【搞定左神算法初级班】第4节:二叉树及相关常见面试题
目 录:
题目1:实现二叉树的先序、中序、后序遍历【递归方式和非递归方式】
题目2:在二叉树中找到一个节点的后继节点
题目3:介绍二叉树的序列化和反序列化
题目4:折纸问题
题目5:判断一棵二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
题目6、判断一棵树是否是搜索二叉树、判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树
题目7:已知一棵完全二叉树,求其节点的个数
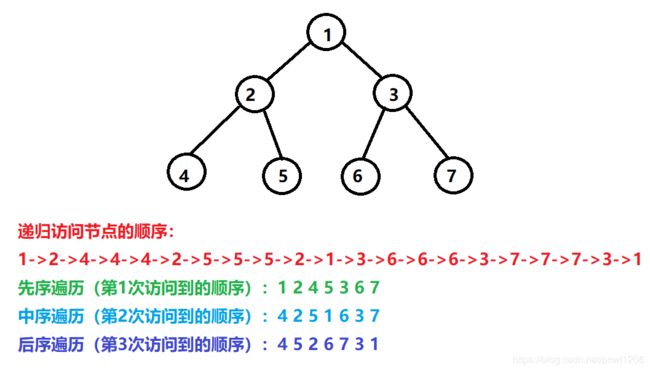
题目1:实现二叉树的先序、中序、后序遍历【递归方式和非递归方式】
递归思想:
-
【分析】:必须想清楚你这一层要返回给你的上一层什么东西,这些信息需要同样的格式
- 左交给我信息
- 右交给我信息
- 我要交给上一层什么信息
-
实际遍历的时候三者是一样的,每个结点会遇见3次,先序、中序、后序遍历只是选择打印的时机不同而已。
- 递归实现
package com.offer.class4;
/**
* @author pengcheng
* @date 2019/3/27 - 22:00
* @content: 二叉树的前、中、后序遍历的递归版
*/
public class BinaryTreeWithRecur {
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
}
// 先序遍历
public void preOrderRecur(Node head){
if(head == null){
return;
}
// 整体的打印顺序是:中->左->右
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
preOrderRecur(head.left);
preOrderRecur(head.right);
}
// 中序遍历
public void inOrderRecur(Node head){
if(head == null){
return;
}
// 整体的打印顺序是:左->中->右
inOrderRecur(head.left);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
inOrderRecur(head.right);
}
// 后序遍历
public void posOrderRecur(Node head){
if(head == null){
return;
}
// 整体的打印顺序是左->右->中
posOrderRecur(head.left);
posOrderRecur(head.right);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
}
// 测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTreeWithRecur tree = new BinaryTreeWithRecur();
Node root = new Node(1);
Node node1 = new Node(2);
Node node2 = new Node(3);
Node node3 = new Node(4);
Node node4 = new Node(5);
Node node5 = new Node(6);
Node node6 = new Node(7);
root.left = node1;
root.right = node2;
node1.left = node3;
node1.right = node4;
node2.left = node5;
node2.right = node6;
System.out.println("=======前序遍历=======");
tree.preOrderRecur(root); // 1 2 4 5 3 6 7
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=======中序遍历=======");
tree.inOrderRecur(root); // 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=======后序遍历=======");
tree.posOrderRecur(root); // 4 5 2 6 7 3 1
}
}
- 非递归实现
1、前序遍历:中 —> 左 —> 右
分析:处理当前结点,有右孩子先压右孩子进栈,有左孩子再压左孩子进栈,那么这样弹出就会是先左,再右。
为什么使用栈而不是队列呢?
