常用的较优排序之快速排序,堆排序,归并排序
1、快速排序
通过一趟排序将要排序的数据分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分的所有数据都比另外一部分的所有数据都要小,然后再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序。可以用递归和非递归的方法分别实现。
平均状况下,排序n个项目要Ο(n log n)次比较。在最坏状况下则需要Ο(n2)次比较,但这种状况并不常见。事实上,快速排序通常明显比其他Ο(n log n) 算法更快。int _QuickSort(int* a,int left,int right,int key)
{
while (left < right)
{
while (left < right&&a[left] <=a[key])
{
left++; //找出比a[key]大的下标
}
while (left < right&&a[right] >=a[key])
{
right--; //找出比a[key]小的下标
}
swap(a[left], a[right]); //交换
}
if (a[left] > a[key]) //如果需要排序的序列都小于a[key]值
swap(a[left],a[key]);//把 key-1 当边界,如图中当第二次a[key]为5时。
return left;
}
return key;
}
int _QuickSort2(int* a, int left, int right, int key)
{
int cur = left;
int prev = left - 1;
while (cur <= right)
{
if (a[cur] <= a[key])
{
prev++;
if(prev!=cur)
swap(a[prev], a[cur]);
}
cur++;
}
swap(a[prev+1],a[key]);
return prev+1;
}
void QuickSort(int* a, int left, int right)
{
assert(a);
if (left < right)
{
int mid = FindMid(a,left,right);//3位取中,把左边右边和中间的数比较,找出中间的数作为key
swap(a[mid],a[right]);
int key = right;
int boundary=_QuickSort2(a,left,right-1,key);//一趟排序后找出边界值
//int boundary=_QuickSort(a,left,right-1,key);//有两种方法找出边界值
QuickSort(a,left,boundary-1);
QuickSort(a, boundary+1,right);
}
}
//非递归借用栈来完成
void NORQucikSort(int* a,int left,int right)
{
stack<int> s1;
s1.push(left);
s1.push(right);
while (!s1.empty())
{
int key = s1.top();
int _right = s1.top();
s1.pop();
int _left = s1.top();
s1.pop();
if (_left >= _right)
continue;
int boundary = _QuickSort(a, _left, _right - 1, key);
//int boundary = _QuickSort2(a, _left, _right - 1, key);
s1.push(boundary + 1); //先压key右边的序列
s1.push(_right);
s1.push(_left);
s1.push(boundary-1);
}
}
//优化快速排序 三数取中
int FindMid(int* a, int left, int right)
{
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (a[left] > a[right])
{
if (a[left] < a[mid])
return left;
else if (a[mid]>a[right])
return mid;
return right;
}
else
{
if (a[left] > a[mid])
return left;
else if (a[mid] < a[right])
return mid;
return right;
}
}
2、堆排序
堆排序的思想就是如果是升序排序,则建最大堆,反之,则建最小堆。
建堆之后,从第一个数开始和最后一个数交换,缩小堆的范围(去除最后一个数),然后第一个数向下调整,则最大的数已在最后。直到堆里只有一个数。
建堆过程就是从最后一个非叶子节点直到跟节点向下调整。假设我们现在要升序排序。即就是向下调整时,把小的交换到父节点。
堆排序的时间复杂度是O(N*lgN),空间复杂度是O(1)。
void AdjustDown(int *a,int size,int parent) //向下对齐
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1; //把左孩子的下标给child
while (child < size) //保证向下对齐直到child超出范围
{
if (child + 1 < size&&a[child + 1] > a[child]) //当右孩子>左孩子时,child变为右孩子下标
{
child++;
}
if (a[parent] < a[child])
{
swap(a[parent],a[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void HeapSort(int *a, int size)
{
assert(a);
for (int i = (size - 2) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
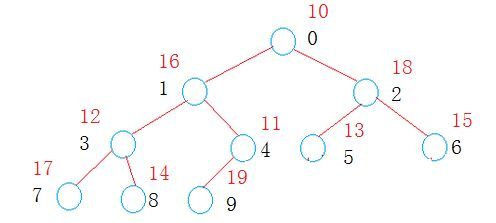
AdjustDown(a,size,i); //从图中下标为4的非叶子节点开始,进行向下对齐
}
for (int i = size - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
swap(a[0],a[i]); //把最大堆中的第一个元素和最后一个元素交换,此时最后一个元素最大
AdjustDown(a,i,0);//把剩余的元素建成最大堆
}
}
3、归并排序
归并排序时的时间复杂度为O(nlgn) 其主要思想是分治法(divide and conquer),分就是要将n个元素的序列划分为两个序列,再分为4个序列,直到每个序列只有一个数,然后合并两个有效序列为一个有效序列,直到整个序列为有序序列。
归并排序的时间复杂度O(N*lgN),空间复杂度是O(N)。
递归实现:
void MergeSort(int *a, int size)
{
assert(a);
int *tmp = new int[size];
int left = 0, right = size - 1;
_MergeSort(a,tmp,left,right);
}
void _MergeSort(int* a, int* tmp, int left, int right)
{
if (left < right)
{
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;//取中间下标
_MergeSort(a,tmp,left,mid); //递归进行
_MergeSort(a, tmp, mid+1, right); //直到递归到左右序列只有一个元素
Combine(a,tmp,left,mid,mid+1,right);//2个有序序列合并成一个
memcpy(a+left,tmp,(right-left+1)*sizeof(int));//把有序序列拷给原数组
}
}
void Combine(int* a, int* tmp, int begin1, int end1,int begin2, int end2)
{
int index = 0;
while (begin1 <= end1&&begin2 <= end2)
{
while (a[begin1] <= a[begin2]&&begin1<=end1)
{
tmp[index++] = a[begin1];
begin1++;
}
while (a[begin1] > a[begin2] && begin2 <= end2)
{
tmp[index++] = a[begin2];
begin2++;
}
}
while (begin1 <= end1)
{
tmp[index++] = a[begin1++];
}
while (begin2 <= end2)
{
tmp[index++] = a[begin2++];
}
}
而递归排序的非递归实现,则采取相反的思路,先把整个数组分成n个序列,每次两个序列合并。每两个序列有序后,合4个序列,以此类推。
void MergeSort2(int *a, int size)
{
assert(a);
int gap = 0;
int *temp = new int[size];
int count = 0;
//gap指begin1和end1每次的差值 所差次数依次为,0,1,3,7(2^n-1)
while (gap < size)
{
int begin1 = 0, end1 = gap, begin2 = end1 + 1, end2 = begin2 + gap;
for (; end2 < size; begin1=end2+1,end1=begin1+gap,begin2=end1+1,end2=begin2+gap)
{
Combine(a,temp,begin1,end1,begin2,end2);
memcpy(a+begin1,temp,(end2-begin1+1)*sizeof(int));
}
if (begin2 < size)
{
end2 = size - 1;
Combine(a, temp, begin1, end1, begin2, size-1);
memcpy(a + begin1, temp, (end2 - begin1 + 1)*sizeof(int));
}
count++;
gap=pow(2,count)-1;
}
}