睿智的目标检测35——Pytorch搭建YoloV4-Tiny目标检测平台
睿智的目标检测35——Pytorch搭建YoloV4-Tiny目标检测平台
- 学习前言
- 什么是YOLOV4-Tiny
- 代码下载
- YoloV4-Tiny结构解析
- 1、主干特征提取网络Backbone
- 2、特征金字塔
- 3、YoloHead利用获得到的特征进行预测
- 4、预测结果的解码
- 5、在原图上进行绘制
- YoloV4-Tiny的训练
- 1、YOLOV4的改进训练技巧
- a)、Mosaic数据增强
- b)、Label Smoothing平滑
- c)、CIOU
- d)、学习率余弦退火衰减
- 2、loss组成
- a)、计算loss所需参数
- b)、y_pre是什么
- c)、y_true是什么。
- d)、loss的计算过程
- 训练自己的YOLOV4模型
学习前言
还有Pyorch版本的。
![]()
什么是YOLOV4-Tiny
![]()
YOLOV4是YOLOV3的改进版,在YOLOV3的基础上结合了非常多的小Tricks。
尽管没有目标检测上革命性的改变,但是YOLOV4依然很好的结合了速度与精度。
根据上图也可以看出来,YOLOV4在YOLOV3的基础上,在FPS不下降的情况下,mAP达到了44,提高非常明显。
YOLOV4整体上的检测思路和YOLOV3相比相差并不大,都是使用三个特征层进行分类与回归预测。
YoloV4-Tiny是YoloV4的简化版,少了一些结构,但是速度大大增加了,YoloV4共有约6000万参数,YoloV4-Tiny则只有600万参数。
YoloV4-Tiny仅使用了两个特征层进行分类与回归预测。
代码下载
https://github.com/bubbliiiing/yolov4-tiny-pytorch
喜欢的可以给个star噢!
YoloV4-Tiny结构解析
1、主干特征提取网络Backbone
当输入是416x416时,特征结构如下:
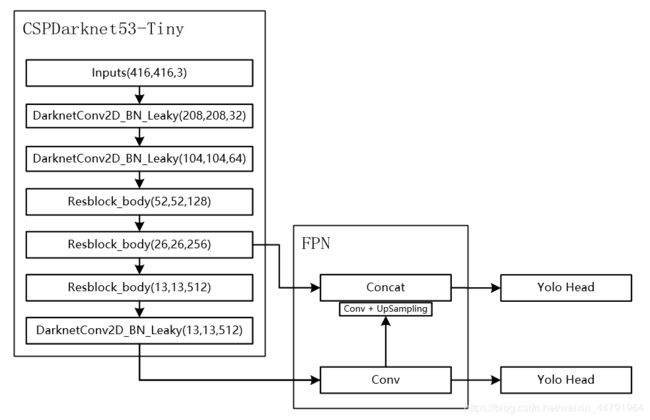
当输入是608x608时,特征结构如下:
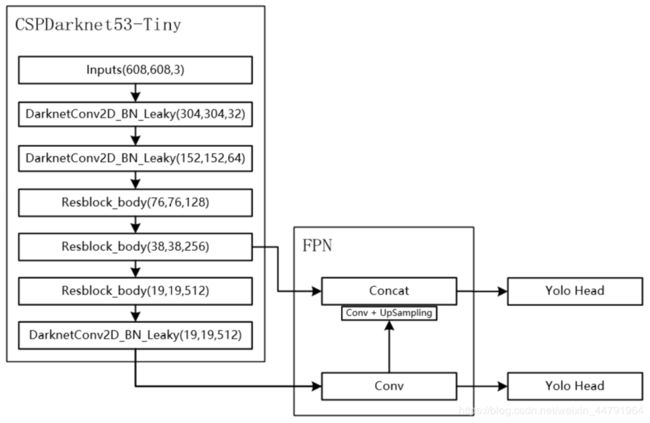
而在YoloV4-Tiny中,其使用了CSPdarknet53_tiny作为主干特征提取网络。
和CSPdarknet53相比,为了更快速,将激活函数重新修改为LeakyReLU。
CSPdarknet53_tiny具有两个特点:
1、使用了CSPnet结构。
![]()
CSPnet结构并不算复杂,就是将原来的残差块的堆叠进行了一个拆分,拆成左右两部分:
主干部分继续进行原来的残差块的堆叠;
另一部分则像一个残差边一样,经过少量处理直接连接到最后。
因此可以认为CSP中存在一个大的残差边。
2、进行通道的分割
在CSPnet的主干部分,CSPdarknet53_tiny会对一次3x3卷积后的特征层进行通道的划分,分成两部分,取第二部分。
#---------------------------------------------------#
# CSPdarknet53-tiny的结构块
# 存在一个大残差边
# 这个大残差边绕过了很多的残差结构
#---------------------------------------------------#
class Resblock_body(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(Resblock_body, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = BasicConv(in_channels, out_channels, 3)
self.conv2 = BasicConv(out_channels//2, out_channels//2, 3)
self.conv3 = BasicConv(out_channels//2, out_channels//2, 3)
self.conv4 = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d([2,2],[2,2])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
route = x
_, c, _, _ = x.size()
x = torch.split(x, c//2, dim=1)[1]
x = self.conv2(x)
route1 = x
x = self.conv3(x)
x = torch.cat([x,route1], dim = 1)
x = self.conv4(x)
feat = x
x = torch.cat([route, x], dim=1)
x = self.maxpool(x)
return x,feat
利用主干特征提取网络,我们可以获得两个shape的有效特征层,即CSPdarknet53_tiny最后两个shape的有效特征层,传入加强特征提取网络当中进行FPN的构建。
全部实现代码为:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.nn as nn
import math
from collections import OrderedDict
#-------------------------------------------------#
# 卷积块
# CONV+BATCHNORM+LeakyReLU
#-------------------------------------------------#
class BasicConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1):
super(BasicConv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.activation = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.activation(x)
return x
#---------------------------------------------------#
# CSPdarknet53-tiny的结构块
# 存在一个大残差边
# 这个大残差边绕过了很多的残差结构
#---------------------------------------------------#
class Resblock_body(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(Resblock_body, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = BasicConv(in_channels, out_channels, 3)
self.conv2 = BasicConv(out_channels//2, out_channels//2, 3)
self.conv3 = BasicConv(out_channels//2, out_channels//2, 3)
self.conv4 = BasicConv(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d([2,2],[2,2])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
route = x
_, c, _, _ = x.size()
x = torch.split(x, c//2, dim=1)[1]
x = self.conv2(x)
route1 = x
x = self.conv3(x)
x = torch.cat([x,route1], dim = 1)
x = self.conv4(x)
feat = x
x = torch.cat([route, x], dim=1)
x = self.maxpool(x)
return x,feat
class CSPDarkNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CSPDarkNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = BasicConv(3, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
self.conv2 = BasicConv(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
self.resblock_body1 = Resblock_body(64, 64)
self.resblock_body2 = Resblock_body(128, 128)
self.resblock_body3 = Resblock_body(256, 256)
self.conv3 = BasicConv(512, 512, kernel_size=3)
self.num_features = 1
# 进行权值初始化
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x, _ = self.resblock_body1(x)
x, _ = self.resblock_body2(x)
x, feat1 = self.resblock_body3(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
feat2 = x
return feat1,feat2
def darknet53_tiny(pretrained, **kwargs):
model = CSPDarkNet()
