【树形DP】树的重心详解+多组例题详解
目录
- 定义:
- 性质:
- 算法分析:
- POJ 1655 Balancing Act(求重心)
- POJ 3107 Godfather
- P1364 医院设置(树形DP)
定义:
树的重心也叫树的质心。对于一棵树n个节点的无根树,找到一个点,使得把树变成以该点为根的有根树时,最大子树的结点数最小。
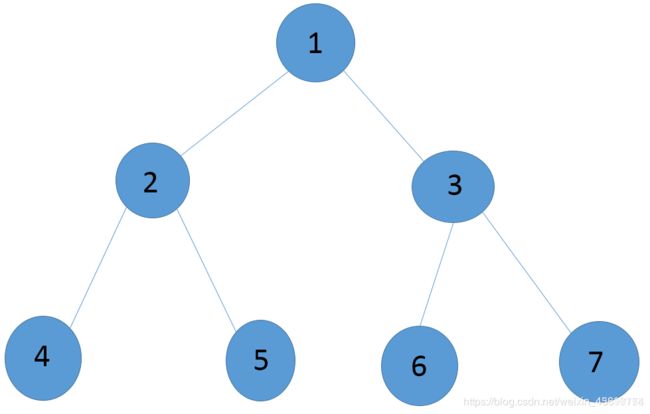
树的重心定义为树的某个节点,当去掉该节点后,树的各个连通分量中,节点数最多的连通分量其节点数达到最小值。树可能存在多个重心。如下图,当去掉点1后,树将分成两个连通块:(2,4,5),(3,6,7),则最大的连通块包含节点个数为3。若去掉点2,则树将分成3个部分,(4),(5),(1,3,6,7)最大的连通块包含4个节点;第一种方法可以得到更小的最大联通分量。可以发现,其他方案不可能得到比3更小的值了。所以,点1是树的重心。
性质:
- 树上所有的点到树的重心的距离之和是最短的,如果有多个重心,那么总距离相等。
- 把两棵树通过一条边相连,新的树的重心在原来两棵树重心的连线上。
- 一棵树添加或者删除一个节点,树的重心最多只移动一条边的位置。
- 一棵树最多有两个重心,且相邻。
算法分析:
和树的最大独立问题类似,先任选一个结点作为根节点,把无根树变成有根树,然后设 d [ i ] d[i] d[i] 表示以i为根的子树的结点的个数。不难发现 d [ i ] = ∑ d [ j ] + 1 d[i]=∑d[j]+1 d[i]=∑d[j]+1, j ∈ s [ i ] j∈s[i] j∈s[i]。 s [ i ] s[i] s[i]为i结点的所有儿子结点的编号的集合。程序也十分简单:只需要DFS一次,在无根树转有根数的同时计算即可,连记忆化都不需要——因为本来就没有重复计算。
那么,删除结点i后,最大的连通块有多少个呢?结点i的子树中最大有 m a x ( d [ j ] ) max({d[j]}) max(d[j])个结点,i的“上方子树”中有 n − d ( i ) n-d(i) n−d(i)个结点,这样,在动态规划的过程中就可 以顺便找出树的重心了。
POJ 1655 Balancing Act(求重心)
Balancing Act
题意:给定一棵树,求树的重心的编号以及重心删除后得到的最大子树的节点个数size,如果size相同就选取编号最小的.
Sample Input
1
7
2 6
1 2
1 4
4 5
3 7
3 1
Sample Output
1 2
#include
const ll N=20005;
const ll base=137;
const ll mod=2147483647;
const int INF = 1<<30;
//const double INF=double(INT_MAX*1.0);
ll head[N];//链式前向星
ll son[N];//son[i]表示以i为根的子树节点个数
ll cnt,n;
ll ans,size;
bool vis[N];//代替了其他做法里的fa (father)
struct Edge//链式前向星
{
ll to;
ll nex;
};
Edge edge[2*N];
inline void init()//初始化
{
cnt=0;
size=INF;
memset(vis,0,sizeof vis);
memset(head,-1,sizeof head);
}
inline void add(ll u,ll v)//链式前向星
{
edge[cnt].to=v;
edge[cnt].nex=head[u];
head[u]=cnt++;
}
inline void dfs(ll cur)
{
vis[cur]=1;
son[cur]=1;//节点本身
ll tmp=0;//tmp为节点cur的最大子树节点个数
for(ll i=head[cur];~i;i=edge[i].nex)
{
ll v=edge[i].to;
if(!vis[v])//if(v!=fa)
{
dfs(v);
son[cur]+=son[v];
tmp=max(tmp,son[v]);//同上
}
}
tmp=max(tmp,n-son[cur]);//更新,最大子树的节点个数size
if(tmp<size||(tmp==size&&cur<ans))//更新,要最小的那一个才是重心
{
ans=cur;
size=tmp;
}
}
int main()
{
ll T;
scanf("%lld",&T);
while(T--)
{
init();
scanf("%lld",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;++i)
{
ll u,v;
scanf("%lld %lld",&u,&v);
add(u,v);//无向图必须双向
add(v,u);
}
dfs(1);
printf("%lld %lld\n",ans,size);
}
return 0;
}
POJ 3107 Godfather
Godfather
题意:给定一棵树,求树的所有重心,按照编号从小到大的顺序输出.
