g2o的基本使用
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/e16ffb5b265d
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/36889150
图是一种数据结构。在图优化中,用顶点(vertex) 表示优化变量,用边(edge) 表示误差项。优化时,顶点的值逐渐趋近最优值,边的作用是计算误差
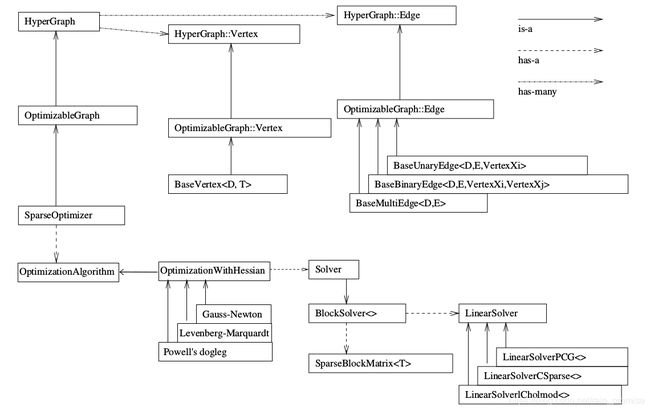
下面是一张关于g2o的整体结构图:
g2o中基本元素介绍
1、关于BaseVertex:
模板参数为优化变量维度和数据类型;需要定义读写函数。
void oplus(double* v)则是节点的更新函数,值存储在变量_estimate(类型为给定的数据类型) 中;
void setToOriginImpl()定义节点的重置值;
定义节点时,利用setEstimate(type)函数来设定初始值;
setId(int)定义节点编号。
2、关于边,包括BaseUnaryEdge(一元边)BaseBinaryEdge(二元边)和BaseMultiEdge(多元边)
• 模版参数为观测值的维度,类型和连接的节点类型;需要重定义读写函数;可以有初始化函数;
• 函数void linearizeOplus() 计算雅可比矩阵;
• void computeError() 函数计算误差,观测值存储在_measurement 中,误差存储在_error 中,节点存储在_vertices[] 中。
• 定义边时,利用setId(int) 来定义边的编号(决定了在H矩阵中的位置);
• setMeasurement(type) 函数来定义观测值;
• setVertex(int, vertex) 来定义节点;其中int指的是第几类参数,如边的定义如下:
EdgeProjectXYZ2UV : public BaseBinaryEdge<2, Vector2D, VertexSBAPointXYZ, VertexSE3Expmap>则第0类参数为空间点(VertexSBAPointXYZ,),第1类参数为位姿(VertexSE3Expmap>)
• setInformation() 来定义协方差矩阵的逆。
• BaseBinaryEdge:二元边需要多设定一个节点类型,_vertices[] 的大小为2,存储顺序和调用setVertex(int, vertex) 与设定的int 有关(0 或1)。
3、BlockSolver:
块求解器,会构建好线性求解器所需要的矩阵块,其中包含了线性求解器。
通常情况下,使用g2o优化有3个步骤:
1、选择一个线性方程求解器;
2、选择一个BlockSolver;
3、选择一个迭代策略,一般为GN或LM;
视觉SLAM14讲中的g2o使用实例:
实例1、曲线拟合
(1)定义顶点及边的模板
// 曲线模型的顶点,模板参数:优化变量维度和数据类型
class CurveFittingVertex: public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Eigen::Vector3d>//继承自g2o的顶点构造函数
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
virtual void setToOriginImpl() // 重置
{
_estimate << 0,0,0;
}
virtual void oplusImpl( const double* update ) // 更新
{
_estimate += Eigen::Vector3d(update); //cc此处应该是为了说明优化变量的更新方式
}
// 存盘和读盘:留空
virtual bool read( istream& in ) {} //虚函数,在继承类中再定义
virtual bool write( ostream& out ) const {}
};
// 误差模型 模板参数:观测值维度,类型,连接顶点类型
class CurveFittingEdge: public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<1,double,CurveFittingVertex> //cc继承自g2o的边构造函数
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
CurveFittingEdge( double x ): BaseUnaryEdge(), _x(x) {}
// 计算曲线模型误差
void computeError()
{
const CurveFittingVertex* v = static_cast (_vertices[0]);
const Eigen::Vector3d abc = v->estimate();
_error(0,0) = _measurement - std::exp( abc(0,0)*_x*_x + abc(1,0)*_x + abc(2,0) ) ;
}
virtual bool read( istream& in ) {}
virtual bool write( ostream& out ) const {}
public:
double _x; // x 值, y 值为 _measurement
};
关于其中的 static_cast关键字
static_cast (expression) static_cast叫做编译时类型检查。该运算符把expression转换为type-id类型,这样做的目的是在程序还没有运行时进行类型检查,来保证转换的安全性。
而与之对应的,dynamic_cast关键字(运行时类型检查)主要用于类层次结构中父类和子类之间指针和引用的转换,由于具有运行时类型检查,因此可以保证下行转换的安全性。即转换成功就返回转换后的正确类型指针,如果转换失败,则返回NULL。
所谓上行转换是指由子类指针到父类指针的转换,下行转换是指由父类指针到子类指针的转换。
(2)调用
// 构建图优化,先设定g2o
typedef g2o::BlockSolver< g2o::BlockSolverTraits<3,1> > Block; // 每个误差项优化变量维度为3,误差值维度为1
Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverDense(); // 1、选择线性方程求解器
Block* solver_ptr = new Block( linearSolver ); //2、选择BlockSolver
//3、选择迭代策略: 梯度下降方法,从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg( solver_ptr );
