputeCellValue(current_values.GetMaximum());
current_values.RemoveValue(intermediate[x + y * stride]);
}
current_values.CheckIsEmpty();
}
没理解怎么将width*width合一了,用1减去grid里的CorrespondenceCost是啥意思,CorrespondenceCost 是1-32768之间的值,回头再研究吧,先放着。。。
未完待续
REFERENCES
cartographer多分辨率地图生成 https://blog.csdn.net/jw123545/article/details/105962135
cartographer 添加约束 /分支界定法 https://blog.csdn.net/xiaoma_bk/article/details/83040559