ZOJ 3762 - ZOJ Monthly, March 2014 几何(0304修正)
浙大月赛的一道几何题
原题:http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=3762
题意是给定 N (N <= 500) 个点,求三角形的最大高
解法一:旋转卡壳思想 复杂度O(n^2logn)
这个问题转换一下其实就是求点到直线的最大距离,我们把直线称为AB
如果我们固定点A,逆时针枚举点B,这时候到这个直线最远的点(AB左侧)也是逆时针变化的,和求凸包高差不多
并且这些个最远点肯定是在凸包上的,想象把枚举的边旋转到水平,最高点肯定在凸包上
于是我们可以枚举点A,然后将其他点按相对于点A的极角排序,然后以旋转卡壳的思想找另外一个点
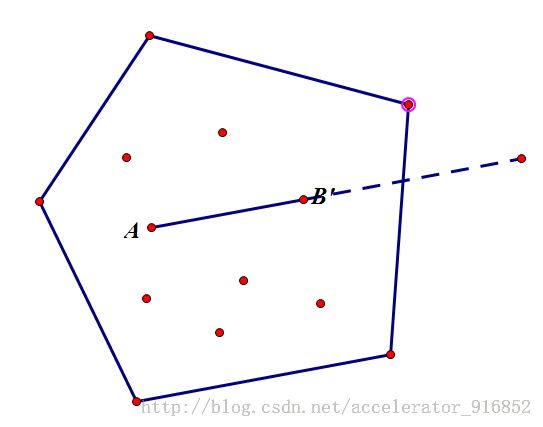
第三个点的起点应该选择凸包上 位于有向直线AB'左侧的第一个点,这里B'是指相对于点A极角最小的点(最好把极角都化为正好看一点)
如图:
写的时候注意可能有共线点的情况,可能会跪旋转那里
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define eps 1e-8
#define mxn 505
const double pi = acos(-1.0);
int dcmp( double x ) {
return (x > eps) - (x < -eps);
}
struct point {
double x, y, ang;
point(){}
point(double x, double y):x(x), y(y) {}
point operator - (const point& b) const {
return point(x - b.x, y - b.y);
}
point operator + (const point& b) const {
return point(x + b.x, y + b.y);
}
bool operator < (const point& b) const {
return x < b.x || x == b.x && y < b.y;
}
double angle() {
return atan2(y, x) + pi;
}
double len() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
void input() {
scanf( "%lf%lf", &x, &y );
}
}pnt[mxn], res[mxn], rot[mxn];
bool cmp(const point& a, const point &b) {
return a.ang < b.ang;
}
double cross( point a, point b ) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
double ptoline( point p, point a, point b ) {
return fabs(cross(a - p, b -p)) / (a - b).len();
}
int andrew( point *p, int n, point *ch ) {
sort(p, p + n);
int m = 0;
for( int i = 0; i < n; ++i ) {
while( m > 1 && dcmp(cross(ch[m-1] - ch[m-2], p[i] - ch[m-1])) < 0) --m;
ch[m++] = p[i];
}
int k = m;
for( int i = n - 2; i >= 0; --i ) {
while( m > k && dcmp(cross(ch[m-1] - ch[m-2], p[i] - ch[m-1])) < 0 ) --m;
ch[m++] = p[i];
}
if( m > 1 ) --m;
return m;
}
double check( int k, int n, int m ) {
double ret = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for( int i = 0; i < n; ++i ) {
if( i != k ) {
rot[cnt] = pnt[i] - pnt[k];
rot[cnt].ang = rot[cnt].angle();
++cnt;
}
}
sort(rot, rot + cnt, cmp);
int j = 0;
while( true ) {
if( dcmp(cross(rot[0], res[j] - pnt[k])) >= 0
&& dcmp(cross(rot[0], res[(j+m-1)%m] - pnt[k])) <=0 )
break;
j = (j + 1) % m;
}
for( int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i ) {
point tmp = pnt[k] + rot[i];
while( ptoline(res[j+1], pnt[k], tmp) > ptoline(res[j], pnt[k], tmp)
|| dcmp(ptoline(res[j], pnt[k], tmp)) == 0)
j = (j + 1) % m;
ret = max(ret, ptoline(res[j], pnt[k], tmp));
}
return ret;
}
double solve( int n, int m ) {
double ans = 0; res[n] =res[0];
for( int i = 0; i < n; ++i )
ans = max(ans, check(i, n, m));
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while( cin >> n ) {
for( int i = 0; i < n; ++i ) pnt[i].input();
int m = andrew(pnt, n, res);
printf( "%.10lf\n", solve(n, m) );
}
return 0;
}
解法二:复杂度O(n^2)
做法,枚举点A,找到距离他最远的点B,再枚举C即可
证明了一晚上,终于证明了这种做法是错的.......能过只能说明数据水.....
数据如下:
5
1 1
2 1
1 10000
7073 7073
1 0.5
正确答案显然是三角形 (1, 1) - (2, 1) - (1, 10000), 高是9999
但是这种O(n^2)的做法得到的答案是9239.4038739974
原因是根本枚举不到上面的三角形,
枚举点(1, 1)时,最远的是(7073, 7073)
枚举点(2, 1)时,最远的是(7073, 7073)
枚举点(1, 10000)时,最远的是(1, 0.5)
枚举点(7073, 7073)时,最远的是(1, 0.5)
枚举点(1, 0.5)时,最远的是(7073, 7073)
大概就是介么个图....
昨晚我还证明成对的来着,越看越不对劲 T_T