人群分析综述--Crowd Scene Understanding from Video: A Survey
Crowd Scene Understanding from Video: A Survey
ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl., Vol. 13, No. 2, Article 19, Publication date: March 2017
针对人群密集场景理解,这篇综述主要关注两个方向:crowd statistics and behavior understanding 人群统计和行为理解
2 Crowd counting
人群计数目前从两个角度来解决,一类方法是回归计数,直接得到图像中总人数的估计,另一类方法是先估计密度图,再有密度图积分求和得到总人数。目前来说密度图提供的信息更多些,得到的精度相对也更高些。这里我们将所有人群计数方法划分为六类:pixel-level analysis, texture-level analysis, object-level analysis, line counting, density mapping, and joint detection and counting
2.1. Pixel-Level Analysis
基于像素水平的分析主要从边缘检测开始,用边缘特征(长度、方向等)来训练一个模型用于人群密度图的估计
begin with edge detection and use edge features (length, orientation, etc.) to train a model
2.2. Texture-Level Analysis
基于纹理的分析对象是图像块,通常使用 statistical, structural, or spectral analyses 来提取特征
coarser grained than pixel-based methods and aims to analyze image patches,use statistical, structural, or spectral
analyses to extract features.
基于像素和基于纹理都是得到总人数,它们不能区分出个体
2.3. Object-Level Analysis
检测出单个个体,精度相对较高,但是只适用于低密度场景
identify individual subjects in a scene, applicable to lower density crowds
这里有一篇文献是基于深度和颜色信息来统计人流量,相机安装方式是垂直的。
People-flow counting in complex environments by combining depth and color information
2.4. Line Counting
这类方法主要统计穿越一条线的人流量
2.5. Density Mapping
估计密度图,目前很多基于CNN深度学习的方法都是用于估计人群密度图的
estimates the density of the scene
2.6. Joint Detection and Counting
利用密度图来更好的做检测和计数
makes use of density maps to better detect and count objects within the scene
Challenging problems still exist in measuring large crowds with high densities. These challenges also require good data with images taken at a variety of standoffs, angles, and resolutions and ground-truth labels for comparisons.
人群计数的挑战性还是很大的,尤其是高密度人群的场景,还是非常需要大量数据来驱动算法性能的提升。
3 Behavior analysis
最基本的行为分析就是 normal behavior and abnormal behavior,对于人群密度场所我们主要提取 Dominant motion,对于不是很密度的场景,则是分析 group interactions,也就是小人群的行为。本文主要关注以下三个方面的内容:1)abnormal behavior detection,2)dominant motion extraction,3) group behavior detection
3.1. Abnormal Behavior Detection
什么是异常行为了? any deviation from the normal crowd flow is considered abnormal activity
这里主要基于场景中的运动信息来判断是否有异常行为的存在,前后运动信息的对比
3.2. Dominant Motion Extraction
主要是提取图像中的主要运动信息

3.3. Group Behavior Detection
主要侧重小规模人群聚集的行为分析

3.4. Crowd Analysis and Tracking
对于密集人群的跟踪难度还是很大
4.1. Crowd Counting
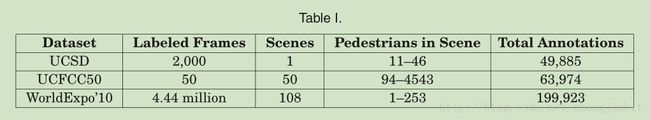
主要有以下几个数据库:The WorldExpo’10 Crowd Counting Dataset [Zhang et al. 2015],
the UCSDdataset [Chan et al. 2008], and the UCF Crowd Counting dataset [Idrees et al. 2013]
4.2. Group Detection
主要有以下几个数据库:The MuseumVisitors [Bartoli et al. 2015], Collective Motion [Zhou et al. 2014], student003 [Solera et al. 2015], and GVEII [Solera et al. 2015] datasets were constructed for group detection. In addition, the Grand Central Station dataset [Zhou et al. 2012] and the Mall dataset [Loy et al. 2013] contain similar attributes as the those previously listed in this group. MuseumVisitors is a dataset for pedestrian and group detection, gaze estimation, and behavior understanding.
4.3. Behavior Understanding
The Unusual Crowd Activity dataset [University of Minnesota 2006], 2009 Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance (PETS2009) dataset [Ferryman and
Shahrokni 2009], and Collective Activity dataset [Choi et al. 2009] are purposed for crowdbehaviorunderstanding.
4.4. Holistic Crowd Movement
The Meta-Tracking for Video Scene Understanding dataset [Jodoin et al. 2013], Data-Driven Crowd Analysis dataset [Rodriguez et al. 2011b], Crowd Segmentation dataset [Ali and Shah 2007], and the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) Crowd dataset [Shao et al. 2014] are largely developed from online video repositories
4.5. Synthetic
The Agoraset dataset [Allain et al. 2012] is a graphical rendering of crowd sequences with associated ground truths, which include include individual trajectories of pedestrians inside the crowd, crowd density, and the velocity field. Seven environments, also called scenes, were created using crowd models proposed by Helbing et al. [2000]
总体来说深度学习对于人群分析正处于方兴未艾阶段!