libtorch的常见tensor操作
目录
初始化
修改shape
切片操作
索引操作
mask操作
拼接操作
算术运算
求最值
数据类型转换
1. int和tensor
2. tensor转vector
3. 二维的tensor转vector
4. std::vector 转tensor {batchsize, c, h, w}
libtorch类似于pytorch的常见tensor操作。
初始化
包含一个很实用的方法: vector和tensor互转。
// 1. 常见的以固定值初始化方法
// pytorch是以[]表明尺度,libtorch是用{}
auto img = torch::zeros({3, 6});
img = torch::ones({3, 6});
img = torch::eye(3);
img = torch::full({ 3, 6 }, 255);
img = torch::tensor({ 11, 22, 33 }); // 3 row.
torch::Tensor offset1 = torch::tensor({ {1}, {2}, {3} }); // 3 row.
torch::Tensor offset2 = torch::tensor({ {1, 2, 3} }); // 1 row, 3 col
// 2. 固定尺度,生成随机数
auto r_num = torch::rand({ 3, 6 }); // 0-1
r_num = torch::randn({ 3, 6 }); // N(0, 1)
r_num = torch::randint(0, 3, { 3, 6 }); // [0, 3)
// 3. 将c++类型的数据转成tensor
// clone是为了深复制,让后面对num_tensor1 的操作不会收到num_array的影响
int num_array[5] = {2, 4, 8}; // 数组形式
std::vector num_vector = { 2, 4, 8 }; // vector形式
std::vector num_tensor0 = torch::tensor(num_vector );
at::Tensor num_tensor1 = torch::from_blob(num_array, { 3 }, torch::kFloat).clone(); // 参数:指针,size,type
at::Tensor num_tensor2 = torch::from_blob(num_vector.data(), { 3 }, torch::kFloat).clone(); // 参数:指针,size,type
std::vector a = { 12, 34, 52, 24, 34, 52 };
at::Tensor num_tensor1 = torch::from_blob(a.data(), { int(a.size()/2),2 }, torch::kInt).clone();
12 34
52 24
34 52
[ CPUIntType{3,2} ]
// 4. 用已有的tensor生成新的tensor
at::Tensor ref_tensor = torch::zeros({ 2, 4 });
at::Tensor new_tensor = torch::Tensor(ref_tensor); // 等于 new_tensor = ref_tensor. 浅拷贝.
new_tensor = torch::zeros_like(ref_tensor);
new_tensor = torch::ones_like(ref_tensor);
new_tensor = torch::rand_like(ref_tensor, torch::kFloat);
new_tensor = ref_tensor.clone(); // ref_tensor的改变完全不会影响到new_tensor. 深拷贝. 修改shape
// 5. 改变tensor的shape: view, transpose, reshape, permute
at::Tensor val_tensor = torch::tensor({1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10});
val_tensor.view({ 1, 2, -1 }); // 不是原地操作
std::cout << val_tensor << std::endl;
val_tensor = val_tensor.view({ 1, 2, -1 }); // 不是原地操作. {10}->{1,2,5}
std::cout << val_tensor;
new_tensor = val_tensor.transpose(0, 1); // {1,2,5}->{2,1,5}
std::cout << new_tensor << std::endl;
new_tensor = val_tensor.reshape({ 1, 1, -1 }); // {1,2,5}->{1,1,10}
std::cout << new_tensor << std::endl;
new_tensor = val_tensor.permute({ 1, 0, 2}); // {1,2,5}->{2,1,5}
std::cout << new_tensor << std::endl;切片操作
// 6. 切片操作,使用[]
val_tensor = torch::rand({ 64, 3, 28, 28 }); // b,c,h,w
std::cout << val_tensor[0].sizes() << std::endl; // 第0张图的维度:[3, 28, 28]
std::cout << val_tensor[0][0].sizes() << std::endl; // 第0张图第0通道的维度:[28,28]
std::cout << val_tensor[0][0][0].sizes() << std::endl; // 宽度:[28]
std::cout << val_tensor[0][0][0][0].sizes() << std::endl; // []
// 7. 切片操作,使用narrow, select, index, index_select函数
std::cout << val_tensor.index_select(0, torch::tensor({ 0, 3, 3 })).sizes() << std::endl; // batch维度,选择第0张图片和两张第3张图片,形成tensor [3,3,28,28]
std::cout << val_tensor.index_select(1, torch::tensor({ 0, 2 })).sizes() << std::endl; // 通道维度,选择第0和2通道,形成tensor [64,2,28,28]
std::cout << val_tensor.index_select(2, torch::arange(0, 8)).sizes() << std::endl; // 行维度,选择所有图片的前8行,形成tensor [64,3,8,28]
std::cout << val_tensor.narrow(1, 0, 2).sizes() << std::endl; // 选择第1维度,即通道维度,从0通道开始裁剪通道长度是2,形成tensor [64,2,28,28]
std::cout << val_tensor.select(3, 2).sizes() << std::endl; // 在第3维度,选择第2个tensor,即第2列,形成tensor [64,3,28].
