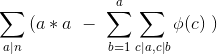HDU5528 迪利克雷卷积
被卡常了wuwuwu,这道题最后也没过,本机测试随机满数据不到2s,20000个1e9 4s
这种做法比较奇葩,我估计没人会这么做
这道题的本质是
左边那个希腊符号是欧拉函数,右边的是因子之和,都是积性函数,数论卷积后还是积性函数
所以n因式分解,化成答案变成几个积性函数的积
总复杂度 ![]()
啊,计蒜客上A了
设F是欧拉函数和因子和函数的数论卷积 ![]()
F函数也是积性函数,因式分解后,按定义乘起来就行
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ll;
const ll N=4e4;
bool P[N+10];
vector V;
ll A[100],B[100];
ll F(ll x){
ll ans=1;
for(int i=0;V[i]*V[i]<=x;++i){
if(x%V[i]==0){
int a=0;
while(x%V[i]==0){
x/=V[i];
++a;
}
A[0]=1;
for(int j=1;j<=a;++j){
A[j]=A[j-1]*V[i]*V[i];
}
for(int j=1;j<=a;++j){
A[j]+=A[j-1];
}
ans*=A[a];
}
}
if(x>1)ans=ans*(x*x+1);
return ans;
}
ll G(ll x){
ll ans=1;
for(int i=0;V[i]*V[i]<=x;++i){
if(x%V[i]==0){
ll a=0;
while(x%V[i]==0){
x/=V[i];
++a;
}
ll b=0;
A[0]=1;
B[0]=1;
for(int j=1;j<=a;++j)A[j]=A[j-1]*V[i];
for(int j=1;j<=a;++j){
B[j]=B[j-1]+A[j];
}
for(int j=1;j<=a;++j){
b+=A[j-1]*(V[i]-1)*B[a-j];
}
b+=B[a];
ans=ans*b;
}
}
if(x>1)ans=ans*2*x;
return ans;
}
int main(){
//freopen("1.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("1.out","w",stdout);
for(int i=2;i<=N;++i){
if(P[i]==0){
V.push_back(i);
for(int j=2*i;j<=N;j+=i)P[j]=1;
}
}
ll T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
ll x;
scanf("%lld",&x);
if(x==0)printf("1\n");
else printf("%lld\n",F(x)-G(x));
}
}