分析:本题与上题基本上一样,只是求的量不同,既然我们在找树的重心的时候用的树型dp,而且是求的子树中节点数的最大值,然后求所有最大值的最小值,那么就有可能存在多个重心,我们每更新到一个最小值的时候就记录其它的最小值也为这个最小值的重心,这样下去就会找到所有的重心.
#include P1364 医院设置(树形DP)
洛谷P1364 医院设置
定义几个数组: f [ u ] f[u] f[u]表示以u为根的总距离, s i z e [ u ] size[u] size[u]表示以u为根的子树的大小(结点数,此题每个点要乘以权值,下文结点数均指此)。
显然, a n s = m i n ( f [ i ] , 1 < = i < = n ) ans=min(f[i],1<=i<=n) ans=min(f[i],1<=i<=n)
首先我们任意以一个点为根dfs一遍,求出以该点为根的总距离。方便起见,我们就以1为根。
接下来就是转移,对于每个u能达到的点v,有:
f [ v ] = f [ u ] + s i z e [ 1 ] − s i z e [ v ] − s i z e [ v ] f[v]=f[u]+size[1]−size[v]−size[v] f[v]=f[u]+size[1]−size[v]−size[v]
怎么来的呢?试想,当根从u变为v的时候,v的子树的所有节点原本的距离要到u,现在只要到v了,每个结点的距离都减少1,那么总距离就减少 s i z e [ v ] size[v] size[v],同时,以v为根的子树以外的所有节点,原本只要到u就行了,现在要到v,每个节点的路程都增加了1,总路程就增加了 s i z e [ 1 ] − s i z e [ v ] size[1]−size[v] size[1]−size[v],其中 s i z e [ 1 ] size[1] size[1]就是我们预处理出来的整棵树的大小,减去 s i z e [ v ] size[v] size[v]就是除以v为根的子树以外的结点数。
最后取最小值,得解。时间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
上述思路来源
#include
const ll N=20005;
const ll base=137;
const ll mod=2147483647;
const int INF = 1<<30;
struct Edge
{
ll to;
ll nex;
}tree[N];
ll head[N],cnt,w[N],n,size[N];
ll ans=INF,f[N];
inline void add(ll u,ll v)//链式前向星建树
{
tree[++cnt].to=v;
tree[cnt].nex=head[u];
head[u]=cnt;
}
inline void init()//初始化
{
memset(head,-1,sizeof head);
cnt=0;
}
inline void dfs(ll u,ll fa,ll dep)//以u为根,father为fa,深度为dep
{
size[u]=w[u];//size[u]表示以u为根的子树的大小(结点数,此题每个点要乘以权值,正常情况下应该是1)
for(int i=head[u];~i;i=tree[i].nex)//遍历所有相连的子树
{
if(tree[i].to!=fa)
{
dfs(tree[i].to,u,dep+1);//往下走
size[u]+=size[tree[i].to];
}
}
f[1]+=w[u]*dep;//f[u]表示以u为根的总距离,先预处理求得以1为根,f[1]的值
}
inline void dp(ll u,ll fa)
{
for(int i=head[u];~i;i=tree[i].nex)
{
if(tree[i].to!=fa)//防止自环
{
//通过转移方程直接把所有的点当作根的deep算出来然后比较
f[tree[i].to]=f[u]+size[1]-size[tree[i].to]*2;
dp(tree[i].to,u);
}
}
ans=min(ans,f[u]);
}
int main()
{
init();
scanf("%lld",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
ll a,b;
scanf("%lld",&w[i]);
scanf("%lld %lld",&a,&b);
if(a)add(i,a),add(a,i);
if(b)add(i,b),add(b,i);
}
dfs(1,0,0);
dp(1,0);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}