(intermediate)最短路(最长路) UVA 1348 - Tomato Automata
1348 - Tomato Automata
Time limit: 3.000 secondsTomato Automata are small cool programs. You give them an infinite sequence of ones and zeros, and they give you a sequence of numbers. They are widely used in the Stanescu Operating System (SOS). They are written in Tomato Programming Language that is very simple. Here is its specification, tutorial and reference:
- Tomato is a very simple but powerful language.
- Lines in a Tomato program are numerated with integers from 1 to N (N
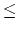 100000) in the order they appear in the input.
100000) in the order they appear in the input. - There is exactly one command on a line.
- The execution starts from the first line.
- There are exactly five Tomato commands - ifgo, jump, pass, loop, and die.
- When executed, each command prints its line number (into the output sequence).
- The ifgo command has one argument - the line number of another instruction. It reads one bit from the input stream. If the bit is one, the execution jumps to the line with the given as argument line number. Otherwise the execution continues with the next line.
- The jump command has one argument - the line number of another instruction. When executed, the execution jumps to the line with the given line number.
- The pass command has no arguments. It does nothing (except printing its line number like all other commands). Then the execution continues with the next line.
- The die command has no arguments. It terminates the execution of the program (printing its line number before that). The die command can not be used inside a loop.
- The loop command is the only one with two arguments. It may be used to construct loops. The first argument is the starting line number < line > (less than the line number of the loop command), and the second is a positive integer < count > . When executed, it loops from the start line a < count > - 1 number of times (because it is already executed once). When the loop is executed the given number of times, the execution continues with the next line.
- The jump and ifgo commands must be used only with line numbers in the scope of the innermost loop containing them (they can not jump outside of the innermost loop or inside loops nested in the innermost loop that does not contain the command).
- The loop command can not be used to create overlapping loops. Nested loops must be strictly nested (they can not use the same starting line).
- When the last line of the program is executed, the execution continues from the first except when the last line is die command.
- White spaces may occur freely before or after the command name and their arguments.
- The maximal length of a line in Tomato Programming Language is 80 characters including spaces.
Stanescu has lots of Tomato programs. He is interested in maximal length of output sequence that specific program can generate, where the length is the number of printed line numbers. Obviously, it is not possible to test each possible input sequence (of ones and zeros), so he needs a program that computes this.
Input
The input contains several programs, separated with an empty line. Each of them is a correct Tomato program.
Output
For each given program your solution has to print on a separate line the maximal length ofthe output sequence the program could generate. Print `infinity' if there is no maximal length for the 9 output sequence. When finite, the maximal length will not exceed 109 .
Sample Input
Ifgo 2
loop 1 3
die
ifgo 2
ifgo 3
pass
die
pass
ifgo 4
jump 5
ifgo 3
loop 2 2
pass
loop 1 2
die
Sample Output
7 4