// slice
// a[:, ::4, ::4] == a[:, 0::4, 0::4]
// slice(int64_t dim=0, int64_t start=0, int64_t end=9223372036854775807, int64_t step=1)
score_maps.slice(0, 0, input_size, 4).slice(1, 0, input_size, 4);
索引操作
这个博主写的更好:LibTorch对tensor的索引/切片/掩码操作:对比PyTorch_libtorch shape tensor_地球被支点撬走啦的博客-CSDN博客
// 索引某个维度
auto a = torch::rand({ 64, 3, 28, 28 }); // b,c,h,w
at::Tensor b = a.index({"...", 2}); // 等价于python: a[..., 2]和a[:, :, :, 2]
// 索引某个值
auto detections = torch::rand({128, 7}); // (num_bbox, attri)
// detections.select(-1,-1) == 1. 在最后维度上(列维度),取最后一个索引(最后一列)
auto detections_class = detections.index({ detections.select(-1,-1) == 1 }); // (num_find, 7)
// 索引某个维度,并修改值 等价于python: a[1,2]
at::Tensor a = torch::rand({ 3, 3, 3 });
std::cout << a << std::endl << "------------" << std::endl;
// 修改第一通道的第一行的所有为0
a.index({ 1, 1 }) = 0; // 等价于python: a[1,2]
std::cout << a << std::endl << "------------" << std::endl;
// 或者修改第一通道的第一行为1,2,3
a.index({ 1, 1 }) = torch::tensor({1, 2, 3});
std::cout << a << std::endl << "------------" << std::endl;
// 等价于python: a[..., 0]
at::Tensor a = torch::rand({ 3, 8 });
std::cout << a << std::endl << "------------" << std::endl;
at::Tensor farthest_idx = torch::full({ 3 }, 1, torch::kLong);
a.index({ "...", 0 }) = farthest_idx; // 等价于python: a[..., 0]
std::cout << a << std::endl << "------------" << std::endl;
0.3409 0.0969 0.6683 0.6367 0.1913 0.8872 0.8825 0.2930
0.8264 0.5140 0.2956 0.5604 0.3158 0.1694 0.2507 0.0142
0.4872 0.5937 0.0473 0.7303 0.9765 0.7226 0.7446 0.6122
[ CPUFloatType{3,8} ]
------------
1.0000 0.0969 0.6683 0.6367 0.1913 0.8872 0.8825 0.2930
1.0000 0.5140 0.2956 0.5604 0.3158 0.1694 0.2507 0.0142
1.0000 0.5937 0.0473 0.7303 0.9765 0.7226 0.7446 0.6122
[ CPUFloatType{3,8} ]mask操作
// 8.mask操作. 深拷贝
val_tensor = torch::randn({ 2, 4 }); // 原图
auto mask = torch::zeros({ 2, 4 }); // mask图
mask[0][0] = 1; // 只取第0,0位置值。
std::cout << val_tensor << std::endl;
std::cout << val_tensor.index({ mask.to(torch::kBool) }) << std::endl; // val. shape:{1}
// 9.maks操作,浅拷贝. 原地操作:index_put_
// 利用mask找到位置,然后修改该位置上的值,再利用index_put_放置对应的位置。
val_tensor = torch::randn({ 2, 4 });
mask = torch::zeros({ 2, 4 });
mask[0][0] = 1;
mask[0][2] = 1;
std::cout << val_tensor << std::endl;
std::cout << val_tensor.index({ mask.to(torch::kBool) }) << std::endl; // 深拷贝
std::cout << val_tensor.index_put_({ mask.to(torch::kBool) }, val_tensor.index(mask.to(torch::kBool)) + 1.5);
// 比较两个tensor:val_tensor1 和val_tensor2,使得val_tensor1 始终保存更小的值
at::Tensor val_tensor1 = torch::randn({ 2, 4 });
at::Tensor val_tensor2 = torch::randn({ 2, 4 });
at::Tensor mask = val_tensor1 < val_tensor2;
std::cout << val_tensor1 << std::endl;
std::cout << val_tensor2 << std::endl;
std::cout << val_tensor1.index_put_({ mask.to(torch::kBool) }, val_tensor2.index(mask.to(torch::kBool)));拼接操作
// 10. 拼接操作
at::Tensor tensor1 = torch::ones({ 3, 4 });
at::Tensor tensor2 = torch::zeros({ 3, 4 });
at::Tensor cat_tensor = torch::cat({ tensor1, tensor2 }, 1); // sizes: [3,8]
at::Tensor stack_tensor = torch::stack({ tensor1, tensor2 }, 1); // sizes: [3, 2, 4]算术运算
// 11. 算术运算
// 乘法: *,.mul, 矩阵用.mm,加上batch维度是用.bmm.
