pongo(csdn英雄会)题解之最小操作数---leetcode之word ladder2
这道题今年暑假在家的时候做过,但是超时了,昨天又重新做了下,由于没写注释,拿出以前写的代码,基本看不懂,以后码代码还是要多写注释和文档,下面是题目:
给了A、B两个单词和一个单词集合Dict,每个的长度都相同。我们希望通过若干次操作把单词A变成单词B,每次操作可以改变单词中的一个字母,同时,新产生的单词必须是在给定的单词集合Dict中。求所有行得通步数最少的修改方法。 举个例子如下: Given: A = "hit" B = "cog" Dict = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"] Return [ ["hit","hot","dot","dog","cog"], ["hit","hot","lot","log","cog"] ] 即把字符串A = "hit"转变成字符串B = "cog",有以下两种可能: "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog"; "hit" -> "hot" -> "lot" -> "log" ->"cog"。
-------------------------------------------分割线-----------------------------------------
1.思路:
这道题是不是跟求最短路径有点神似,那么方法就是广度优先搜索BFS,这是图论的知识,显然广度优先搜索需要用到邻接矩阵或者是邻接表(~!我就知道这两种),在此我选择邻接表,因为在BFS图的时候,邻接表在查找邻接关系时较邻接矩阵容易。
那么这道题的解题步骤就是:1)构建邻接表;2)BFS,并对A通往B的路径做标记;3)遍历2)中的路径。
2.解释:
(1)在构建邻接链表的时候,我采用的是头插法;
(2)BFS时,我采用的是以B作为起点,向A搜索,即以目的字符串为起点,这样做我是为了易于返回路径;
(3)对A通往B的路径做标记,我采用了一个元素为vector的动态数组,即std::vector<size_t>*pointTo=new std::vector<size_t>[dictV.size()];
,数组的索引表明这个点的ID,对应的vector存放的是路径中这个点指向的其他点ID。
(4)遍历路径:其实上面的几步已经将图层次化,遍历所有无非就是通过递归或者栈实现,我采用的是递归程序。
下面是示例:
start="bbdk",end="abcd",dict={"cbck","bbck","bbdd","dcck","bbcd","abdd","dccd","accd"};
下面是上述点的对应的图如下:
邻接表如下:
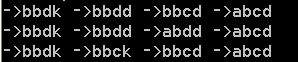
广度优先搜索后,A通往B的路径标记数组值(为了便于浏览,下图将点ID转换成了字符串)如下:-->后面是路径中指向的点
上面的标记数组对应下面层次化的图:
递归遍历 A通往B的所有路径,得到路径:
3.复杂度分析
显然生成邻接表的复杂度是O(n*n*length),BFS和递归寻找路径的复杂度都是O(边数),综上复杂度是O(n*n*length),是n^2级的,复杂度较高,一种在n很大时降低复杂度的方法见http://blog.csdn.net/caopengcs/article/details/9919341,但是cp修改字母方法来构建邻接表的复杂度我认为应该是O(26*length*n *logn *length),其中logn是查找map(c++中map的实现是通过树实现的),额外的length是查找map时的字符串比较。
4.代码
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
//#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
class Node{//用于邻接链表的节点结构
public:
size_t id;
Node * next;
Node(){
static size_t i=0;
id=i++;
next=NULL;
}
Node(size_t i,Node* n):id(i),next(n){}
~Node(){
if(next){
delete next;
next=NULL;
}
}
};
class Solution
{
public:
std::vector<std::string>dictV;
std::map<std::string,size_t>dictM;
void findPaths(std::vector<size_t>*pointTo,size_t id,size_t endID,std::vector<std::string>&v,vector<vector<string>>&paths){
//根据标记数组,递归遍历A到B的所有路径
if(pointTo[id].at(0)==endID){
v.push_back(dictV[endID]);
paths.push_back(v);
}else{
for(size_t i=0;i<pointTo[id].size();++i){
std::vector<std::string>v1(v);
v1.push_back(dictV[pointTo[id].at(i)]);
findPaths(pointTo,pointTo[id].at(i),endID,v1,paths);
}
}
}
bool isOnceDiff(const std::string &str1,const std::string &str2){
//判断两个字符串是否是仅一个字符不一样
bool flag=false;
for(std::string::size_type sst=0;sst<str1.size();sst++){
if(str1[sst]!=str2[sst]){
if(!flag)flag=true;
else {
flag=false;
break;
}//else
}//if
}//for
return flag;
}//isoncediff