if pretrained:
if isinstance(pretrained, str):
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pretrained))
else:
raise Exception("darknet request a pretrained path. got [{}]".format(pretrained))
return model
2、特征金字塔
当输入是416x416时,特征结构如下:

当输入是608x608时,特征结构如下:

YoloV4-Tiny中使用了FPN的结构,主要是对第一步获得的两个有效特征层进行特征融合。
FPN会将最后一个shape的有效特征层卷积后进行上采样,然后与上一个shape的有效特征层进行堆叠并卷积。
实现代码如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from collections import OrderedDict
from nets.CSPdarknet53_tiny import darknet53_tiny
#-------------------------------------------------#
# 卷积块
# CONV+BATCHNORM+LeakyReLU
#-------------------------------------------------#
class BasicConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1):
super(BasicConv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.activation = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.activation(x)
return x
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 卷积 + 上采样
#---------------------------------------------------#
class Upsample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(Upsample, self).__init__()
self.upsample = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_channels, out_channels, 1),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
)
def forward(self, x,):
x = self.upsample(x)
return x
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 最后获得yolov4的输出
#---------------------------------------------------#
def yolo_head(filters_list, in_filters):
m = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_filters, filters_list[0], 3),
nn.Conv2d(filters_list[0], filters_list[1], 1),
)
return m
#---------------------------------------------------#
# yolo_body
#---------------------------------------------------#
class YoloBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_anchors, num_classes):
super(YoloBody, self).__init__()
# backbone
self.backbone = darknet53_tiny(None)
self.conv_for_P5 = BasicConv(512,256,1)
self.yolo_headP5 = yolo_head([512, num_anchors * (5 + num_classes)],256)
self.upsample = Upsample(256,128)
self.yolo_headP4 = yolo_head([256, num_anchors * (5 + num_classes)],384)
def forward(self, x):
# backbone
feat1, feat2 = self.backbone(x)
P5 = self.conv_for_P5(feat2)
out0 = self.yolo_headP5(P5)
P5_Upsample = self.upsample(P5)
P4 = torch.cat([feat1,P5_Upsample],axis=1)
out1 = self.yolo_headP4(P4)
return out0, out1
3、YoloHead利用获得到的特征进行预测
当输入是416x416时,特征结构如下:

当输入是608x608时,特征结构如下:

1、在特征利用部分,YoloV4-Tiny提取多特征层进行目标检测,一共提取两个特征层,两个特征层的shape分别为(38,38,128)、(19,19,512)。
2、输出层的shape分别为(19,19,75),(38,38,75),最后一个维度为75是因为该图是基于voc数据集的,它的类为20种,YoloV4-Tiny只有针对每一个特征层存在3个先验框,所以最后维度为3x25;
如果使用的是coco训练集,类则为80种,最后的维度应该为255 = 3x85,两个特征层的shape为(19,19,255),(38,38,255)
实现代码如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from collections import OrderedDict
from nets.CSPdarknet53_tiny import darknet53_tiny
#-------------------------------------------------#
# 卷积块
# CONV+BATCHNORM+LeakyReLU
#-------------------------------------------------#
class BasicConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1):
super(BasicConv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.activation = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.activation(x)
return x
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 卷积 + 上采样
#---------------------------------------------------#
class Upsample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(Upsample, self).__init__()
self.upsample = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_channels, out_channels, 1),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
)
def forward(self, x,):
x = self.upsample(x)
return x
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 最后获得yolov4的输出
#---------------------------------------------------#
def yolo_head(filters_list, in_filters):
m = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_filters, filters_list[0], 3),
nn.Conv2d(filters_list[0], filters_list[1], 1),
)
return m
#---------------------------------------------------#
# yolo_body
#---------------------------------------------------#
class YoloBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_anchors, num_classes):
super(YoloBody, self).__init__()
# backbone
self.backbone = darknet53_tiny(None)
self.conv_for_P5 = BasicConv(512,256,1)
self.yolo_headP5 = yolo_head([512, num_anchors * (5 + num_classes)],256)
