Cell Distance(数论)
题目描述
We have a grid of squares with N rows and M columns. Let (i,j) denote the square at the i-th row from the top and j-th column from the left. We will choose K of the squares and put a piece on each of them.
If we place the K pieces on squares (x1,y1), (x2,y2), …, and (xK,yK), the cost of this arrangement is computed as:
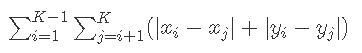
Find the sum of the costs of all possible arrangements of the pieces. Since this value can be tremendous, print it modulo 109+7.
We consider two arrangements of the pieces different if and only if there is a square that contains a piece in one of the arrangements but not in the other.
Constraints
·2≤N×M≤2×105
·2≤K≤N×M
·All values in input are integers.
输入
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M K
输出
Print the sum of the costs of all possible arrangements of the pieces, modulo 109+7.
样例输入
2 2 2
样例输出
8
思路
本题通过计算两个块之间的曼哈顿距离来计算总贡献,因此可以通过已知结论任意两个块之间的曼哈顿距离的平均值为(n+m)/3来求得结果,已知从nm个块中任意选择k个块为C(nm,k),从k个块中任意选择2个块为
C(k,2),所以结果为C(n * m,k) * C(k,2) * (n+m)/3
代码实现
#pragma GCC optimize(3,"Ofast","inline")
#include