二叉树有从上到下和从下到上的路径,所以需要一个结构让它回去,只有栈【队列只能从上到下,回不去】
- 模拟前序遍历元素的进栈出栈过程:
// 前序遍历:中->左->右:处理当前节点,有右先压右,有左再压左,这样就会先弹出左,再弹出右
public void preOrderUnRecur(Node head){
if(head == null){
return;
}
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.push(head);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
head = stack.pop(); // 先弹出当前节点
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
// 先压右孩子
if(head.right != null){
stack.push(head.right);
}
// 再压左孩子
if(head.left != null){
stack.push(head.left);
}
}
} 2、后序遍历:左 —> 右 —> 中
两个栈实现,由先序过程改进而来,先序中左右->中右左->左右中。
- 【分析】:先序中左右,先处理当前结点,然后改为先压左孩子,再压右孩子,那么弹出的顺序就成为了右左【中右左】,利用一个栈即可变为左右中。
// 后序遍历:左->右->中 可以由前序遍历转变而来:中左右--> 中右左 --> 左右中
public void postOrderUnRecur(Node head){
if(head == null){
return;
}
Stack stack1 = new Stack();
Stack stack2 = new Stack(); // 用于将中右左变为左右中
stack1.push(head);
// stack1中最后弹出的顺序是:中、右、左,所以先压左再压右
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
head = stack1.pop(); // 弹出当前节点
// 将stack1弹出的元素压入stack2中,这样压入顺序是中、右、左,弹出顺序就是:左、中、右了
stack2.push(head);
if(head.left != null){
stack1.push(head.left);
}
if(head.right != null){
stack1.push(head.right);
}
}
while(stack2.isEmpty()){
System.out.print(stack2.pop().value + " ");
}
} 3、中序遍历: 左 —> 中 —> 右
当前节点会把自己的左边界一次性都压到栈里,然后依次弹出,直到遇到一个有右孩子的节点,处理它的右孩子,这样就模拟了“左、中、右”这样的一个过程。
当前节点为空,从栈拿一个打印,当前节点向右移动。当前节点不为空,当前节点压入栈,当前节点往左移动。
// 中序遍历:左 —> 中 —> 右
public void inOrderUnRecur(Node head){
if(head == null){
return;
}
Stack stack = new Stack();
// 压一绺左边界,再从尾端依次往外弹,弹出一个节点,再去遍历它的右孩子。这个过程就模拟了:左、中、右这个过程
// 需要判断head是否为null,是因为后序不同于先序和中序在循环前就将head压入栈中了
while(!stack.isEmpty() || head != null){
if(head != null){
// 一压压一绺左边界节点
while(head != null){
stack.push(head);
head = head.left; // 遍历左边界节点
}
}else{
// 当前节点为空,说明上面已经压完了一绺,弹出节点(中点),再处理右边
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
} 题目2:在二叉树中找到一个节点的后继节点
【题目】 现在有一种新的二叉树节点类型如下:
public class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int data) { this.value = data; }
}
二叉树节点结构多了一个指向父节点的parent指针。假设有一棵Node类型的节点组成的二叉树,树中每个节点的parent指针都正确地指向自己的父节点,头节点的parent指向null。现在只给一个在二叉树中的某个节点 node,请实现返回node的后继节点的函数。在二叉树的中序遍历的序列中,node的下一个节点叫作node的后继节点,node的上一个节点叫做它的前驱节点。
- 思路:根据当前节点有无右子节点分为两种情况:
- 有右子树:则当前节点的后继节点则是右子树中最左的左子节点;
- 无右子树:则当前节点的后继节点则是向上查找当前节点属于哪个节点的左子树下面,即向上找到一个父节点作为左子节点的,那么这个作为左子节点的父节点的父节点就是当前节点的后继节点。(画图感受!)