self.upsample = Upsample(256,128)
self.yolo_headP4 = yolo_head([256, num_anchors * (5 + num_classes)],384)
def forward(self, x):
# backbone
feat1, feat2 = self.backbone(x)
P5 = self.conv_for_P5(feat2)
out0 = self.yolo_headP5(P5)
P5_Upsample = self.upsample(P5)
P4 = torch.cat([feat1,P5_Upsample],axis=1)
out1 = self.yolo_headP4(P4)
return out0, out1
4、预测结果的解码
由第三步我们可以获得两个特征层的预测结果,shape分别为(N,19,19,255),(N,38,38,255)的数据,对应每个图分为19x19、38x38的网格上3个预测框的位置。
但是这个预测结果并不对应着最终的预测框在图片上的位置,还需要解码才可以完成。
此处要讲一下yolo的预测原理,yolo的特征层分别将整幅图分为19x19、38x38的网格,每个网络点负责一个区域的检测。
我们知道特征层的预测结果对应着三个预测框的位置,我们先将其reshape一下,其结果为(N,19,19,3,85),(N,38,38,3,85)。
最后一个维度中的85包含了4+1+80,分别代表x_offset、y_offset、h和w、置信度、分类结果。
yolo的解码过程就是将每个网格点加上它对应的x_offset和y_offset,加完后的结果就是预测框的中心,然后再利用 先验框和h、w结合 计算出预测框的长和宽。这样就能得到整个预测框的位置了。
![]()
当然得到最终的预测结构后还要进行得分排序与非极大抑制筛选
这一部分基本上是所有目标检测通用的部分。不过该项目的处理方式与其它项目不同。其对于每一个类进行判别。
1、取出每一类得分大于self.obj_threshold的框和得分。
2、利用框的位置和得分进行非极大抑制。
实现代码如下:
class DecodeBox(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors, num_classes, img_size):
super(DecodeBox, self).__init__()
self.anchors = anchors
self.num_anchors = len(anchors)
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.bbox_attrs = 5 + num_classes
self.img_size = img_size
def forward(self, input):
# input为bs,3*(1+4+num_classes),13,13
# 一共多少张图片
batch_size = input.size(0)
# 13,13
input_height = input.size(2)
input_width = input.size(3)
# 计算步长
# 每一个特征点对应原来的图片上多少个像素点
# 如果特征层为13x13的话,一个特征点就对应原来的图片上的32个像素点
# 416/13 = 32
stride_h = self.img_size[1] / input_height
stride_w = self.img_size[0] / input_width
# 把先验框的尺寸调整成特征层大小的形式
# 计算出先验框在特征层上对应的宽高
scaled_anchors = [(anchor_width / stride_w, anchor_height / stride_h) for anchor_width, anchor_height in self.anchors]
# bs,3*(5+num_classes),13,13 -> bs,3,13,13,(5+num_classes)
prediction = input.view(batch_size, self.num_anchors,
self.bbox_attrs, input_height, input_width).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
# 先验框的中心位置的调整参数
x = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 0])
y = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 1])
# 先验框的宽高调整参数
w = prediction[..., 2] # Width
h = prediction[..., 3] # Height
# 获得置信度,是否有物体
conf = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 4])
# 种类置信度
pred_cls = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 5:]) # Cls pred.
FloatTensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.FloatTensor
LongTensor = torch.cuda.LongTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.LongTensor
# 生成网格,先验框中心,网格左上角 batch_size,3,13,13
grid_x = torch.linspace(0, input_width - 1, input_width).repeat(input_width, 1).repeat(
batch_size * self.num_anchors, 1, 1).view(x.shape).type(FloatTensor)
grid_y = torch.linspace(0, input_height - 1, input_height).repeat(input_height, 1).t().repeat(
batch_size * self.num_anchors, 1, 1).view(y.shape).type(FloatTensor)
# 生成先验框的宽高
anchor_w = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors).index_select(1, LongTensor([0]))
anchor_h = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors).index_select(1, LongTensor([1]))
anchor_w = anchor_w.repeat(batch_size, 1).repeat(1, 1, input_height * input_width).view(w.shape)
anchor_h = anchor_h.repeat(batch_size, 1).repeat(1, 1, input_height * input_width).view(h.shape)
# 计算调整后的先验框中心与宽高
pred_boxes = FloatTensor(prediction[..., :4].shape)
pred_boxes[..., 0] = x.data + grid_x
pred_boxes[..., 1] = y.data + grid_y
pred_boxes[..., 2] = torch.exp(w.data) * anchor_w
pred_boxes[..., 3] = torch.exp(h.data) * anchor_h
# 用于将输出调整为相对于416x416的大小
_scale = torch.Tensor([stride_w, stride_h] * 2).type(FloatTensor)
output = torch.cat((pred_boxes.view(batch_size, -1, 4) * _scale,
conf.view(batch_size, -1, 1), pred_cls.view(batch_size, -1, self.num_classes)), -1)
return output.data
def bbox_iou(box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=True):
"""
计算IOU
"""
if not x1y1x2y2:
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[:, 0] - box1[:, 2] / 2, box1[:, 0] + box1[:, 2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[:, 1] - box1[:, 3] / 2, box1[:, 1] + box1[:, 3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[:, 0] - box2[:, 2] / 2, box2[:, 0] + box2[:, 2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[:, 1] - box2[:, 3] / 2, box2[:, 1] + box2[:, 3] / 2
else:
