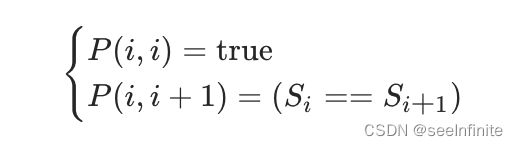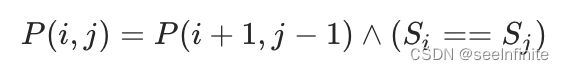Leetcode top200
优先队列
import queue
q = queue.PriorityQueue()
# 判空
q.empty()
# 进队
q.put()
# 出队
q.get()2. 两数相加
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1, l2):
"""
:type l1: ListNode
:type l2: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not l1:
return l2
if not l2:
return l1
dummy = ListNode(-1)
p = dummy
carry = 0
while l1 or l2 or carry:
curSum = carry
if l1:
curSum += l1.val
l1 = l1.next
if l2:
curSum += l2.val
l2 = l2.next
p.next = ListNode(curSum%10)
carry = curSum//10
p = p.next
return dummy.next
3. 无重复字符的最长子串(*)
滑动窗口
class Solution(object):
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
charQueue = set()
l, maxLen = 0, 0
for i in range(len(s)):
# 维护滑动窗口的左侧,保持滑动窗口内无重复
while s[i] in charQueue:
charQueue.remove(s[l])
l += 1
# 注意无论s[i]之前是否在队列中,此时要重新入队
charQueue.add(s[i])
maxLen = max(maxLen, i - l + 1)
return maxLen76. 最小覆盖子串(*)
同上,但是更麻烦
from collections import defaultdict
class Solution(object):
def minWindow(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: str
"""
tCharDict = defaultdict(int)
res = (0,float("+inf"))
l = 0
for char in t:
tCharDict[char] += 1
needCnt = len(t)
for i,char in enumerate(s):
if tCharDict[char] > 0:
needCnt -= 1
tCharDict[char] -= 1
if needCnt == 0: # 滑动窗口包含了所有t元素
while True: # 增加l,排除多余元素
c = s[l]
# 移动到t中含有到字符,停止移动左边界
if tCharDict[c] == 0:
break
tCharDict[c] += 1
l += 1
if i-l < res[1]-res[0]:
res = (l,i)
# l增加一个位置,寻找新的满足条件滑动窗口
needCnt += 1
tCharDict[s[l]] += 1
l += 1
if res[1] > len(s):
return ""
return s[res[0]:res[1]+1]
4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数(*)
class Solution(object):
def findMedianSortedArrays(self, nums1, nums2):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:rtype: float
"""
m, n = len(nums1), len(nums2)
if not (m+n)%2:
return (self.getKth(nums1,nums2,(m+n)//2)+self.getKth(nums1,nums2,(m+n)//2+1))*0.5
else:
return self.getKth(nums1,nums2,(m+n)//2+1)
def getKth(self,nums1,nums2,k):
# 保证1比2短
if len(nums1) > len(nums2):
return self.getKth(nums2,nums1,k)
# 当1为空时,直接返回2的kth
if not nums1:
return nums2[k-1]
if k == 1:
return min(nums1[0],nums2[0])
i,j = min(len(nums1),k//2)-1,min(len(nums2),k//2)-1
# 注意这里对数组对截断
if nums1[i] < nums2[j]:
return self.getKth(nums1[i+1:],nums2,k-i-1)
else:
return self.getKth(nums1, nums2[j+1:], k - j-1)5. 最长回文子串(*)
边界条件:
转移方程:
class Solution(object):
def longestPalindrome(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: str
"""
if len(s) < 2:
return s
n = len(s)
dp = [[False]*n for _ in range(n)]
res = (0,0)
for i in range(n):
dp[i][i] = True
# 注意这里的循环嵌套,从左往右,从上往下,确保每次左下角已经被判断过
for j in range(1,n):
for i in range(0,j):
if j-i < 3:
dp[i][j] = (s[i] == s[j])
else:
dp[i][j] = (dp[i+1][j-1] and s[i] == s[j])
if dp[i][j] and j-i > res[1]-res[0]:
res = (i,j)
return s[res[0]:res[1]+1]
6. N 字形变换(*)
不要找规律,不然太繁琐了,直接模拟这个过程,flag的使用很妙
class Solution(object):
def convert(self, s, numRows):
"""
:type s: str
:type numRows: int
:rtype: str
"""
if numRows < 2:
return s
res = ["" for _ in range(numRows)]
i,flag = 0,-1
for c in s:
