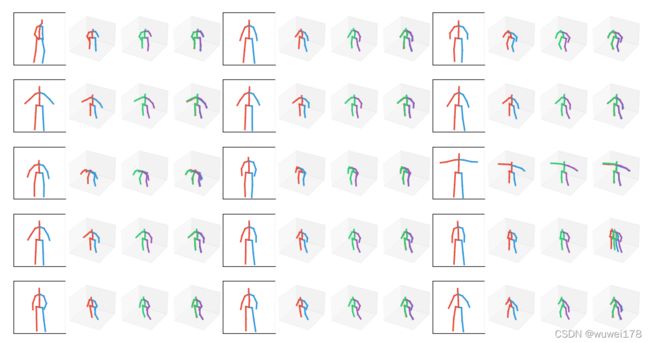
人体姿态估计中的可视化---画出预测关节位置3D图和地面真实图
根据模型预测关节位置和真实关节位置画3维图
import pickle
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
# Joints in H3.6M -- data has 32 joints, but only 17 that move; these are the indices.
H36M_NAMES = ['']*17
H36M_NAMES[0] = 'LFoot'
H36M_NAMES[1] = 'LKnee'
H36M_NAMES[2] = 'LHip'
H36M_NAMES[3] = 'RHip'
H36M_NAMES[4] = 'RKnee'
H36M_NAMES[5] = 'RFoot'
H36M_NAMES[6] = 'Hip'
H36M_NAMES[7] = 'Belly'
H36M_NAMES[8] = 'Neck'
H36M_NAMES[9] = 'Head'
H36M_NAMES[10] = 'LHand'
H36M_NAMES[11] = 'LElbow'
H36M_NAMES[12] = 'LShoulder'
H36M_NAMES[13] = 'RShoulder'
H36M_NAMES[14] = 'RElbow'
H36M_NAMES[15] = 'RHand'
H36M_NAMES[16] = 'Nose'
def show3Dpose(channels, ax, lcolor="#3498db", rcolor="#e74c3c", add_labels=False): # blue, orange
"""
Visualize a 3d skeleton
Args
channels: 96x1 vector. The pose to plot.
ax: matplotlib 3d axis to draw on
lcolor: color for left part of the body
rcolor: color for right part of the body
add_labels: whether to add coordinate labels
Returns
Nothing. Draws on ax.
"""
assert channels.size == len(H36M_NAMES)*3, "channels should have 51 entries, it has %d instead" % channels.size
vals = np.reshape( channels, (len(H36M_NAMES), -1) )
I = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 8, 11, 8, 13, 14, 10]) # start points
J = np.array([1, 2, 6, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 16, 16, 12, 12, 13, 14, 15, 11]) # end points
LR = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0], dtype=bool)#右半边的颜色
# Make connection matrix
for i in np.arange( len(I) ):
x, y, z = [np.array( [vals[I[i], j], vals[J[i], j]] ) for j in range(3)]
ax.plot(x, y, z, lw=2, c=lcolor if LR[i] else rcolor)#lw线条宽度
#画点
# lcolor = "#FF9500"
# for i in np.arange(len(I)):
# x, y, z = vals[i]
# print(x,y,z)
# ax.scatter(x, y, z, lw=2, c=lcolor)#lw线条宽度
RADIUS = 750 # space around the subject
xroot, yroot, zroot = vals[6,0], vals[6,1], vals[6,2] #hip的位置
ax.set_xlim3d([-RADIUS+xroot, RADIUS+xroot])
ax.set_zlim3d([-RADIUS+zroot, RADIUS+zroot])
ax.set_ylim3d([-RADIUS+yroot, RADIUS+yroot])
ax.grid(True)
if add_labels:
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_zlabel("z")
# Get rid of the ticks and tick labels
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.set_zticks([])
ax.get_xaxis().set_ticklabels([])
ax.get_yaxis().set_ticklabels([])
ax.set_zticklabels([])
# Get rid of the panes (actually, make them white)
white = (1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0)
# ax.w_xaxis.set_pane_color(white)
# ax.w_yaxis.set_pane_color(white)
# # Keep z pane
#
# Get rid of the lines in 3d
ax.w_xaxis.line.set_color(white)
ax.w_yaxis.line.set_color(white)
ax.w_zaxis.line.set_color(white)
def show2Dpose(channels, ax, lcolor="#3498db", rcolor="#e74c3c", add_labels=False):
"""Visualize a 2d skeleton
Args
channels: 64x1 vector. The pose to plot.
ax: matplotlib axis to draw on
lcolor: color for left part of the body
rcolor: color for right part of the body
add_labels: whether to add coordinate labels
Returns
Nothing. Draws on ax.
