洛谷P3379 【模板】最近公共祖先(LCA)
P3379 【模板】最近公共祖先(LCA)
题目描述
如题,给定一棵有根多叉树,请求出指定两个点直接最近的公共祖先。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第一行包含三个正整数N、M、S,分别表示树的结点个数、询问的个数和树根结点的序号。
接下来N-1行每行包含两个正整数x、y,表示x结点和y结点之间有一条直接连接的边(数据保证可以构成树)。
接下来M行每行包含两个正整数a、b,表示询问a结点和b结点的最近公共祖先。
输出格式:
输出包含M行,每行包含一个正整数,依次为每一个询问的结果。
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
5 5 4
3 1
2 4
5 1
1 4
2 4
3 2
3 5
1 2
4 5
输出样例#1:
4
4
1
4
4
说明
时空限制:1000ms,128M
数据规模:
对于30%的数据:N<=10,M<=10
对于70%的数据:N<=10000,M<=10000
对于100%的数据:N<=500000,M<=500000
样例说明:
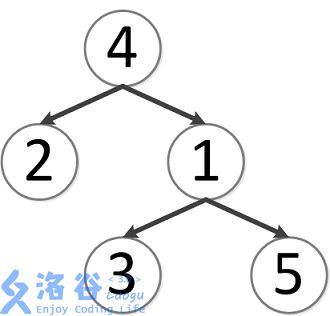
该树结构如下:
模板题。。。
- 什么是LCA?
对于有根树T的两个结点u、v,最近公共祖先LCA(T,u,v)表示一个结点x,满足x是u、v的祖先且x的深度尽可能大。 - Tarjan:离线做法 。dfs+并查集 复杂度O(n+m)。先记录下询问a,b。a,b的LCA是包含a,b的最小子树的根节点。dfs遍历图,当遍历到a时,判断b是否被遍历过, 如果遍历过,则记录答案find(b),即子树的根节点(想想为什么?如果难以理解,不妨自己手动模拟一下)。遍历完一个点x的孩子以及以孩子为根节点的子树, 将孩子的父亲指向x,即fa[孩子] = x。
- 倍增:在线做法。复杂度O(mlogn)。当我们第一眼看到这题时一定会想一步一步往上跳,这样虽然可行,但效率不高,于是我们可以想一次多跳些。倍增就是向上跳2^i 个点。我们可以先预处理出anc[i][j] 表示第i个点向上跳2^j个点到达的点。因为 2^i == 2^(i-1)+2^(i-1),所以有anc[x][i] = anc[anc[x][i-1]][i-1],anc[x][0] = 它的父亲, 这样就可以处理好anc数组了。 接着就在线求LCA了。先将深度深的点跳至与另一个点相同的高度。然后,两个点同时向上跳2^i个点, 直到跳到了同一个点。(注意:如果跳到LCA要跳2^i个点,我们不会直接跳2^i个点,而是跳2^(i-1),2^(i-2),2^(i-3),……,2^0, 2^0。如果跳到LCA要跳2^i - 1个点,则跳 2^(i-1),2^(i-2),……,2^0。)
Tarjan代码:
#include倍增代码:
#includex]; i++)
anc[x][i] = anc[anc[x][i-1]][i-1];
for(int i = last[x]; i; i = g[i].next)
if(fa[x] != g[i].to)
{
fa[g[i].to] = x;
deep[g[i].to] = deep[x]+1;
work(g[i].to);
}
return ;
}
int lca(int x, int y)
{
if(deep[x] < deep[y])
swap(x, y); //x比y深
for(int i = 20; i >= 0; i--)
if(deep[y] <= deep[x]-(1<x = anc[x][i];
if(x == y)
return x;
for(int i = 20; i >= 0; i--)
{
if(anc[x][i]!=anc[y][i])
{
x=anc[x][i];
y=anc[y][i];
}
}
return anc[x][0];//最后一次肯定跳一个点
}
int main()
{
int n = read(), m = read(), s = read();
for(RG int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
int x=read(),y=read();
add(x,y);add(y,x);
}
work(s);
for(RG int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int x=read(), y=read();
write(lca(x,y));
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}