package com.offer.class4;
/**
* @author pengcheng
* @date 2019/3/28 - 11:23
* @content: 找二叉树中一个节点的后继节点:即中序遍历中一个节点的下一个节点
*/
public class SuccessorNode {
public static class Node{
private int value;
private Node left;
private Node right;
private Node parent; // 新增:父节点指针
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
}
// 找到任一node节点的后继节点
public Node getSuccessorNode(Node node){
if(node == null){
return null;
}
if(node.right != null){
// 情况1:如果该节点存在右子节点,后继节点是右子树中的最左边节点
return getLeafMost(node.right);
}else{
// 情况2:如果没有右子树,向上查找当前节点属于哪个节点的左子树下面,即找到一个父节点是左子节点的
// 整棵树只有最后一个节点没有后继节点,会查找到根节点的父节点为null
Node parent = node.parent;
while(parent != null && node != parent.left){
// parent != null 是为最后一个节点设置的,其后继节点就是根节点的父节点为null
node = parent;
parent = node.parent; // 向上遍历
}
return parent;
}
}
// 找到node节点的最左边的节点
public Node getLeafMost(Node node){
if(node == null){
return node;
}
while(node.left != null){
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
}
- 补充:找一个节点的前驱节点其实和找该节点的后继节点是对应的,根据该节点是否有左子树进行划分:
- 1、当前节点有左子树,则找左子树中最右的节点即为当前节点的前驱节点;
- 2、当前节点没有左子树,则向上找到一个父节点是作为右子节点的,那么这个父节点的父节点即为当前节点的前驱节点。
题目3:介绍二叉树的序列化和反序列化
- 【分析】:序列化:怎么记录下来(包括结构这些),反序列化:怎么还原结构。
- “_”:用于分开节点中的值;
- “#”:用于表示null空节点,用这些符号表示null节点把位置给占住,不然无法区分一些节点值都相等的情况。
- 【技巧】:利用递归,怎么序列化就用同样的方式反序列化【先序、中序、后序都是一个套路】
package com.offer.class4;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author pengcheng
* @date 2019/3/28 - 13:55
* @content:二叉树的序列化和反序列化,代码实现都是以前序遍历为例的
*/
public class SerializeAndReconstuct {
public static class Node{
private int val;
private Node left;
private Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
// 前序遍历来序列化一颗二叉树
public String serialByPre(Node head){
if(head == null){
return "#_"; // 空节点用#表示,不同节点值之间用_隔开
}
String res = head.val + "_"; // 中
res += serialByPre(head.left); // 左
res += serialByPre(head.right); // 右
return res;
}
// 前序遍历:反序列化一棵二叉树,怎么序列化的就怎么反序列化
public Node reconByPreString(String str){
String[] values = str.split("_"); // 将字符串分割成节点值组成的数组
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
for(String i : values){
queue.add(i); // 将数组中的节点元素添加到队列中,也可以直接使用数组
}
return reconPreOrder(queue);
}
// 根据一个队列构建一棵树
public Node reconPreOrder(Queue queue){
String val = queue.poll();
if(val.equals("#")){
return null; // 如果值为#,则构建一个空节点
}
// 还是按照中、左、右的方式去构建二叉树
Node head = new Node(Integer.valueOf(val));
head.left = reconPreOrder(queue);
head.right = reconPreOrder(queue);
return head;
}
}
- 上面的代码实现都是基于前序遍历的。我们有时候会遇到按层来序列化一棵二叉树,在这里补充下代码:
package com.offer.class4;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* @author pengcheng
* @date 2019/3/28 - 14:20
* @content: 按层来序列化和反序列化二叉树
*/
public class SerializeAndReconstructByLevel {
public static class Node{
private int val;
private Node left;
private Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
// 按层序列化
public String serializeByLevel(Node head){
if(head == null){
return "#_";
}
String res = head.val + "_";
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
queue.offer(head);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
// 中
head = queue.poll();
// 左
if(head.left != null){
res += head.left.val + "_";
queue.offer(head.left);
}else{
res += "#_";
}
// 右
if(head.right != null){
res += head.right.val + "_";
queue.offer(head.right);
}else{
res += "#_";
}
}
return res;
}
// 按层反序列化
public Node recornByLevelString(String levelStr){
String[] values = levelStr.split("_");
int index = 0;
Node head = generateNodeByString(values[index++]);
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
if(head != null){
queue.offer(head); // 中
}
Node node = null;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
node = queue.poll();
node.left = generateNodeByString(values[index++]);
node.right = generateNodeByString(values[index++]);
if(node.left != null){
queue.offer(node.left); // 左
}
if(node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.right); // 右
}
}
return head;
}
// 根据字符串构建一个节点
public Node generateNodeByString(String str){
if(str.equals("#")){
return null;
}
return new Node(Integer.valueOf(str));
}
}
题目4:折纸问题
【题目】 请把一段纸条竖着放在桌子上,然后从纸条的下边向 上方对折1次,压出折痕后展开。此时 折痕是凹下去的,即折痕 突起的方向指向纸条的背面。如果从纸条的下边向上方连续对折 2 次,压出折痕后展开,此时有三条折痕,从上到下依次是下折 痕、下折痕和上折痕。 给定一 个输入参数N,代表纸条都从下边向上方连续对折N次, 请从上到下打印所有折痕的方向。 例如:N=1时,打印: down N=2时,打印: down down up
题目5:判断一棵二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
5.1 二叉树大套路:递归很好用【每个结点会被访问三次,不要去想什么先、中、后序,有没有打印递归都是存在的】
- 【套路】:
- 1.列出所有可能性
- 2.整理出返回值的类型ReturnData【整个递归要按照同样的返回值的结构】
- 3.得到左右子树的信息
- 4.整合子树的信息
- 5.返回我的信息
5.2 平衡二叉树:对任何一棵树,其左右子树高度差不超过1
- 【分析】:只要以每个结点作为根节点的树都是平衡的,则整棵树就是平衡的
- 1.左子树不平衡?