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[:, 0], box1[:, 1], box1[:, 2], box1[:, 3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[:, 0], box2[:, 1], box2[:, 2], box2[:, 3]
inter_rect_x1 = torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)
inter_rect_y1 = torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)
inter_rect_x2 = torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2)
inter_rect_y2 = torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2)
inter_area = torch.clamp(inter_rect_x2 - inter_rect_x1 + 1, min=0) * \
torch.clamp(inter_rect_y2 - inter_rect_y1 + 1, min=0)
b1_area = (b1_x2 - b1_x1 + 1) * (b1_y2 - b1_y1 + 1)
b2_area = (b2_x2 - b2_x1 + 1) * (b2_y2 - b2_y1 + 1)
iou = inter_area / (b1_area + b2_area - inter_area + 1e-16)
return iou
def non_max_suppression(prediction, num_classes, conf_thres=0.5, nms_thres=0.4):
# 求左上角和右下角
box_corner = prediction.new(prediction.shape)
box_corner[:, :, 0] = prediction[:, :, 0] - prediction[:, :, 2] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 1] = prediction[:, :, 1] - prediction[:, :, 3] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 2] = prediction[:, :, 0] + prediction[:, :, 2] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 3] = prediction[:, :, 1] + prediction[:, :, 3] / 2
prediction[:, :, :4] = box_corner[:, :, :4]
output = [None for _ in range(len(prediction))]
for image_i, image_pred in enumerate(prediction):
# 利用置信度进行第一轮筛选
conf_mask = (image_pred[:, 4] >= conf_thres).squeeze()
image_pred = image_pred[conf_mask]
if not image_pred.size(0):
continue
# 获得种类及其置信度
class_conf, class_pred = torch.max(image_pred[:, 5:5 + num_classes], 1, keepdim=True)
# 获得的内容为(x1, y1, x2, y2, obj_conf, class_conf, class_pred)
detections = torch.cat((image_pred[:, :5], class_conf.float(), class_pred.float()), 1)
# 获得种类
unique_labels = detections[:, -1].cpu().unique()
if prediction.is_cuda:
unique_labels = unique_labels.cuda()
for c in unique_labels:
# 获得某一类初步筛选后全部的预测结果
detections_class = detections[detections[:, -1] == c]
# 按照存在物体的置信度排序
_, conf_sort_index = torch.sort(detections_class[:, 4], descending=True)
detections_class = detections_class[conf_sort_index]
# 进行非极大抑制
max_detections = []
while detections_class.size(0):
# 取出这一类置信度最高的,一步一步往下判断,判断重合程度是否大于nms_thres,如果是则去除掉
max_detections.append(detections_class[0].unsqueeze(0))
if len(detections_class) == 1:
break
ious = bbox_iou(max_detections[-1], detections_class[1:])
detections_class = detections_class[1:][ious < nms_thres]
# 堆叠
max_detections = torch.cat(max_detections).data
# Add max detections to outputs
output[image_i] = max_detections if output[image_i] is None else torch.cat(
(output[image_i], max_detections))
return output
5、在原图上进行绘制
通过第四步,我们可以获得预测框在原图上的位置,而且这些预测框都是经过筛选的。这些筛选后的框可以直接绘制在图片上,就可以获得结果了。
YoloV4-Tiny的训练
1、YOLOV4的改进训练技巧
a)、Mosaic数据增强
Yolov4的mosaic数据增强参考了CutMix数据增强方式,理论上具有一定的相似性!
CutMix数据增强方式利用两张图片进行拼接。
![]()
但是mosaic利用了四张图片,根据论文所说其拥有一个巨大的优点是丰富检测物体的背景!且在BN计算的时候一下子会计算四张图片的数据!
就像下图这样:
实现思路如下:
1、每次读取四张图片。
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
2、分别对四张图片进行翻转、缩放、色域变化等,并且按照四个方向位置摆好。
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
3、进行图片的组合和框的组合
![]()
def get_random_data_with_Mosaic(self, annotation_line, input_shape, hue=.1, sat=1.5, val=1.5):
'''random preprocessing for real-time data augmentation'''
h, w = input_shape
min_offset_x = 0.4
min_offset_y = 0.4
scale_low = 1-min(min_offset_x,min_offset_y)
scale_high = scale_low+0.2
image_datas = []
box_datas = []
index = 0
place_x = [0,0,int(w*min_offset_x),int(w*min_offset_x)]
place_y = [0,int(h*min_offset_y),int(w*min_offset_y),0]
for line in annotation_line:
# 每一行进行分割
line_content = line.split()
# 打开图片
image = Image.open(line_content[0])
image = image.convert("RGB")
# 图片的大小
iw, ih = image.size
# 保存框的位置
box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line_content[1:]])
# 是否翻转图片
flip = rand()<.5
if flip and len(box)>0:
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
box[:, [0,2]] = iw - box[:, [2,0]]
# 对输入进来的图片进行缩放
new_ar = w/h
scale = rand(scale_low, scale_high)
if new_ar < 1:
nh = int(scale*h)
nw = int(nh*new_ar)
else:
nw = int(scale*w)
nh = int(nw/new_ar)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
# 进行色域变换
hue = rand(-hue, hue)
sat = rand(1, sat) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, sat)
val = rand(1, val) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, val)
x = rgb_to_hsv(np.array(image)/255.)