if i == 0 or i == numRows-1:
flag *= -1
res[i] += c
i += flag
return "".join(res)
7. 整数反转
class Solution(object):
def reverse(self, x):
"""
:type x: int
:rtype: int
"""
res = 0
sign = 1
if x < 0:
sign = -1
x = x*-1
while x:
tmp = x%10
x //= 10
if res > 214748364 or (res == 214748364 and ((tmp > 7 and sign == 1) or (tmp > 8 and sign == -1))):
return 0
res = res*10 + tmp
return res*sign
146. LRU 缓存
class DuelListNode(object):
def __init__(self, key = 0, val=0):
self.pre = None
self.next = None
self.key = key
self.val = val
class LRUCache(object):
def __init__(self, capacity):
"""
:type capacity: int
"""
self.cache = {}
self.head = DuelListNode()
self.tail = DuelListNode()
self.head.next = self.tail
self.tail.pre = self.head
self.capacity = capacity
self.size = 0
def get(self, key):
"""
:type key: int
:rtype: int
"""
if key not in self.cache:
return -1
node = self.cache[key]
self.moveToHead(node)
return node.val
def put(self, key, value):
"""
:type key: int
:type value: int
:rtype: None
"""
if key in self.cache:
node = self.cache[key]
node.val = value
# 这里是移动到头
self.moveToHead(node)
else:
node = DuelListNode(key,value)
# 注意加入缓存中
self.cache[key] = node
# 这里是直接加到头,因为本来不在双向链表中,所以不需要移动
self.addToHead(node)
self.size += 1
if self.size > self.capacity:
removeNode = self.removeTail()
self.cache.pop(removeNode.key)
self.size -= 1
def moveToHead(self,node):
self.removeNode(node)
self.addToHead(node)
def addToHead(self,node):
node.next = self.head.next
node.pre = self.head
self.head.next.pre = node
self.head.next = node
def removeNode(self,node):
node.pre.next = node.next
node.next.pre = node.pre
def removeTail(self):
removeNode = self.tail.pre
self.removeNode(removeNode)
return removeNode
9. 回文数
class Solution(object):
def isPalindrome(self, x):
"""
:type x: int
:rtype: bool
"""
x = str(x)
i,j = 0,len(x)-1
while i < j:
if x[i] != x[j]:
return False
i += 1
j -= 1
return True11. 盛最多水的容器(*)
双指针
移动长板的时候,宽度变窄,同时最高高度仍然是短板,所以面积一定变小
class Solution(object):
def maxArea(self, height):
"""
:type height: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
l,r = 0,len(height)-1
maxContain = 0
while l < r:
maxContain = max(maxContain, min(height[l],height[r])*(r-l))
# 移动两者之间的短板
if height[l] < height[r]:
l += 1
else:
r -= 1
return maxContain12. 整数转罗马数字(*)
贪心,直接从大到小开始枚举,没有特殊情况
class Solution(object):
def intToRoman(self, num):
"""
:type num: int
:rtype: str
"""
hashmap = {1000: 'M', 900: 'CM', 500: 'D', 400: 'CD', 100: 'C', 90: 'XC', 50: 'L', 40: 'XL', 10: 'X', 9: 'IX',
5: 'V', 4: 'IV', 1: 'I'}
romanNums = [1000,900,500,400,100,90,50,40,10,9,5,4,1]
res = ""
for key in romanNums:
cnt = num // key
if cnt != 0:
res += hashmap[key]*cnt
num %= key
return res14. 最长公共前缀
class Solution(object):
def longestCommonPrefix(self, strs):
"""
:type strs: List[str]
:rtype: str
"""
if not strs:
return None
if len(strs) < 2:
return strs[0]
maxPre,minLen = 0,float("+inf")
prefix = ""
for s in strs:
minLen = min(minLen,len(s))
for i in range(minLen):
c = strs[0][i]
for s in strs[1:]:
if s[i] != c:
return prefix
prefix += c
maxPre += 1
return prefix15. 三数之和(*)
排序+双指针,注意去重逻辑!
