python绘制旅行商(TSP)问题的路线图
用python绘制旅行商问题路线图
最近在研究TSP问题,然后在最后需要绘制旅游路线,自己摸索了一会儿最终整理出来供自己将来备用【防止自己又忘记】
附TSP程序,备注已经很详细了,应该完全可以看懂!
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pdb
"旅行商问题 ( TSP , Traveling Salesman Problem )"
coordinates = np.array([[66.83,25.36], [61.95,26.34], [40,44.39], [24.39,14.63], [17.07,22.93], [22.93,76.1 ],
[51.71,94.14], [87.32,65.36], [68.78,52.19], [84.88,36.09], [50,30 ],[40,20 ],[25,26]])
#得到距离矩阵的函数
def getdistmat(coordinates):
num = coordinates.shape[0] #52个坐标点
distmat = np.zeros((num,num)) #52X52距离矩阵
for i in range(num):
for j in range(i,num):
distmat[i][j] = distmat[j][i]=np.linalg.norm((coordinates[i]-coordinates[j]), ord=2) # 求2范数,即距离
# print('距离矩阵', distmat)
return distmat # 对称距离矩阵
# 初始化参数
def initpara():
alpha = 0.99
t = (1,100) # 元祖
markovlen = 1000
return alpha,t,markovlen
num = coordinates.shape[0]
distmat = getdistmat(coordinates) #得到距离矩阵
solutionnew = np.arange(num) # [0,1,...,num-1],即新路线图
#valuenew = np.max(num)
solutioncurrent = solutionnew.copy() # [0,1,...,num-1],即当前路线图
valuecurrent = 99000 # np.max这样的源代码可能同样是因为版本问题被当做函数不能正确使用,应取一个较大值作为初始值
# print(valuecurrent)
solutionbest = solutionnew.copy()
valuebest = 99000 # np.max
alpha,t2,markovlen = initpara()
t = t2[1] # t=100
t_min = t2[0]
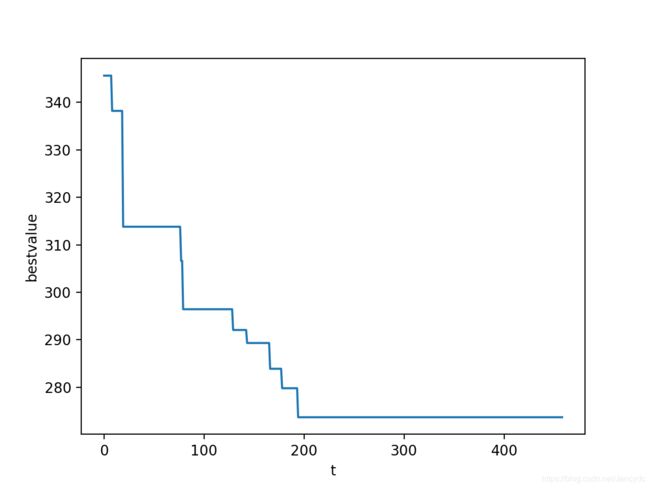
result = [] # 记录迭代过程中的最优距离解
while t > t_min:
for i in np.arange(markovlen):
# 下面的两交换和三角换是两种扰动方式,用于产生新解
if np.random.rand() > 0.5: # 交换路径中的这2个节点的顺序
# np.random.rand()产生[0, 1)区间的均匀随机数
while True: # 产生两个不同的随机数
loc1 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand()*(num-1))) # np.ceil表示向大于等于该值的向上取整;np.floor:向下取整
loc2 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand()*(num-1)))
## print(loc1,loc2)
if loc1 != loc2:
break
solutionnew[loc1],solutionnew[loc2] = solutionnew[loc2],solutionnew[loc1]
else: #三交换
while True:
loc1 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand()*(num-1)))
loc2 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand()*(num-1)))
loc3 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand()*(num-1)))
if((loc1 != loc2)&(loc2 != loc3)&(loc1 != loc3)):
break
# 下面的三个判断语句使得loc1 loc2:
loc1,loc2 = loc2,loc1
if loc2 > loc3:
loc2,loc3 = loc3,loc2
if loc1 > loc2:
loc1,loc2 = loc2,loc1
#下面的三行代码将[loc1,loc2)区间的数据插入到loc3之后
tmplist = solutionnew[loc1:loc2].copy()
solutionnew[loc1:loc3-loc2+1+loc1] = solutionnew[loc2:loc3+1].copy()
solutionnew[loc3-loc2+1+loc1:loc3+1] = tmplist.copy()
valuenew = 0
for i in range(num-1):
valuenew += distmat[solutionnew[i]][solutionnew[i+1]]
valuenew += distmat[solutionnew[0]][solutionnew[num-1]]
# print (valuenew)
if valuenew plot_x_set = []
plot_y_set = []
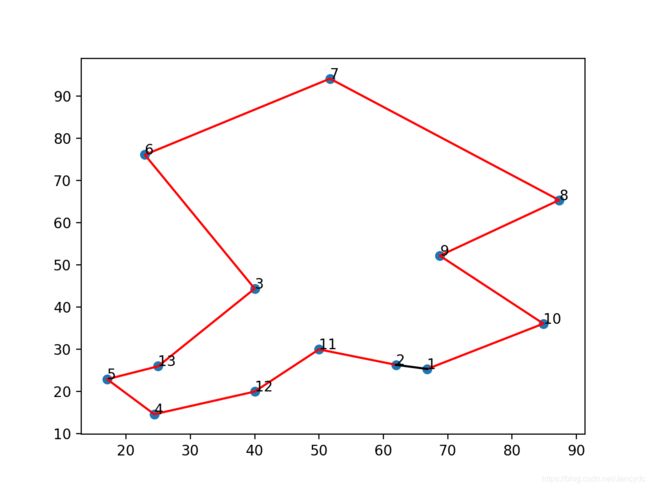
print(solutioncurrent+1) # 输出最优路径图
for i in solutioncurrent:
# plt.plot(coordinates[i])
plot_x_set.append(coordinates[i][0])
plot_y_set.append(coordinates[i][1])
plt.plot(plot_x_set,plot_y_set,'r')
plt.scatter(plot_x_set,plot_y_set,)
for i,txt in enumerate(solutionnew+1): # 标注每个点的序号
plt.annotate(txt, (plot_x_set[i],plot_y_set[i]))
# 首尾2个点的连线
x = [plot_x_set[0],plot_x_set[-1]]
y = [plot_y_set[0],plot_y_set[-1]]
plt.plot(x, y, 'k') # 用黑色标识
plt.show()
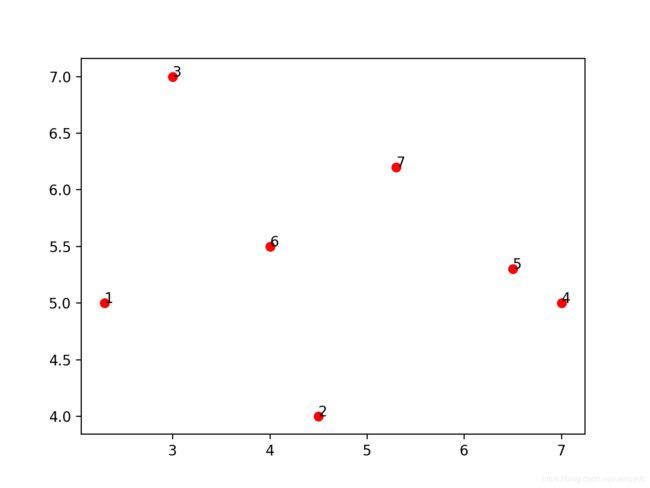
如果去掉TSP实际背景,单纯绘制路线图的并标注各个点的序号的话,代码如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [2.3, 4.5, 3, 7, 6.5, 4, 5.3]
y = [5, 4, 7, 5, 5.3, 5.5, 6.2]
n = np.arange(len(x))
plt.scatter(x, y, c='r')
for i, txt in enumerate(n):
plt.annotate(txt, (x[i], y[i]))
plt.show()