x[..., 0] += hue
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]>1] -= 1
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]<0] += 1
x[..., 1] *= sat
x[..., 2] *= val
x[x>1] = 1
x[x<0] = 0
image = hsv_to_rgb(x)
image = Image.fromarray((image*255).astype(np.uint8))
# 将图片进行放置,分别对应四张分割图片的位置
dx = place_x[index]
dy = place_y[index]
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image_data = np.array(new_image)
index = index + 1
box_data = []
# 对box进行重新处理
if len(box)>0:
np.random.shuffle(box)
box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)]
box_data = np.zeros((len(box),5))
box_data[:len(box)] = box
image_datas.append(image_data)
box_datas.append(box_data)
# 将图片分割,放在一起
cutx = np.random.randint(int(w*min_offset_x), int(w*(1 - min_offset_x)))
cuty = np.random.randint(int(h*min_offset_y), int(h*(1 - min_offset_y)))
new_image = np.zeros([h,w,3])
new_image[:cuty, :cutx, :] = image_datas[0][:cuty, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, :cutx, :] = image_datas[1][cuty:, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, cutx:, :] = image_datas[2][cuty:, cutx:, :]
new_image[:cuty, cutx:, :] = image_datas[3][:cuty, cutx:, :]
# 对框进行进一步的处理
new_boxes = np.array(merge_bboxes(box_datas, cutx, cuty))
if len(new_boxes) == 0:
return new_image, []
if (new_boxes[:,:4]>0).any():
return new_image, new_boxes
else:
return new_image, []
b)、Label Smoothing平滑
标签平滑的思想很简单,具体公式如下:
new_onehot_labels = onehot_labels * (1 - label_smoothing) + label_smoothing / num_classes
当label_smoothing的值为0.01得时候,公式变成如下所示:
new_onehot_labels = y * (1 - 0.01) + 0.01 / num_classes
其实Label Smoothing平滑就是将标签进行一个平滑,原始的标签是0、1,在平滑后变成0.005(如果是二分类)、0.995,也就是说对分类准确做了一点惩罚,让模型不可以分类的太准确,太准确容易过拟合。
实现代码如下:
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 平滑标签
#---------------------------------------------------#
def smooth_labels(y_true, label_smoothing,num_classes):
return y_true * (1.0 - label_smoothing) + label_smoothing / num_classes
c)、CIOU
IoU是比值的概念,对目标物体的scale是不敏感的。然而常用的BBox的回归损失优化和IoU优化不是完全等价的,寻常的IoU无法直接优化没有重叠的部分。
于是有人提出直接使用IOU作为回归优化loss,CIOU是其中非常优秀的一种想法。
CIOU将目标与anchor之间的距离,重叠率、尺度以及惩罚项都考虑进去,使得目标框回归变得更加稳定,不会像IoU和GIoU一样出现训练过程中发散等问题。而惩罚因子把预测框长宽比拟合目标框的长宽比考虑进去。
![]()
CIOU公式如下
C I O U = I O U − ρ 2 ( b , b g t ) c 2 − α v CIOU = IOU - \frac{\rho^2(b,b^{gt})}{c^2} - \alpha v CIOU=IOU−c2ρ2(b,bgt)−αv
其中, ρ 2 ( b , b g t ) \rho^2(b,b^{gt}) ρ2(b,bgt)分别代表了预测框和真实框的中心点的欧式距离。 c代表的是能够同时包含预测框和真实框的最小闭包区域的对角线距离。
而 α \alpha α和 v v v的公式如下
α = v 1 − I O U + v \alpha = \frac{v}{1-IOU+v} α=1−IOU+vv
v = 4 π 2 ( a r c t a n w g t h g t − a r c t a n w h ) 2 v = \frac{4}{\pi ^2}(arctan\frac{w^{gt}}{h^{gt}}-arctan\frac{w}{h})^2 v=π24(arctanhgtwgt−arctanhw)2
把1-CIOU就可以得到相应的LOSS了。
L O S S C I O U = 1 − I O U + ρ 2 ( b , b g t ) c 2 + α v LOSS_{CIOU} = 1 - IOU + \frac{\rho^2(b,b^{gt})}{c^2} + \alpha v LOSSCIOU=1−IOU+c2ρ2(b,bgt)+αv
def box_ciou(b1, b2):
"""
输入为:
----------
b1: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
b2: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
返回为:
-------
ciou: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 1)
"""
# 求出预测框左上角右下角
b1_xy = b1[..., :2]
b1_wh = b1[..., 2:4]
b1_wh_half = b1_wh/2.
b1_mins = b1_xy - b1_wh_half
b1_maxes = b1_xy + b1_wh_half
# 求出真实框左上角右下角
b2_xy = b2[..., :2]
b2_wh = b2[..., 2:4]
b2_wh_half = b2_wh/2.
b2_mins = b2_xy - b2_wh_half
b2_maxes = b2_xy + b2_wh_half
# 求真实框和预测框所有的iou
intersect_mins = torch.max(b1_mins, b2_mins)
intersect_maxes = torch.min(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
intersect_wh = torch.max(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, torch.zeros_like(intersect_maxes))
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
b1_area = b1_wh[..., 0] * b1_wh[..., 1]
b2_area = b2_wh[..., 0] * b2_wh[..., 1]
union_area = b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area
iou = intersect_area / torch.clamp(union_area,min = 1e-6)
# 计算中心的差距
center_distance = torch.sum(torch.pow((b1_xy - b2_xy), 2), axis=-1)
# 找到包裹两个框的最小框的左上角和右下角
enclose_mins = torch.min(b1_mins, b2_mins)
enclose_maxes = torch.max(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
enclose_wh = torch.max(enclose_maxes - enclose_mins, torch.zeros_like(intersect_maxes))
# 计算对角线距离
enclose_diagonal = torch.sum(torch.pow(enclose_wh,2), axis=-1)
ciou = iou - 1.0 * (center_distance) / torch.clamp(enclose_diagonal,min = 1e-6)
v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow((torch.atan(b1_wh[..., 0]/torch.clamp(b1_wh[..., 1],min = 1e-6)) - torch.atan(b2_wh[..., 0]/torch.clamp(b2_wh[..., 1],min = 1e-6))), 2)
alpha = v / torch.clamp((1.0 - iou + v),min=1e-6)
ciou = ciou - alpha * v
return ciou
d)、学习率余弦退火衰减
余弦退火衰减法,学习率会先上升再下降,这是退火优化法的思想。(关于什么是退火算法可以百度。)
上升的时候使用线性上升,下降的时候模拟cos函数下降。执行多次。
效果如图所示:
![]()
余弦退火衰减有几个比较必要的参数:
1、learning_rate_base:学习率最高值。
2、warmup_learning_rate:最开始的学习率。
3、warmup_steps:多少步长后到达顶峰值。
实现方式如下,利用Callback实现,与普通的ReduceLROnPlateau调用方式类似:
lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=5, eta_min=1e-5)
2、loss组成
a)、计算loss所需参数
在计算loss的时候,实际上是y_pre和y_true之间的对比:
y_pre就是一幅图像经过网络之后的输出,内部含有两个特征层的内容;其需要解码才能够在图上作画
y_true就是一个真实图像中,它的每个真实框对应的(19,19)、(38,38)网格上的偏移位置、长宽与种类。其仍需要编码才能与y_pred的结构一致
实际上y_pre和y_true内容的shape都是
(batch_size,19,19,3,85)
(batch_size,38,38,3,85)
b)、y_pre是什么
网络最后输出的内容就是两个特征层每个网格点对应的预测框及其种类,即两个特征层分别对应着图片被分为不同size的网格后,每个网格点上三个先验框对应的位置、置信度及其种类。
对于输出的y1、y2、y3而言,[…, : 2]指的是相对于每个网格点的偏移量,[…, 2: 4]指的是宽和高,[…, 4: 5]指的是该框的置信度,[…, 5: ]指的是每个种类的预测概率。
现在的y_pre还是没有解码的,解码了之后才是真实图像上的情况。
c)、y_true是什么。
y_true就是一个真实图像中,它的每个真实框对应的(19,19)、(38,38)网格上的偏移位置、长宽与种类。其仍需要编码才能与y_pred的结构一致
d)、loss的计算过程
在得到了y_pre和y_true后怎么对比呢?不是简单的减一下!
