Positionable Camera
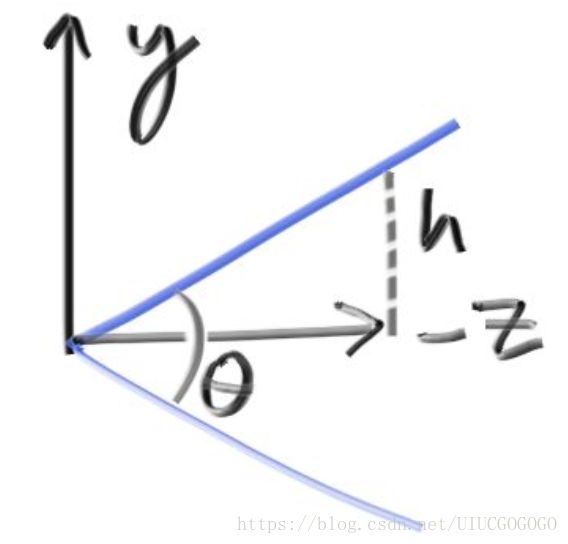
#ifndef CAMERAH
#define CAMERAH
#define M_PI 3.1415926
#include"ray.h"
//之前关于image plain的信息和viewing ray的生成
//都直接写在main里,现在要将它们封装进camera
//类里,毕竟image plain本来就是camera的可视范围
//而viewing ray也是由camera生成的
class camera
{
public:
//vfov是角度/degree
camera(vec3 lookfrom,vec3 lookat,vec3 vup,float vfov,float aspect)
{
vec3 u, v, w;//camera frame中各轴(方向向量)
float theta=vfov*M_PI/180;//将角度转化为弧度
float half_height = tan(theta / 2);
float half_width = aspect*half_height;
//确定视角
//注意,在场景中只存在一个真正的坐标系,即全局坐标系
//之前camera的origin和全局坐标系的原点重合
//因此camera frame也和全局坐标系重合
//现在camera不再置于原点,于是camera frame要
//重新用全局坐标系表示
origin = lookfrom;
w = unit_vector(lookfrom - lookat);
u = unit_vector(cross(vup, w));
v = cross(w, u);
//利用camera frame求出现在的lower_left_corner
lower_left_corner = origin - half_width*u - half_height*v - w;
//确定视野
horizontal = 2 * half_width*u;//fov/视野的宽
vertical = 2*half_height*v;//fov/视野的高
}
ray get_ray(float u, float v)
{
//直接写在main里时并没有最后减origin,那是因为origin为(0.0,0.0,0.0)
//然而实际上是需要的
return ray(origin, lower_left_corner + u*horizontal + v*vertical - origin);
}
vec3 origin;
vec3 lower_left_corner;
vec3 horizontal;
vec3 vertical;
};
#include "stdafx.h"
#include"vector.h"
#include"ray.h"
#include"sphere.h"
#include"hitable_list.h"
#include"camera.h"
#include"material.h"
#include"random.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//此处的world就是把整个场景里的所有object视为一体(即hitable_list)
//depth是ray的传播深度,scatter一次加一
vec3 color(const ray& r,hitable *world,int depth)
{
hit_record rec;
//如果viewing ray(反向光线)与hitable object相交
//tmin采用0.001是基于对showdow的考量,见fundamentals p86
//然而当前还没有引入light,阴影部分是因为当光线到达此处时经历了太多次反射
if (world->hit(r, 0.001, FLT_MAX, rec))
{
//当前还不能确定是difusse还是reflection,取决于hitable的material
ray scattered;
vec3 attenuation;//削弱
//如果scatter次数小于50
//并且ray接触的hitable object的material能成功调用scattered函数
if (depth < 50 && rec.mat_ptr->scatter(r, rec, attenuation, scattered))
{
return attenuation*color(scattered, world, depth + 1);
}
else//scatter超过50次,能量全被吸完了;scattered函数调用失败
{
return vec3(0, 0, 0);//黑
}
}
else//注意当前还是没有引入light,依然是由最后一条ray的direction的y值决定color
//实际上可以认为是background在发光
{
vec3 unit_direction = unit_vector(r.direction());//得到单位方向向量,将y限定在-1至1之间
float t = 0.5*(unit_direction.y() + 1.0);//间接用t代表y,将其限制在0至1之间
return (1.0 - t)*vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) + t*vec3(0.5, 0.7, 1.0);
//所谓插值法,不同的ray对应的t不同,这些t决定了其对应的color为(1.0,1.0,1.0)和(0.5,0.7,1.0)之间某一RGB颜色
//RGB各分量实际就是一个介于0.0至1.0的小数
}
}
int main()
{
int nx = 200;//200列
int ny = 100;//100行
int ns = 100;
ofstream out("d:\\theFirstPpm.txt");
out << "P3\n" << nx << " " << ny << "\n255" << endl;
hitable *list[5];//我们自己定义world是什么,此处定义为两个sphere
list[0] = new sphere(vec3(0, 0, -1), 0.5,new lambertian(vec3(0.1,0.2,0.5)));
list[1] = new sphere(vec3(0, -100.5, -1), 100, new lambertian(vec3(0.8, 0.8, 0.0)));
list[2] = new sphere(vec3(1, 0, -1), 0.5, new metal(vec3(0.8, 0.6, 0.2),0.3));
list[3] = new sphere(vec3(-1, 0, -1), 0.5, new dielectric(1.5));
list[4] = new sphere(vec3(-1, 0, -1), -0.45, new dielectric(1.5));
hitable *world = new hitable_list(list, 5);//初始化world
camera cam(vec3(-2,2,1),vec3(0,0,-1),vec3(0,1,0),90,float(nx)/float(ny));
for (int j = ny - 1;j >= 0;j--)//行从上到下
{
for (int i = 0;i < nx;i++)//列从左到右
{
vec3 col(0, 0, 0);
for (int s = 0;s < ns;s++)
{
float u = float(i + drand48()) / float(nx);
float v = float(j + drand48()) / float(ny);
ray r = cam.get_ray(u, v);
vec3 p = r.point_at_parameter(2.0);
col += color(r,world,0);
}
col /= float(ns);
//进行gamma校正,一般来说取gamma=2,原理及公式见fundamentals p63
col = vec3(sqrt(col[0]), sqrt(col[1]), sqrt(col[2]));
int ir = int(255.99*col[0]);
int ig = int(255.99*col[1]);
int ib = int(255.99*col[2]);
out << ir << " " << ig << " " << ib << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