class Solution(object):
def threeSum(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if len(nums) < 3:
return []
self.result = []
nums.sort()
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] > 0:
return self.result
if i > 0 and i < len(nums) and nums[i-1] == nums[i]:
continue
l,r = i+1,len(nums)-1
while l < r:
curSum = nums[i]+nums[l]+nums[r]
if curSum < 0:
l += 1
elif curSum > 0:
r -= 1
else:
self.result.append([nums[i],nums[l],nums[r]])
# 去重
while l < r and nums[l] == nums[l+1]:
l += 1
while l < r and nums[r] == nums[r-1]:
r -= 1
l += 1
r -= 1
return self.result
128. 最长连续序列16. 最接近的三数之和128. 最长连续序列
class Solution(object):
def threeSumClosest(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(nums)
if n < 4:
return sum(nums)
minDist = 1 << 32
nums.sort()
for i in range(n-2):
cur = nums[i]+self.twoSumClosest(nums,i+1,target-nums[i])
if abs(cur-target) < minDist:
closest = cur
minDist = abs(cur-target)
return closest
def twoSumClosest(self,nums,start,target):
minDis = 1 << 32
closet = 0
l, r = start, len(nums) - 1
while l < r:
curSum = nums[l]+nums[r]
if curSum > target:
r -= 1
elif curSum <= target:
l += 1
if abs(curSum-target) < minDis:
minDis = abs(curSum-target)
closet = curSum
return closet17. 电话号码的字母组合
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
self.numLetter = {2: "abc", 3: "def", 4:"ghi", 5: "jkl", 6: "mno", 7: "pqrs", 8: "tuv", 9: "wxyz"}
def letterCombinations(self, digits):
"""
:type digits: str
:rtype: List[str]
"""
return self.dfs(digits)
def dfs(self, digits):
"""
:type digits: str
:rtype: List[str]
"""
if not digits:
return []
num = int(digits[0])
if len(digits) == 1:
return list(self.numLetter[num])
res = self.dfs(digits[1:])
newRes = []
for word in res:
for l in self.numLetter[num]:
newRes.append(l + word)
return newRes20. 有效的括号
栈
class Solution(object):
def isValid(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: bool
"""
stack = []
cDict = {"}":"{","]":"[",")":"("}
for c in s:
if c in ["{", "[", "("]:
stack.append(c)
else:
if not stack or stack[-1] != cDict[c]:
return False
stack.pop(-1)
return len(stack) == 022. 括号生成
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
self.res = []
def generateParenthesis(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: List[str]
"""
self.dfs("",n,n)
return self.res
def dfs(self,path,pre,back):
if not pre and not back:
self.res.append(path)
if pre > 0:
self.dfs(path+"(",pre-1,back)
if pre < back:
self.dfs(path+")",pre,back-1)
23. 合并 K 个升序链表
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
import queue
class Solution(object):
def mergeKLists(self, lists):
"""
:type lists: List[ListNode]
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not lists:
return None
dummy = ListNode(-1)
cur = dummy
q = queue.PriorityQueue()
for i in range(len(lists)):
if lists[i]:
q.put([lists[i].val,i])
while not q.empty():
num,i = q.get()
cur.next = lists[i]
cur = cur.next
if lists[i].next:
lists[i] = lists[i].next
q.put([lists[i].val,i])
return dummy.next
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
dummy = ListNode(-1)
dummy.next = head
cur = dummy
while cur.next and cur.next.next:
tmp = cur.next
cur.next = cur.next.next
cur = cur.next
tmp.next = cur.next
cur.next = tmp
cur = cur.next
return dummy.next
25. K 个一组翻转链表(*)
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(-1)
dummy.next = head
pre, end = dummy, dummy
while end.next:
for i in range(k):
if end:
end = end.next
if not end:
break
start = pre.next
next = end.next
end.next = None
pre.next = self.reverse(start)
start.next = next
pre = start
end = pre
return dummy.next
def reverse(self, start):
dummy = ListNode(-1)
while start:
tmp = start.next
start.next = dummy.next
dummy.next = start
start = tmp
return dummy.next
128. 最长连续序列
class Solution(object):
def longestConsecutive(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
maxLen = 0
numDict = {}
for num in nums:
if num not in numDict:
l,r = 0,0
l = numDict.get(num-1,0)
r = numDict.get(num+1,0)
curLength = l+r+1
maxLen = max(maxLen,curLength)
numDict[num] = curLength
numDict[num-l] = curLength
numDict[num+r] = curLength
return maxLen