loss值需要对俩个特征层进行处理,这里以最小的特征层为例。
1、利用y_true取出该特征层中真实存在目标的点的位置(m,19,19,3,1)及其对应的种类(m,19,19,3,80)。
2、将prediction的预测值输出进行处理,得到reshape后的预测值y_pre,shape为(m,19,19,3,85)。还有解码后的xy,wh。
3、对于每一幅图,计算其中所有真实框与预测框的IOU,如果某些预测框和真实框的重合程度大于0.5,则忽略。
4、计算ciou作为回归的loss,这里只计算正样本的回归loss。
5、计算置信度的loss,其有两部分构成,第一部分是实际上存在目标的,预测结果中置信度的值与1对比;第二部分是实际上不存在目标的,在第四步中得到其最大IOU的值与0对比。
6、计算预测种类的loss,其计算的是实际上存在目标的,预测类与真实类的差距。
其实际上计算的总的loss是三个loss的和,这三个loss分别是:
- 实际存在的框,CIOU LOSS。
- 实际存在的框,预测结果中置信度的值与1对比;实际不存在的框,预测结果中置信度的值与0对比,该部分要去除被忽略的不包含目标的框。
- 实际存在的框,种类预测结果与实际结果的对比。
其实际代码如下:
def jaccard(_box_a, _box_b):
b1_x1, b1_x2 = _box_a[:, 0] - _box_a[:, 2] / 2, _box_a[:, 0] + _box_a[:, 2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = _box_a[:, 1] - _box_a[:, 3] / 2, _box_a[:, 1] + _box_a[:, 3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = _box_b[:, 0] - _box_b[:, 2] / 2, _box_b[:, 0] + _box_b[:, 2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = _box_b[:, 1] - _box_b[:, 3] / 2, _box_b[:, 1] + _box_b[:, 3] / 2
box_a = torch.zeros_like(_box_a)
box_b = torch.zeros_like(_box_b)
box_a[:, 0], box_a[:, 1], box_a[:, 2], box_a[:, 3] = b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2
box_b[:, 0], box_b[:, 1], box_b[:, 2], box_b[:, 3] = b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2
A = box_a.size(0)
B = box_b.size(0)
max_xy = torch.min(box_a[:, 2:].unsqueeze(1).expand(A, B, 2),
box_b[:, 2:].unsqueeze(0).expand(A, B, 2))
min_xy = torch.max(box_a[:, :2].unsqueeze(1).expand(A, B, 2),
box_b[:, :2].unsqueeze(0).expand(A, B, 2))
inter = torch.clamp((max_xy - min_xy), min=0)
inter = inter[:, :, 0] * inter[:, :, 1]
# 计算先验框和真实框各自的面积
area_a = ((box_a[:, 2]-box_a[:, 0]) *
(box_a[:, 3]-box_a[:, 1])).unsqueeze(1).expand_as(inter) # [A,B]
area_b = ((box_b[:, 2]-box_b[:, 0]) *
(box_b[:, 3]-box_b[:, 1])).unsqueeze(0).expand_as(inter) # [A,B]
# 求IOU
union = area_a + area_b - inter
return inter / union # [A,B]
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 平滑标签
#---------------------------------------------------#
def smooth_labels(y_true, label_smoothing,num_classes):
return y_true * (1.0 - label_smoothing) + label_smoothing / num_classes
def box_ciou(b1, b2):
"""
输入为:
----------
b1: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
b2: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
返回为:
-------
ciou: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 1)
"""
# 求出预测框左上角右下角
b1_xy = b1[..., :2]
b1_wh = b1[..., 2:4]
b1_wh_half = b1_wh/2.
b1_mins = b1_xy - b1_wh_half
b1_maxes = b1_xy + b1_wh_half
# 求出真实框左上角右下角
b2_xy = b2[..., :2]
b2_wh = b2[..., 2:4]
b2_wh_half = b2_wh/2.