vector<vector<string>> findLadders(string start, string end, set<string> &dict){
std::vector<std::vector<std::string>> paths;
if(start==end)return paths;//A==B直接返回
dict.insert(start);
dict.insert(end);
bool *flagHasQued=new bool[dict.size()];//用于BFS的标记
bool *flagWillQue=new bool[dict.size()];//用于BFS的标记
size_t num=0;
for(std::set<std::string>::iterator it=dict.begin();it!=dict.end();it++){
//为了使用字符串的索引,引入map和vector
dictV.push_back(*it);
dictM.insert(make_pair(*it,num));
flagHasQued[num]=false;
flagWillQue[num]=false;
num++;
}
//双层循环构建邻接表
Node *graph=new Node[dict.size()];//
for(size_t i=0;i<dictV.size();++i){
for(size_t j=i+1;j<dictV.size();++j){
if(isOnceDiff(dictV[i],dictV[j])){
graph[i].next=new Node(j,graph[i].next);
graph[j].next=new Node(i,graph[j].next);
}
}
}
//BFS
std::vector<size_t>*pointTo=new std::vector<size_t>[dictV.size()];
std::queue<size_t> *que1=new std::queue<size_t>,*que2=new std::queue<size_t>;
size_t startID=dictM[start];
size_t endID=dictM[end];
size_t tmpID=endID;
que1->push(tmpID);
flagHasQued[tmpID]=true;
bool hasArrive=false;
while(!que1->empty()){//
tmpID=que1->front();
que1->pop();//出队
Node *tmpNode=graph[tmpID].next;//
while(tmpNode){
if(!hasArrive){//这一层第一个找到start的前几个还是添加了指向,这些其实没必要
if(!flagHasQued[tmpNode->id])
pointTo[tmpNode->id].push_back(tmpID);
if(tmpNode->id==startID){
hasArrive=true;
break;
}//if
if(!flagWillQue[tmpNode->id]){
que2->push(tmpNode->id);
flagWillQue[tmpNode->id]=true;
}//if
}else{
if(tmpNode->id==startID){
pointTo[tmpNode->id].push_back(tmpID);
break;
}
}//else
tmpNode=tmpNode->next;
}//while
if(hasArrive)
continue;
if(que1->empty()){
while(!que2->empty()){
que1->push(que2->front());
flagHasQued[que2->front()]=true;
que2->pop();
}//while
}//if
}//while
if(!hasArrive)
return paths;
//递归遍历所有路径
std::vector<string>path;
path.push_back(start);
findPaths(pointTo,startID,endID,path,paths);
return paths;
}
};
//start 提示:自动阅卷起始唯一标识,请勿删除或增加。
int main()
{
//
char* a[]={"cbck","bbck","bbdd","akkd","bbcd","abdd","abkd","accd"};
std::string start("bbdk");
std::string end("abcd");
vector<vector<string>> res;
std::set<string>dict;
for(int i=0;i<sizeof(a)/sizeof(char*);i++)
dict.insert(a[i]);
for(std::set<std::string>::iterator it=dict.begin();it!=dict.end();it++)
std::cout<<*it<<" ";
std::cout<<std::endl;
Solution s;
clock_t begT=clock();
res=s.findLadders(start, end, dict);
clock_t endT=clock();
std::cout<<"time spent:"<<(endT-begT)/(1.0*CLOCKS_PER_SEC)<<std::endl;
//std::cout<<res.size()<<std::endl;
for(size_t i=0;i<res.size();i++){
for(size_t j=0;j<res[i].size();++j)
std::cout<<"->"<<res[i][j]<<" ";
std::cout<<std::endl;
}
//"hot","dot","dog","lot","log";
return 0;
}
//end //提示:自动阅卷结束唯一标识,请勿删除或增加
以上代码通过了hero,因为hero只要求3s内,但是leetcode当集合达到3K左右时,就超时了。