"""
assert channels.size == len(H36M_NAMES)*2, "channels should have 64 entries, it has %d instead" % channels.size
vals = np.reshape(channels, (len(H36M_NAMES), -1) )
I = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 8, 11, 8, 13, 14, 10]) # start points
J = np.array([1, 2, 6, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 16, 16, 12, 12, 13, 14, 15, 11]) # end points
LR = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0], dtype=bool)#右半边的颜色
# Make connection matrix
for i in np.arange( len(I) ):
x, y = [np.array( [vals[I[i], j], vals[J[i], j]] ) for j in range(2)]
ax.plot(x, y, lw=2, c=lcolor if LR[i] else rcolor)
# Get rid of the ticks
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
# Get rid of tick labels
ax.get_xaxis().set_ticklabels([])
ax.get_yaxis().set_ticklabels([])
RADIUS = 1000 # space around the subject
xroot, yroot = vals[6,0], vals[6,1]
ax.set_xlim([-RADIUS+xroot, RADIUS+xroot])
ax.set_ylim([-RADIUS+yroot, RADIUS+yroot])
if add_labels:
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("z")
ax.set_aspect('equal')
def get_data():
path = 'results.pkl'
f = open(path, 'rb')
data = pickle.load(f)
# f1 = open(r'F:/Python codes/pose_lcn/dataset/h36m_test.pkl', 'rb')
# dataitem_gt = pickle.load(f1)
return data
def get_3d_data(idx,data_pre,data_gt):
pre3d = data_pre[idx]
gt3d = data_gt[idx]
gt2d = np.delete(gt3d, 1, axis=1)
return pre3d, gt3d, gt2d
def plt_one(fig,pre3d,gt3d,gt2d,subplot_idx):
# Plot 2d pose
print(gs1[subplot_idx - 1])
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs1[subplot_idx - 1])
show2Dpose(gt2d, ax1)
# ax1.invert_yaxis()
# Plot 3d gt
print(gs1[subplot_idx])
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs1[subplot_idx], projection='3d')
ax2.grid(True)
show3Dpose(pre3d, ax2)
# Plot 3d predictions
print(gs1[subplot_idx + 1])
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs1[subplot_idx + 1], projection='3d')
ax3.grid(True)
show3Dpose(gt3d, ax3, lcolor="#9b59b6", rcolor="#2ecc71")
print(gs1[subplot_idx + 2])
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(gs1[subplot_idx + 2], projection='3d')
ax4.grid(True)
show3Dpose(pre3d, ax4)
show3Dpose(gt3d, ax4, lcolor="#9b59b6", rcolor="#2ecc71")
if __name__ == '__main__':
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8))
gs1 = gridspec.GridSpec(5, 12) # 5 rows, 12 columns
gs1.update(wspace=-0.00, hspace=0.05) # set the spacing between axes.
subplot_idx = 1
idxs = [0, 320, 1020, 1356, 1620, 2068, 2316, 2492, 2872, 3156, 3704, 3944, 4256, 4516, 4796]
for i in range(len(idxs)):
if i == 10:
idxs[i] += 5
else:
idxs[i] += 5
data_pre, data_gt = get_data()['keypoints_3d'][0:1086], get_data()['keypoints_gt'][0:1086]
# indexs = get_data()['proj_matricies_batch']
# print(indexs)
data_gt = np.array(data_gt).reshape(-1, 17, 3)
data_pre = np.array(data_pre).reshape(-1, 17, 3)
data_gt = np.insert(data_gt, -1, np.array(get_data()["keypoints_gt"][-1]), axis=0)
data_pre = np.insert(data_pre, -1, np.array(get_data()["keypoints_3d"][-1]), axis=0)
# print(data_pre.shape)
for idx in idxs:
pre3d, gt3d, gt2d = get_3d_data(idx,data_pre,data_gt)
plt_one(fig, pre3d, gt3d, gt2d, subplot_idx)
subplot_idx += 4
plt.show()
效果如下
从左到右依次是2D的、预测的、真实的和预测真实合并的。