b2_mins = b2_xy - b2_wh_half
b2_maxes = b2_xy + b2_wh_half
# 求真实框和预测框所有的iou
intersect_mins = torch.max(b1_mins, b2_mins)
intersect_maxes = torch.min(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
intersect_wh = torch.max(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, torch.zeros_like(intersect_maxes))
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
b1_area = b1_wh[..., 0] * b1_wh[..., 1]
b2_area = b2_wh[..., 0] * b2_wh[..., 1]
union_area = b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area
iou = intersect_area / torch.clamp(union_area,min = 1e-6)
# 计算中心的差距
center_distance = torch.sum(torch.pow((b1_xy - b2_xy), 2), axis=-1)
# 找到包裹两个框的最小框的左上角和右下角
enclose_mins = torch.min(b1_mins, b2_mins)
enclose_maxes = torch.max(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
enclose_wh = torch.max(enclose_maxes - enclose_mins, torch.zeros_like(intersect_maxes))
# 计算对角线距离
enclose_diagonal = torch.sum(torch.pow(enclose_wh,2), axis=-1)
ciou = iou - 1.0 * (center_distance) / torch.clamp(enclose_diagonal,min = 1e-6)
v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow((torch.atan(b1_wh[..., 0]/torch.clamp(b1_wh[..., 1],min = 1e-6)) - torch.atan(b2_wh[..., 0]/torch.clamp(b2_wh[..., 1],min = 1e-6))), 2)
alpha = v / torch.clamp((1.0 - iou + v),min=1e-6)
ciou = ciou - alpha * v
return ciou
def clip_by_tensor(t,t_min,t_max):
t=t.float()
result = (t >= t_min).float() * t + (t < t_min).float() * t_min
result = (result <= t_max).float() * result + (result > t_max).float() * t_max
return result
def MSELoss(pred,target):
return (pred-target)**2
def BCELoss(pred,target):
epsilon = 1e-7
pred = clip_by_tensor(pred, epsilon, 1.0 - epsilon)
output = -target * torch.log(pred) - (1.0 - target) * torch.log(1.0 - pred)
return output
class YOLOLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors, num_classes, img_size, label_smooth=0, cuda=True):
super(YOLOLoss, self).__init__()
self.anchors = anchors
self.num_anchors = len(anchors)
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.bbox_attrs = 5 + num_classes
self.img_size = img_size
self.feature_length = [img_size[0]//32,img_size[0]//16]
self.label_smooth = label_smooth
self.ignore_threshold = 0.5
self.lambda_conf = 1.0
self.lambda_cls = 1.0
self.lambda_loc = 1.0
self.cuda = cuda
def forward(self, input, targets=None):
# input为bs,3*(5+num_classes),13,13
# 一共多少张图片
bs = input.size(0)
# 特征层的高
in_h = input.size(2)
# 特征层的宽
in_w = input.size(3)
# 计算步长
# 每一个特征点对应原来的图片上多少个像素点
# 如果特征层为13x13的话,一个特征点就对应原来的图片上的32个像素点
stride_h = self.img_size[1] / in_h
stride_w = self.img_size[0] / in_w
# 把先验框的尺寸调整成特征层大小的形式
# 计算出先验框在特征层上对应的宽高
scaled_anchors = [(a_w / stride_w, a_h / stride_h) for a_w, a_h in self.anchors]
# bs,3*(5+num_classes),13,13 -> bs,3,13,13,(5+num_classes)
prediction = input.view(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2),
self.bbox_attrs, in_h, in_w).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
# 对prediction预测进行调整
conf = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 4]) # Conf
pred_cls = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 5:]) # Cls pred.
# 找到哪些先验框内部包含物体
mask, noobj_mask, t_box, tconf, tcls, box_loss_scale_x, box_loss_scale_y = self.get_target(targets, scaled_anchors,in_w, in_h,self.ignore_threshold)
noobj_mask, pred_boxes_for_ciou = self.get_ignore(prediction, targets, scaled_anchors, in_w, in_h, noobj_mask)
if self.cuda:
mask, noobj_mask = mask.cuda(), noobj_mask.cuda()
box_loss_scale_x, box_loss_scale_y= box_loss_scale_x.cuda(), box_loss_scale_y.cuda()
tconf, tcls = tconf.cuda(), tcls.cuda()
pred_boxes_for_ciou = pred_boxes_for_ciou.cuda()
t_box = t_box.cuda()
box_loss_scale = 2-box_loss_scale_x*box_loss_scale_y
# losses.
ciou = (1 - box_ciou( pred_boxes_for_ciou[mask.bool()], t_box[mask.bool()]))* box_loss_scale[mask.bool()]
loss_loc = torch.sum(ciou / bs)
loss_conf = torch.sum(BCELoss(conf, mask) * mask / bs) + \
torch.sum(BCELoss(conf, mask) * noobj_mask / bs)
# print(smooth_labels(tcls[mask == 1],self.label_smooth,self.num_classes))
loss_cls = torch.sum(BCELoss(pred_cls[mask == 1], smooth_labels(tcls[mask == 1],self.label_smooth,self.num_classes))/bs)
# print(loss_loc,loss_conf,loss_cls)
loss = loss_conf * self.lambda_conf + loss_cls * self.lambda_cls + loss_loc * self.lambda_loc
return loss, loss_conf.item(), loss_cls.item(), loss_loc.item()
def get_target(self, target, anchors, in_w, in_h, ignore_threshold):
# 计算一共有多少张图片
bs = len(target)
# 获得先验框
anchor_index = [[3,4,5],[1,2,3]][self.feature_length.index(in_w)]
# 创建全是0或者全是1的阵列
mask = torch.zeros(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2), in_h, in_w, requires_grad=False)
noobj_mask = torch.ones(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2), in_h, in_w, requires_grad=False)
tx = torch.zeros(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2), in_h, in_w, requires_grad=False)