// g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton( solver_ptr );
// g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmDogleg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmDogleg( solver_ptr );
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm( solver ); // 设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose( true ); // 打开调试输出
// 往图中增加顶点
CurveFittingVertex* v = new CurveFittingVertex();
v->setEstimate( Eigen::Vector3d(0,0,0) );
v->setId(0);
optimizer.addVertex( v );
// 往图中增加边
for ( int i=0; isetId(i);
edge->setVertex( 0, v ); // 设置连接的顶点
edge->setMeasurement( y_data[i] ); // 观测数值
edge->setInformation( Eigen::Matrix::Identity()*1/(w_sigma*w_sigma) ); // 信息矩阵:协方差矩阵之逆
optimizer.addEdge( edge );
}
// 执行优化
cout<<"start optimization"< time_used = chrono::duration_cast>( t2-t1 );
cout<<"solve time cost = "< 实例2:简单的bundleAdjustment
// 初始化g2o
typedef g2o::BlockSolver< g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6,3> > Block; // pose 维度为 6, landmark 维度为 3
Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverCSparse(); // 线性方程求解器
Block* solver_ptr = new Block ( linearSolver ); // 矩阵块求解器
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg ( solver_ptr );
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;//图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm ( solver );//设置求解器
// vertex
g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* pose = new g2o::VertexSE3Expmap(); // camera pose
Eigen::Matrix3d R_mat;
R_mat <<
R.at ( 0,0 ), R.at ( 0,1 ), R.at ( 0,2 ),
R.at ( 1,0 ), R.at ( 1,1 ), R.at ( 1,2 ),
R.at ( 2,0 ), R.at ( 2,1 ), R.at ( 2,2 );//初始值
pose->setId ( 0 );
pose->setEstimate ( g2o::SE3Quat (
R_mat,
Eigen::Vector3d ( t.at ( 0,0 ), t.at ( 1,0 ), t.at ( 2,0 ) )
) );//经过R,t作用的估计值
optimizer.addVertex ( pose );
int index = 1;
for ( const Point3f p:points_3d ) // landmarks 空间点位置
{
g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ* point = new g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ();
point->setId ( index++ );
point->setEstimate ( Eigen::Vector3d ( p.x, p.y, p.z ) );
point->setMarginalized ( true ); // g2o 中必须设置 marg
optimizer.addVertex ( point );
}
// parameter: camera intrinsics //相机内参
g2o::CameraParameters* camera = new g2o::CameraParameters (
K.at ( 0,0 ), Eigen::Vector2d ( K.at ( 0,2 ), K.at ( 1,2 ) ), 0
);
camera->setId ( 0 );
optimizer.addParameter ( camera );
// edges
index = 1;
for ( const Point2f p:points_2d ) //测量得到的关键点坐标
{
g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV* edge = new g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV();
edge->setId ( index );
edge->setVertex ( 0, dynamic_cast ( optimizer.vertex ( index ) ) );
edge->setVertex ( 1, pose );
edge->setMeasurement ( Eigen::Vector2d ( p.x, p.y ) );
edge->setParameterId ( 0,0 );
edge->setInformation ( Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity() );
optimizer.addEdge ( edge );
index++;
}
optimizer.setVerbose ( true );
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize ( 100 );
cout<<"optimization costs time: "<