- 2.右子树不平衡?
- 3.都平衡,左树和右树的高度差超过1,则不是平衡树
- 4.都平衡,左树和右树的高度差不超过1,则说明是平衡树
递归实现返回信息:左树递归返回左树是否平衡和左树的高度,右树同样。
package com.offer.class4;
/**
* @author pengcheng
* @date 2019/3/28 - 15:58
* @content: 判断一棵树是否是平衡树
*/
public class IsBalanceTree {
public static class Node{
private int val;
private Node left;
private Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
// 构建递归过程中的返回值结构
public class ReturnData{
public boolean isB; // 是否平衡
public int h; // 高度
public ReturnData(boolean B, int h){
this.isB = B;
this.h = h;
}
}
// 主函数
public boolean isBalance(Node head){
return process(head).isB;
}
public ReturnData process(Node head){
if(head == null){
return new ReturnData(true, 0);
}
ReturnData leftData = process(head.left); // 得到左子树是否平衡和高度信息
if(leftData.isB == false){
// 当前节点的左子树不平衡,整棵树都不平衡了,高度信息没有用了,直接就-1
return new ReturnData(false, -1);
}
ReturnData rightData = process(head.right);
if(rightData.isB == false){
// 当前节点的右子树不平衡,整棵树都不平衡了,高度信息没有用了,直接就-1
return new ReturnData(false, -1);
}
// 来到这里,说明当前节点的左右子树都平衡,需要对比左右子树的高度差是否大于1
if(Math.abs(rightData.h - leftData.h) > 1){
return new ReturnData(false, -1);
}
// 左右子树都平衡,且高度差小于等于1,则此节点作为根节点的子树是平衡的
// 高度则为左右子树中最高的高度+1
return new ReturnData(true, Math.max(rightData.h, leftData.h) + 1);
}
}
题目6、判断一棵树是否是搜索二叉树、判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树
-
6.1 搜索二叉树
没有重复结点(有重复的值可以放到同一个节点中,拉个链表),对任何一节点,左子树都比它小,右子树都比它大
- 【分析】:判断方法:实际就是中序遍历的结果,如果是依次升序,就是搜索二叉树。只用在中序遍历打印节点的时机进行前一个数和当前数值大小的判断即可。
package com.offer.class4;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @author pengcheng
* @date 2019/3/28 - 16:38
* @content:判断一棵树是否是搜索二叉树
*/
public class IsBinarySearchTree {
public static class Node{
private int val;
private Node left;
private Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
// 判断一棵树是否是二叉搜索树
public Boolean isBinarySearchTree(Node head){
if(head == null){
return true; // 空树是二叉搜索树
}
int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // 这里最好将值设置为int类型的最小值,因为树里面第一个节点可能存的也是很小的值
Stack stack = new Stack();
// 压一绺左边界,再从最下面依次往上弹,直到遇到一个有右孩子的节点,去遍历它的右孩子
while(!stack.isEmpty() || head != null){
if(head != null){
while (head != null){
stack.push(head.left); // 压一绺左节点
head = head.left;
}
}else{
// 当前节点为空,说明左边界压完了,则弹出节点(中),再处理右边界
head = stack.pop(); // 中
// 判断前一个数是否小于二叉树
if(pre > head.val){
return false;
}
pre = head.val;
head = head.right; // 右
}
}
return true;
}
}
-
6.2 完全二叉树:从左往右对齐
【分析】:进行层序遍历每个结点:
- 情况1:左右双全,则看下一个结点
- 情况2:如果一个结点不是左右双全
- 2.1 如果一个结点无左结点,有右节点,则一定不是完全二叉树
- 2.2 如果一个结点有左结点,无右节点,则后面遇到的结点必须都是叶节点才能使完全二叉树,否则false
- 2.3 如果一个结点无左结点,无右结点,则后面遇到的结点必须都是叶节点才能使完全二叉树,否则false