ty = torch.zeros(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2), in_h, in_w, requires_grad=False)
tw = torch.zeros(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2), in_h, in_w, requires_grad=False)
th = torch.zeros(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2), in_h, in_w, requires_grad=False)
t_box = torch.zeros(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2), in_h, in_w, 4, requires_grad=False)
tconf = torch.zeros(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2), in_h, in_w, requires_grad=False)
tcls = torch.zeros(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2), in_h, in_w, self.num_classes, requires_grad=False)
box_loss_scale_x = torch.zeros(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2), in_h, in_w, requires_grad=False)
box_loss_scale_y = torch.zeros(bs, int(self.num_anchors/2), in_h, in_w, requires_grad=False)
for b in range(bs):
for t in range(target[b].shape[0]):
# 计算出在特征层上的点位
gx = target[b][t, 0] * in_w
gy = target[b][t, 1] * in_h
gw = target[b][t, 2] * in_w
gh = target[b][t, 3] * in_h
# 计算出属于哪个网格
gi = int(gx)
gj = int(gy)
# 计算真实框的位置
gt_box = torch.FloatTensor(np.array([0, 0, gw, gh])).unsqueeze(0)
# 计算出所有先验框的位置
anchor_shapes = torch.FloatTensor(np.concatenate((np.zeros((self.num_anchors, 2)),
np.array(anchors)), 1))
# 计算重合程度
anch_ious = bbox_iou(gt_box, anchor_shapes)
# Find the best matching anchor box
best_n = np.argmax(anch_ious)
if best_n not in anchor_index:
continue
# Masks
if (gj < in_h) and (gi < in_w):
best_n = anchor_index.index(best_n)
# 判定哪些先验框内部真实的存在物体
noobj_mask[b, best_n, gj, gi] = 0
mask[b, best_n, gj, gi] = 1
# 计算先验框中心调整参数
tx[b, best_n, gj, gi] = gx
ty[b, best_n, gj, gi] = gy
# 计算先验框宽高调整参数
tw[b, best_n, gj, gi] = gw
th[b, best_n, gj, gi] = gh
# 用于获得xywh的比例
box_loss_scale_x[b, best_n, gj, gi] = target[b][t, 2]
box_loss_scale_y[b, best_n, gj, gi] = target[b][t, 3]
# 物体置信度
tconf[b, best_n, gj, gi] = 1
# 种类
tcls[b, best_n, gj, gi, int(target[b][t, 4])] = 1
else:
print('Step {0} out of bound'.format(b))
print('gj: {0}, height: {1} | gi: {2}, width: {3}'.format(gj, in_h, gi, in_w))
continue
t_box[...,0] = tx
t_box[...,1] = ty
t_box[...,2] = tw
t_box[...,3] = th
return mask, noobj_mask, t_box, tconf, tcls, box_loss_scale_x, box_loss_scale_y
def get_ignore(self,prediction,target,scaled_anchors,in_w, in_h,noobj_mask):
bs = len(target)
anchor_index = [[3,4,5],[1,2,3]][self.feature_length.index(in_w)]
scaled_anchors = np.array(scaled_anchors)[anchor_index]
# 先验框的中心位置的调整参数
x = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 0])
y = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 1])
# 先验框的宽高调整参数
w = prediction[..., 2] # Width
h = prediction[..., 3] # Height
FloatTensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.FloatTensor
LongTensor = torch.cuda.LongTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.LongTensor
# 生成网格,先验框中心,网格左上角
grid_x = torch.linspace(0, in_w - 1, in_w).repeat(in_w, 1).repeat(
int(bs*self.num_anchors/2), 1, 1).view(x.shape).type(FloatTensor)
grid_y = torch.linspace(0, in_h - 1, in_h).repeat(in_h, 1).t().repeat(
int(bs*self.num_anchors/2), 1, 1).view(y.shape).type(FloatTensor)
# 生成先验框的宽高
anchor_w = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors).index_select(1, LongTensor([0]))
anchor_h = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors).index_select(1, LongTensor([1]))
anchor_w = anchor_w.repeat(bs, 1).repeat(1, 1, in_h * in_w).view(w.shape)
anchor_h = anchor_h.repeat(bs, 1).repeat(1, 1, in_h * in_w).view(h.shape)
# 计算调整后的先验框中心与宽高
pred_boxes = FloatTensor(prediction[..., :4].shape)
pred_boxes[..., 0] = x + grid_x
pred_boxes[..., 1] = y + grid_y
pred_boxes[..., 2] = torch.exp(w) * anchor_w
pred_boxes[..., 3] = torch.exp(h) * anchor_h
for i in range(bs):
pred_boxes_for_ignore = pred_boxes[i]
pred_boxes_for_ignore = pred_boxes_for_ignore.view(-1, 4)
if len(target[i]) > 0:
gx = target[i][:, 0:1] * in_w
gy = target[i][:, 1:2] * in_h
gw = target[i][:, 2:3] * in_w
gh = target[i][:, 3:4] * in_h
gt_box = torch.FloatTensor(np.concatenate([gx, gy, gw, gh],-1)).type(FloatTensor)
anch_ious = jaccard(gt_box, pred_boxes_for_ignore)
for t in range(target[i].shape[0]):
anch_iou = anch_ious[t].view(pred_boxes[i].size()[:3])
noobj_mask[i][anch_iou>self.ignore_threshold] = 0
return noobj_mask, pred_boxes
训练自己的YOLOV4模型
yolo4整体的文件夹构架如下:
![]()
本文使用VOC格式进行训练。
训练前将标签文件放在VOCdevkit文件夹下的VOC2007文件夹下的Annotation中。
![]()
训练前将图片文件放在VOCdevkit文件夹下的VOC2007文件夹下的JPEGImages中。
![]()
在训练前利用voc2yolo3.py文件生成对应的txt。
![]()
再运行根目录下的voc_annotation.py,运行前需要将classes改成你自己的classes。
classes = ["aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat", "bottle", "bus", "car", "cat", "chair", "cow", "diningtable", "dog", "horse", "motorbike", "person", "pottedplant", "sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor"]
![]()
就会生成对应的2007_train.txt,每一行对应其图片位置及其真实框的位置。
![]()
在训练前需要修改model_data里面的voc_classes.txt文件,需要将classes改成你自己的classes。
![]()
运行train.py即可开始训练。
![]()