// 除法:/, .div
at::Tensor b = torch::rand({ 2, 4 });
at::Tensor c = torch::rand({ 2, 4 });
std::cout << b << c << b * c << b / c << b.mm(c.t()); // t()是转置求最值
at::Tensor a = torch::rand({ 2, 4 });
std::cout << a << std::endl;
// 求a第0维度的最大值
std::tuple max_classes = (torch::max)(a, 0);
auto max_val = std::get<0>(max_classes); //求得最大值
auto max_index = std::get<1>(max_classes); //求得最大值的索引
cout << max_val << endl;
cout << max_index << endl;
// 求a第1维度的最大值
auto min_classes = (torch::min)(a, 1);
auto min_val = std::get<0>(min_classes); //求得最小值
auto min_index = std::get<1>(min_classes); //求得最小值的索引
cout << min_val << endl;
cout << min_index << endl; 数据类型转换
1. int和tensor
//int转tensor
torch::Tensor t = torch::tensor({2});
// tensor转int
int i = t.item().toInt();
2. tensor转vector
template
void tensor2vector(torch::Tensor x, std::vector& v) {
v = std::vector(x.data_ptr(), x.data_ptr() + x.numel());//将tensor转换为vector
}
int main()
{
auto t = torch::rand({ 2, 4 });
std::cout << t << std::endl;
std::vector tmp;
tensor2vector(t, tmp);
std::cout << tmp << std::endl;
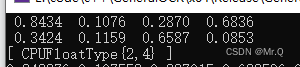
} 3. 二维的tensor转vector
效果如下。可以看到是先行后列。
4. std::vector 转tensor {batchsize, c, h, w}
用时0.015s.
clock_t start = clock();
cv::Mat resized_image;
torch::Tensor tensor_images = torch::zeros({ int(images.size()), 3, this->height, this->width }, torch::kFloat);
for (int i = 0; i < images.size(); i++)
{
// input_size
cv::resize(images[i], resized_image, cv::Size(this->width, this->height), cv::INTER_CUBIC);
// tensor
torch::Tensor tensor_image = torch::from_blob(resized_image.data, { this->height, this->width,3 }, torch::kByte).to(device);
tensor_image = tensor_image.permute({ 2,0,1 }).to(torch::kFloat);
tensor_image = tensor_image.div(255.0);
tensor_images[i] = tensor_image;
}
std::cout << "pre time: " << double(clock() - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl;用时0.017s。
clock_t start = clock();
cv::Mat resized_image;
std::vector tensor_list(images.size());
for (int i = 0; i < images.size(); i++)
{
// input_size
cv::resize(images[i], resized_image, cv::Size(this->width, this->height), cv::INTER_CUBIC);
// tensor
torch::Tensor tensor_image = torch::from_blob(resized_image.data, {1, this->height, this->width, 3 }, torch::kByte).to(device);
tensor_image = tensor_image.permute({ 0,3,1,2 }).to(torch::kFloat);
tensor_image = tensor_image.div(255.0);
tensor_list[i] = tensor_image;
}
torch::Tensor tensor_images = torch::cat(tensor_list, 0);
std::cout << "pre time: " << double(clock() - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; 待续。。。
参考:
https://github.com/AllentDan/LibtorchTutorials/tree/main/lesson2-TensorOperations