package com.offer.class4;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* @author pengcheng
* @date 2019/3/28 - 17:18
* @content:层序遍历:判断一棵树是否为完全二叉树
*/
public class IsCompleteBT {
public static class Node{
private int val;
private Node left;
private Node right;
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public Boolean isCompleteBT(Node head){
if(head == null){
return true;
}
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
Boolean afterMustLeaf = false; // 当前节点后面的节点都必须是子节点的开启标志
Node left = null;
Node right = null;
queue.offer(head);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
head = queue.poll();
// 当开启所有子节点都必须为叶节点时,出现非叶节点,或者出现左子节点为空,右子节点不为空的情况直接返回false
if(afterMustLeaf && (left != null || right != null) || (left == null && right != null)){
return false;
}
// 压入左子节点
if(left != null){
queue.offer(left);
}
// 压入右子节点
if(right != null){
queue.offer(right);
}else{
// 前面的节点都是左右双全,但是到这里少了右子节点【左子节点可能有也可能没有】,后序节点都必须为叶节点,开启标志
afterMustLeaf = true;
}
}
return true;
}
}
题目7:已知一棵完全二叉树,求其节点的个数
- 已知一棵完全二叉树,求其节点的个数。 要求:时间复杂度低于O(N),N为这棵树的节点个数
- 【分析】:如果是按照遍历,复杂度会是O(N),所以不可以用遍历整棵树来求,所以要利用满二叉树的性质:结点个数为2^h-1。
- 1)如果树为空,返回0;
- 2)不为空,遍历左子树左边界,得到左子树高度
- 3)遍历右子树左边界得到右子树高度
- 若右子树的高度等于左子树,说明左子树一定是满二叉树,总结点数 = 2^hl-1【左子树结点数】 +1【是父结点】+ 递归得到的右子树结点个数
- 若右子树的高度不等于(少1)左子树,说明右子树一定是满二叉树,总结点数 = 2^hr-1【右子树结点数】 +1【是父结点】+ 递归得到的左子树结点个数
- 【时间复杂度分析】:总共要找到 logN 个结点【每层一个】,每个结点要找它的左子树高度+右子树高度 logN,所以时间复杂度是O[(logN)^2]
- 如果树有2^32个结点,用遍历是2^32,而我们的算法得到的是32^2,所以 O[(logN)^2] 小于 O(N)
package com.offer.class4;
/**
* @author pengcheng
* @date 2019/3/28 - 21:47
* @content: 求一棵完全二叉树的节点个数
*/
public class TreeNodeNum_CBT {
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
}
public int getNodeNum(Node head){
if(head == null){
return 0;
}
int left_h = high(head.left); // 当前节点的左子树高度
int right_h = high(head.right); // 当前节点的右子树高度
if(left_h == right_h){
/**
* 如果右子树的高度等于左子树的高度,说明左子树一定是满二叉树。
* 因为右子树的高度是遍历它的左边界得到的,和左子树相等,则说明右子树的左边界子树也是到了最下面一层了
* 此时总节点个数 = 2^(left_h) - 1 + 1(根节点) + 右子树个数(递归处理,和根节点一样的问题)
*/
return ((1 << left_h) - 1 + 1 + getNodeNum(head.right));
}else{
/**
* 如果右子树的高度不等于左子树的高度,则右子树肯定是比左子树高度小1的满二叉树
* 此时总节点个数 = 2^(right_h) - 1 + 1(根节点) + 左子树个数(递归处理,和根节点一样的问题)
*/
return ((1 << right_h) - 1 + 1 + getNodeNum(head.left));
}
}
// 求node作为根节点时,树的高度。遍历完全二叉树的左边界得到的肯定是树的高度
public int high(Node node){
if(node == null){
return 0;
}
int h = 0;
while(node != null){
node = node.left;
h++;
}
return h;
}
}
- 本题的关键在于首先判断根节点的右子树的高度是否和左子树一样进行情况划分:如果高度相等,则左子树一定是满二叉树,右子树再根据递归求节点个数(子问题和父问题一样);如果高度不相等,则右子树一定是比左子树高度小1的满二叉树,则递归求解左子树的节点个数。