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; #define LL long long const int maxn = 100000+5; const int inf = 1e9; int n , m , ans , size; LL d[maxn] , cnt[maxn] , succ[maxn] , len[maxn]; int dfn , pre[maxn] , low[maxn]; bool sccno[maxn]; stack<int> S; int sign[maxn]; int pos[maxn]; bool inq[maxn] , die[maxn]; char cmd[maxn][82]; char buffer[82]; struct Node { int v , w , pre , t; bool loop; Node *next; }edge[2*maxn] , *first[maxn]; void add(int x,int y,int w,int pre,int t,bool loop) { edge[++m].v = y; edge[m].w = w; edge[m].pre = pre; edge[m].t = t; edge[m].loop = loop; edge[m].next = first[x]; first[x] = &edge[m]; } void init() { m = 0; while (S.size()) S.pop(); memset(pre,0,sizeof(pre)); memset(sccno,false,sizeof(sccno)); dfn = 0; memset(first,0,sizeof(first)); } bool cmd_modify() { bool die = false; for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++i) { if (cmd[i][0]=='d') die = true; if (cmd[i][0]=='i' || cmd[i][0]=='j') { int v; sscanf(cmd[i],"%*s%d",&v); --v; if ((i+1)%n==v) cmd[i][0] = 'p'; if (i==v && !die) return false; } } return die; } bool dfs(int u) { pre[u] = low[u] = ++dfn; S.push(u); for (Node * p = first[u] ; p ; p=p->next) { int v = p->v; if (!pre[v]) { if (!dfs(v)) return false; low[u] = min(low[u],low[v]); } else if (!sccno[v]) low[u] = min(low[u],pre[v]); } if (pre[u]==low[u]) { if (u==0 && S.size() > 1) return false; while (true) { int x = S.top() ; S.pop(); sccno[x] = true; if (x==u) break; } } return true; } void BuildGraph() { memset(sign,-1,sizeof(sign)); memset(pos,-1,sizeof(pos)); memset(die,0,sizeof(die)); sign[0] = ++size; pos[size] = 0; int u , v , w , pre , t; for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++i) { if (cmd[i][0]=='l') { sscanf(cmd[i],"%*s%d%d",&pre,&t); --pre; if (sign[pre]==-1) { sign[pre] = ++size; pos[size] = pre; } if (sign[i]==-1) { sign[i] = ++size; pos[size] = i; } succ[i] = i; } else if (cmd[i][0]=='i' || cmd[i][0]=='j') { sscanf(cmd[i],"%*s%d",&v); --v; if (cmd[i][0]=='i' && sign[i]==-1) { sign[i] = ++size; pos[size] = i; } succ[i] = v; } else if (cmd[i][0]=='d' ) { if (sign[i]==-1) { sign[i] = ++size; pos[size] = i; } die[sign[i]] = true; succ[i] = i; } else { succ[i] = (i+1)%n; } len[i] = succ[i]==i ? 0 : 1; } for (int i = size ; i >=1 ; --i) { if (die[i]) continue; int u = pos[i] , v , w , pre = -1 , t = -1; v = succ[u] , w = len[u]; memset(inq,false,sizeof(inq)); inq[u] = true; bool lp = false; while (sign[v]==-1) { inq[v] = true; w += len[v]; v = succ[v]; if (inq[v]) { lp = true; break; } } if (lp) { add(sign[u],sign[u],inf,-1,-1,false); continue; } len[u] = w; succ[u] = v; if (v!=u) { add(sign[u],sign[v],w,-1,-1,false); } if (cmd[u][0]=='j') continue; v = (u+1)%n , w = 1; memset(inq,false,sizeof(inq)); lp = false; inq[u] = true; while (sign[v]==-1) { inq[v] = true; w += len[v]; v = succ[v]; if (inq[v]) { lp = true; break; } } if (lp) { add(sign[u],sign[u],inf,-1,-1,false); continue; } if (cmd[u][0]=='l') sscanf(cmd[u],"%*s%d%d",&pre,&t); --pre; add(sign[u],sign[v],w,sign[pre],t,cmd[u][0]=='l'); } } void spfa() { memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt)); memset(inq,0,sizeof(inq)); memset(d,0,sizeof(d)); queue<int> q; q.push(sign[0]); ++cnt[sign[0]]; d[sign[0]] = 1; int u , v , w; while (q.size()) { u = q.front(); q.pop(); inq[u] = false; if (die[u] && ans < d[u]) ans = d[u]; for (Node * p = first[u] ; p ; p = p->next) { int v = p->v , w = p->w; if (p->loop) w += (d[u]-d[p->pre]+1)*(p->t-1); if (d[v] < d[u]+w) { d[v] = d[u]+w; if (!inq[v]) { inq[v] = true; q.push(v); ++cnt[v]; if (cnt[v] >= size) { printf("infinity\n"); return; } } } } } cout << ans << endl; } void get_cmd() { for (int i = 0 ; i < strlen(buffer) ; ++i) buffer[i] = tolower(buffer[i]); char * p = strtok(buffer," "); while (p) { strcat(cmd[n],p); strcat(cmd[n]," "); p = strtok(NULL," "); } ++n; } int main() { //freopen("input.in","r",stdin); while (gets(buffer)) { if (buffer[0]==0) break; memset(cmd,0,sizeof(cmd)); n = size = 0; get_cmd(); while (gets(buffer)) { if (buffer[0]==0) break; for (int i = 0 ; i < strlen(buffer) ; ++i) if (isspace(buffer[i])) buffer[i] = ' '; get_cmd(); } if (!cmd_modify()) { printf("infinity\n"); continue; } init(); BuildGraph(); if (!dfs(0)) { printf("infinity\n"); continue; } ans = -1; spfa(); } }